2. 东北大学 理学院, 辽宁 沈阳 110819
2. School of Sciences, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China.
Corresponding author: YUAN Hui-qun, E-mail: yuan_hq@163.com
叶盘系统理论上应该是圆周循环对称结构,但是由于加工、安装、磨损及为了抑制颤振等原因,造成了各叶片之间质量、刚度和固有频率的不同,即失谐.失谐会导致叶盘系统振动能量集中在少数叶片上,造成严重的局部化现象,导致疲劳失效,进而影响压气机叶盘系统的使用寿命.
国内外对失谐叶盘系统振动局部化开展了广泛的研究,Ewins 等 [1]认为失谐导致模态振型出现局部化现象.Wei 等和Pierre等[2, 3]研究了叶盘系统参数对模态局部化的影响规律.Ottarsson 等[4]采用传递矩阵法和蒙特卡罗仿真方法对失谐叶盘自由振动局部化进行了研究.Castanier等和Hussein等[5, 6]研究了激励阶次对失谐叶盘系统幅值的影响,王建军等[7, 8, 9, 10]基于集中参数模型和有限元模型对叶盘系统的失谐振动特性进行了深入研究,为了定量评价失谐造成的模态局部化,定义了模态振型的局部化因子来描述随机失谐叶盘结构模态局部化的统计特性.
贺尔铭等[11]基于质量弹簧模型,对随机失谐叶盘系统用Monte Carlo方法对各种耦合强度特别是中度耦合强度下的随机失谐响应进行系统分析.王红建等[12]研究了频率转向特征对失谐系统模态局部化的作用规律.
根据三重点原理[13],叶盘系统的固有频率等于激振力频率,且激励阶次等于节径数时发生共振.叶盘失谐导致振型不符合谐波展开形式,并随着失谐扩展到不同的节径上,而且不同阶次的振型对失谐敏感程度也不同[9].因此,针对失谐叶盘系统在不同激励阶次间的振动响应特性进行深入研究是十分必要的.本文针对压气机叶盘系统有限元模型,基于激励阶次对失谐叶盘系统振动响应局部化进行了研究,定义了相对振动局部化因子,并从振动幅值和应变能的角度,结合相对局部化因子分析了不同激励阶次对失谐叶盘系统振动响应局部化的影响.
1 失谐叶盘系统结构模型 1.1 有限元模型某型发动机压气机叶盘系统有38个叶片,叶片由叶身与榫头两部分组成,叶片和轮盘采用燕尾型榫头榫槽接触连接成叶盘系统.由于各个部分的接触状态是随着转速的变化而变化,所以叶盘系统分析模型必须考虑榫头与榫槽的接触状态对叶片及叶片轮盘系统振动的影响.
由于失谐叶盘系统结构复杂,划分网格后生成的单元与节点数较大,采用整体模型计算分析比较耗时,如果再考虑叶片榫头与轮盘榫槽的接触关系,分析将变得更为困难.对于失谐叶盘系统动力学分析,普遍采用子结构模态综合法[14, 15, 16, 17].将整个叶盘系统划分为38个基本扇区,每一个扇区作为一个子结构,采用solid45单元对叶片进行映射网格划分,轮盘和榫头榫槽采用solid187单元,榫头与榫槽的接触采用面面接触,榫头与榫槽的接触面如图 1所示.选择standard作为接触行为,子结构基本扇区划分单元数为52 163,节点数为79 174.压气机叶盘系统整体结构模型和基本扇区有限元模型如图 2所示.
 | 图 1 榫头和榫槽接触面 Fig.1 Contact areas of tenon and mortise |
 | 图 2 叶盘系统有限元模型 Fig.2 Finite element model of a bladed disk |
叶盘系统的真实受力极为复杂,对其进行谐响应分析时,将各叶片所承受的气动激励简化为单点激励形式,即将气动激励力施加在每个叶片叶尖前缘处相对应的同一节点上,载荷在空间上满足行波的形式.
叶盘结构的动力学方程可表示为
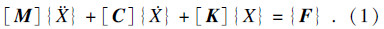
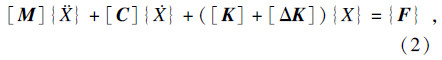
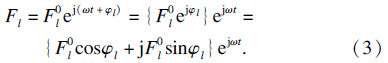
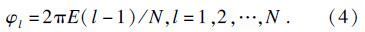
实部值:
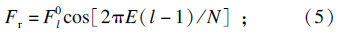
虚部值:
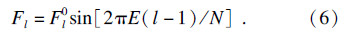
在谐响应分析中,选取Fl0=8,模态阻尼比ζ=0.1%.行波激励力在时间和空间上的分布均呈简谐形式,相邻叶片之间的激励力相差固定的相位角,其大小由激励阶次E决定.因此确定叶盘系统谐响应行波激励主要是确定激励阶次E和激励频率ω的取值范围.本文选择低阶激励阶次E为1~6,激励频率ω取谐调系统的振幅最大无量纲的共振频率1.062附近的频率范围0.96~1.16.
