Corresponding author: ZHANG Guo-wei, professor, E-mail: gwzhangneum@sina.com
设E是实赋范线性空间,θ表示E中的零元素,K是E中的锥,见文献[1]. 在乘积空间E×E={(u1,u2)|u1,u2∈E}中定义范数为‖(u1,u2)‖=‖u1‖+‖u2‖. 设K1和K2是E中的两个锥,易证K1×K2为乘积空间E×E中的锥. 如果0<ri<ri(i=1,2),定义Kr,R=(K1)r1,R1×(K2)r2,R2,其中
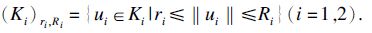
如果算子Ai:K1×K2→E(i=1,2)是全连续的,则称A=(A1,A2)是全连续的. 文献[2]在乘积空间中证明了由锥导出的半序型锥拉伸与压缩不动点定理. 泛函型锥拉伸与压缩全连续算子的不动点定理及其应用见文献[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]. 本文在乘积空间证明了几个凹泛函型混合锥拉伸与压缩条件下的不动点定理. 设α:K→[0,+∞)为凹泛函,如果α(λx)=λα(x),∀λ≥0,∀x∈K,则称α正齐次.
1 主要结论以下均假设A=(A1,A2):Kr,R→K1× K2全连续,αi:Ki→[0,+∞)是非负正齐次凹泛函,αi(x)>0,∀x∈Ki\{θ} (i=1,2).
定理1 如果下列条件满足:
‖u1‖=r1⇒α1(A1(u))≥α1(u1),
‖u1‖=R1⇒α1(A1(u))≤α1(u1),
‖u2‖=r2⇒α2(A2(u))≥α2(u2),
‖u2‖=R2⇒α2(A2(u))≤α2(u2),
其中u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R,那么A在Kr,R中存在不动点.
证明 令h=(h1,h2)∈K1×K2,hi≠θ (i=1,2). 定义A :K1×K2→K1×K2如下(其中记[ri]= ri/‖ui‖,[Ri]=Ri/‖ui‖ (i=1,2)):
如果u1=0或u2=0,则A (u)=h;
如果0<‖u1‖<r1且0<‖u2‖<r2,则A(u)=min{[r1]-1,[r2]-1}A([r1]u1,[r2]u2)+ (1-min{[r1]-1,[r2]-1})h;
如果0<‖u1‖<r1且r2≤‖u2‖≤R2,则
A(u)=[r1]-1A([r1]u1,u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h;
如果0<‖u1‖<r1且‖u2‖>R2,则
A(u)=[r1]-1A([r1]u1,[R2]u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h;
如果r1≤‖u1‖≤R1且0<‖u2‖<r2,则
A(u)=[r2]-1A(u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r2]-1)h;
如果r1≤‖u1‖≤R1且r2≤‖u2‖≤R2,则 A(u)=A(u);
如果r1≤‖u1‖≤R1且‖u2‖>R2,则
A(u)=A(u1,[R2]u2);
如果‖u1‖>R1且0<‖u2‖<r2,则
A(u)=[r2]-1A([R1]u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r2]-1)h;
如果‖u1‖>R1且r2≤‖u2‖≤R2,则
A(u)=A([R1]u1,u2);
如果‖u1‖>R1且‖u2‖>R2,则
A(u)=A([R1]u1,[R2]u2).
易见A是连续的,由于它的值域包含于紧集co {A(Kr,R)∪{h}},所以又是紧的. 根据Schauder不动点定理[1],存在u∈K1×K2使得A(u)=u. 下面证明u∈Kr,R,否则与条件矛盾,于是A(u)=u. 由于hi≠0<(i=1,2),显然‖u1‖>0<且‖u2‖>0.
如果0<‖u1‖<r1且0<‖u2‖<r2,不妨设min{[r1]-1,[r2]-1}=[r1]-1,那么
u=A(u)=[r1]-1A([r1]u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h,
u1=[r1]-1A1([r1]u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h1.
由α1的凹性知
α1(u1)≥[r1]-1α1(A1([r1]u1,[r2]u2))+(1-[r1]-1)α1(h1)>[r1]-1α1(A1([r1]u1,[r2]u2)),
α1([r1]u1)=[r1]α1(u1)>α1(A1([r1]u1,[r2]u2)).
如果0<‖u1‖<r1且r2≤‖u2‖≤R2,则
u=A(u)=[r1]-1A([r1]u1,u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h,
u1=[r1]-1A1([r1]u1,u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h1.
由α1的凹性知
α1(u1)≥[r1]-1α1(A1([r1]u1,u2))+(1-[r1]-1)α1(h1)>[r1]-1α1(A1([r1]u1,u2)),
α1([r1]u1)=[r1]α1(u1)>α1(A1([r1]u1,u2)).
如果0<‖u1‖<r1且‖u2‖>R2,那么
u=A(u)=[r1]-1A([r1]u1,[R2]u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h,
u1=[r1]-1A1([r1]u1,[R2]u2)+(1-[r1]-1)h1.