2 不同激励阶次下失谐叶盘系统局部化特性 2.1 失谐参数的确定由于研究的是随机失谐叶盘系统结构振动响应幅值的最大值问题,从极值统计理论可知叶盘结构振动响应的最大值服从威布尔分布,可以采用威布尔分布与Monte Carlo模拟技术相结合[5, 18, 19],通过少数随机失谐数据来模拟大量随机失谐,并能获得与大量数据相一致的结果.叶片失谐参数通过对叶片弹性模量在标准差1%,3%,5%和8%情况下,引入叶片刚度的随机失谐量,分析整数阶次激励对叶盘系统的影响,通过威布尔分布与Monte Carlo模拟技术相结合计算获得各失谐标准差下的叶片振动幅值最大值的均值.
2.2 相对振动局部化因子为了评估不同激励阶次下,不同失谐标准差对失谐叶盘系统结构振动的局部化影响,在文献[7, 8, 9]定义的振动局部化因子基础上,提出了相对振动局部化因子.基本思想是分别提取各激励阶次下谐调和失谐叶盘系统结构的最大位移和应变能,以式(7)计算相对振动局部化因子.
相对局部化因子:
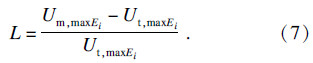
为了提取谐调叶盘系统最大振动幅值和应变能,激励阶次选择1,2,3,4,5,6阶次,对谐调叶盘系统进行振动响应特性分析.谐调叶盘系统的幅频特性如图 3所示.
 | 图 3 谐调叶盘系统幅频特性 Fig.3 Amplitude-frequency characteristics of tuned disks |
由图 3可知,谐调叶盘系统各激励阶次作用下的叶片最大振幅只有一个峰值.叶盘系统的振幅在激励阶次为6时达到最大,在激励阶次为2时幅值最小.随着激励阶次的增加,谐调叶盘系统发生共振的频率逐渐增加.
2.4 失谐叶盘系统响应特性在激励阶次1~6下,分别选择不同失谐标准差对叶盘系统进行振动响应特性分析,通过计算不同激励阶次和失谐标准差下的相对局部化因子,获得失谐叶盘系统的振动响应位移、应变能局部化特性.图 4为失谐叶盘系统最大无量纲幅值随失谐标准差的变化趋势,这一幅值变化趋势与文献[9, 10]中分析获得的结论相似,从而验证了所建立计算模型的准确性.
 | 图 4 不同失谐程度下的幅值 Fig.4 Amplitude for different detuning strengths |
图 5为失谐叶盘系统位移相对局部化因子随激励阶次的变化规律.从图上可以看出,随着激励阶次的增加,位移相对局部化因子呈现先增大再减小的趋势,在激励阶次3时出现峰值,位移相对局部化因子最大.图 6为当激励阶次为3时,失谐叶盘系统位移相对局部化因子随失谐标准差的变化规律.从图上可以看出,当失谐标准差为3%时位移相对局部化因子较大.随着失谐标准差的增大,位移相对局部化因子呈现先上升然后再下降的趋势,当失谐标准差为3%时,出现峰值.图 7为激励阶次为3和失谐标准为3%时叶盘系统各叶片的振幅,可以看出5号叶片的振幅最大,局部化较严重.
 | 图 5 失谐叶盘系统叶片位移相对局部化因子 Fig.5 Displacement relative localization factor of mistuned bladed disks |
 | 图 6 激励阶次为3时叶片位移相对局部化因子 Fig.6 Displacement relative localization factor of mistuned bladed disks when engine order of excitation is 3 |
 | 图 7 失谐标准差为3%时各叶片振幅 Fig.7 Displacement of the standard deviation is 3% for every mistuned bladed |
图 8为失谐叶盘系统叶片应变能相对局部化因子随激励阶次变化规律.从图上可以看出,随着激励阶次的增加,应变能相对局部化因子在激励阶次3时出现峰值. 图 9是激励阶次为3和失谐标准差为3%时,各叶片的应变能局部化程度,从图上可以看出叶盘系统最大应变能集中在5号叶片上,局部化程度较高.
 | 图 8 失谐叶盘系统叶片应变能相对局部化因子 Fig.8 Strain energy relative localization factor of mistuned bladed disks |
 | 图 9 失谐标准差为3%时各叶片应变能 Fig.9 Strain energy of the standard deviation is 3% for every mistuned bladed |
1) 随着激励阶次的增加,相对局部化因子呈现先增大然后再降低的趋势.
2) 利用相对局部化因子,能够更好地描述不同激励阶次间的叶盘系统振动响应局部化程度.
| [1] | Ewins D J, Imregun M.Vibration modes of packeted bladed disks[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress and Reliability in Design, 1984, 106 :175-180.( 1) 1) |
| [2] | Wei S T, Pierre C.Localization phenomena in mistuned assemblies with cyclic symmetry part 2 :forced vibrations[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress and Reliability in Design, 1988, 110 :439-449.( 1) 1) |
| [3] | Pierrre C, Murthy D V.Aeroelastic modal characteristics of mistuned blade assemblies:mode localization and loss of eigenstructure[J]. AIAA Journal, 1992, 30(10):2483-2496.( 1) 1) |
| [4] | Ottarsson G, Pierre C.A transfer matrix approach to free vibration localization in mistuned bladed assemblies[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1996, 197(5):589-618.( 1) 1) |
| [5] | Castanier M P,Pierre C.Modeling and analysis of mistuned bladed disk vibration:status and emerging directions[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2006, 22(2):354-396.( 2) 2) |
| [6] | Hussein M I, Pierre C, Castanier M P.Correlation of tuned free vibration characteristics with mistuning sensitivity for a bladed disk[C]// 44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference.Norfolk, Virginia:AIAA, 2003:1544.( 1) 1) |
| [7] | 王建军,姚建尧,李其汉.刚度随机失谐叶盘结构概率模态特性分析[J]. 航空动力学报,2008, 23(2):256-262. (Wang Jian-jun, Yao Jian-yao, Li Qi-han.Probability characteristics of vibratory mode of bladed disk assemblies with random stiffness mistuning[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2008, 23(2):256-262.)( 2) 2) |
| [8] | 于长波,王建军,李其汉.失谐叶盘结构的概率响应局部化特性[J]. 航空动力学报,2010, 25(9):2006-2012. (Yu Chang-bo, Wang Jian-jun, Li Qi-han.Probability characteristics for response localization of mistuned bladed disk assemblies[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2010, 25(9):2006-2012.)( 2) 2) |
| [9] | 姚建尧,王建军,李其汉.基于振型节径谱的失谐叶盘结构动态特性评价[J]. 推进技术,2011, 32(5):645-653. (Yao Jian-yao, Wang Jian-jun, Li Qi-han.Dynamic characteristics assessment of mistuned bladed disk using nodal diameter spectrum of mode shapes[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2011, 32(5):645-653.)( 4) 4) |
| [10] | 辛健强, 王建军.失谐流体激励下叶盘结构响应特性[J]. 航空动力学报,2012, 27(4):801-810. (Xin Jian-qiang, Wang Jian-jun.Forced response characteristic of bladed disk with aerodynamic mistuning[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2012, 27(4):801-810.)( 2) 2) |
| [11] | 贺尔铭, 余仕侠, 王红建.随机失谐叶盘系统受迫振动响应的统计特性研究[J]. 机械强度, 2007, 29(1):20-24. (He Er-ming Yu Shi-xia Wang Hong-jian.Statistic analysis of the forced response of random mistuning bladed disk[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2007, 29(1):20-24.)( 1) 1) |
| [12] | 王红建, 贺尔铭, 赵志彬.频率转向特征对失谐叶盘模态局部化的作用[J]. 中国机械工程, 2009, 20(1):82-85. (Wang Hong-jian, He Er-ming, Zhao Zhi-bin.Effects of frequency veering features on mode localization of mistuned bladed disks[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 20(1):82-85.)( 1) 1) |
| [13] | 宋兆泓.航空燃气涡轮发动机强度设计[M]. 北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 1988. (Song Zhao-hong.The strength design of aero gas turbine engine[M]. Beijing:Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 1988.)( 1) 1) |
| [14] | Craig R R.Coupling of substructures for dynamic analyses[J]. AIAA Journal, 1968, 6(7):1313-1319.( 1) 1) |
| [15] | Bladh R, Pierre C, Castanier M P, et al.Dynamic response predictions for a mistuned industrial turbomachinery rotor using reduced-order modeling[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2002, 124(2):311-324.( 1) 1) |
| [16] | 白斌, 白广忱, 费成巍, 等.改进的混合界面子结构模态综合法在失谐叶盘结构模态分析中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 49(6):89-97. (Bai Bin, Bai Guang-chen, Fei Chen-wei, et al.Application of improved hybrid interface substructural component modal synthesis method in dynamic characteristics analysis of mistuned bladed disk assemblies[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 49(6):89-97.)( 1) 1) |
| [17] | 寇海江, 袁惠群, 李岩, 等.一体化转子系统动力分析的预应力模态综合法[J]. 东北大学学报 (自然科学版), 2014, 35(2):263-267. (Kou Hai-jiang, Yuan Hui-qun, Li Yan, et al.A prestressed component mode synthesis method for dynamics analysis of blisk-shaft integrated rotor[J]. Journal of Northeastern University( Natural Science), 2014, 35(2):263-267.)( 1) 1) |
| [18] | Bladh R, Pierre C, Castanier M P, et al.Dynamic response predictions for a mistuned industrial turbomachinery rotor using reduced-order modeling[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2002, 124(2):311-324.( 1) 1) |
| [19] | 兰海强, 臧朝平.叶片安装角对叶盘结构受迫响应特性的影响[J]. 航空动力学报, 2012, 27(11):2547-2552. (Lan Hai-qiang, Zang Chao-ping.Effect of blade stagger angle on forced response of bladed disk assemblies[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2012, 27(11):2547-2552.)( 1) 1) |