由α1的凹性知
α1(u1)≥[r1]-1α1(A1([r1]u1,[R2]u2))+(1-[r1]-1)α1(h1)>[r1]-1α1(A1([r1]u1,[R2]u2)),
α1([r1]u1)=[r1]α1(u1)>α1(A1([r1]u1,[R2]u2)).
如果r1≤‖u1‖≤R1且0<‖u2‖<r2,则
u=A(u)=[r2]-1A(u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r2]-1)h,
u2=[r2]-1A2(u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r2]-1)h2.
由α2的凹性知
α2(u2)≥[r2]-1α2(A2(u1,[r2]u2))+(1-[r2]-1)α2(h2)>[r2]-1α2(A2(u1,[r2]u2)),
α2([r2]u2)=[r2]α2(u2)>α2(A2(u1,[r2]u2)).
如果r1≤‖u1‖≤R1且‖u2‖>R2,那么
u=A(u)=A(u1,[R2]u2),从而
u2=A2(u1,[R2]u2). 于是
α2(A2(u1,[R2]u2))=α2(u2)>[R2]α2(u2)=α2([R2]u2).
如果‖u1‖>R1且0<‖u2‖<r2,那么
u=A(u)=[r2]-1A([R1]u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r2]-1)h,
u2=[r2]-1A2([R1]u1,[r2]u2)+(1-[r2]-1)h2,
由α2的凹性知
α2(u2)≥[r2]-1α2(A2([R1]u1,[r2]u2))+(1-[r2]-1)α2(h2)> [r2]-1α2(A2([R1]u1,[r2]u2)),
α2([r2]u2)=[r2]α2(u2)>α2(A1([R1]u1,[r2]u2)).
如果‖u1‖>R1且r2≤‖u2‖≤R2,那么
u=A(u)=A([R1]u1,u2),
从而u1=A1([R1]u1,u2). 于是
α1(A1([R1]u1,u2))=α1(u1)>[R1]α1(u1)=α1([R1]u1).
如果‖u1‖>R1且‖u1‖>R1,那么
u=A(u)=A([R1]u1,[R2]u2),
从而ui=Ai([R1]u1,[R2]u2). 于是
αi(Ai([R1]u1,[R2]u2))=αi(ui)>[Ri]αi(ui)=αi([Ri]ui)(i=1,2).
定理2 如果下列条件满足:
‖u1‖=r1⇒α1(A1(u))≥α1(u1),
‖u1‖=R1⇒α1(A1(u))≤α1(u1),
‖u2‖=r2⇒α2(A2(u))≤α2(u2),
‖u2‖=R2⇒α2(A2(u))≥α2(u2),
其中u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R,那么A在Kr,R中存在不动点.
证明 因为∀u2∈(K2)r2,R2,
([R2]+[r2]-1)u2∈(K2)r2,R2,
所以可设A1*:Kr,R→K1×K2为
A1*(u)=A1(u1,([R2]+[r2]-1)u2);
可设A2*:Kr,R→K1×K2为
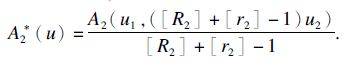
显然当‖u2‖=r2时,‖([R2]+[r2]-1)× u2‖=R2;当‖u2‖=R2时,‖([R2]+[r2]-1)u2‖=r2. 因此算子A*=(A1*,A2*)满足定理1的条件,从而A*存在不动点v=(v1,v2)∈Kr,R.
令u=(u1,u2)为u1=v1,
u2=(R2/‖v2‖+r2/‖v2‖-1)v2,
易见u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R是A的不动点.
定理3 如果下列条件满足:
‖u1‖=r1⇒α1(A1(u))≤α1(u1),
‖u1‖=R1⇒α1(A1(u))≥α1(u1),
‖u2‖=r2⇒α2(A2(u))≥α2(u2),
‖u2‖=R2⇒α2(A2(u))≤α2(u2),
其中u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R,那么A在Kr,R中存在不动点.
证明 因为∀u1∈(K1)r1,R1,
([R1]+[r1]-1)u1∈(K1)r1,R1,
所以可设A1 **:Kr,R→K1×K2为
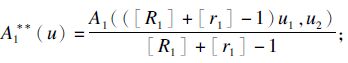
可设A2 **:Kr,R→K1×K2为
A2 **(u)=A2(([R1]+[r1]-1)u1,u2).
显然当 ‖u1‖=r1时,‖([R1]+[r1]-1)× u1‖=R1; 当‖u1‖=R1时,‖([R1]+[r1]-1)u1‖=r1. 因此算子A* *=(A1 **,A2 **)满足定理1的条件,从而A* *存在不动点v=(v1,v2)∈Kr,R.
令u=(u1,u2)为u2=v2,
u1=(R1/‖v1‖+r1/‖v1‖-1)v1,
易见u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R是A的不动点.
定理4 如果下列条件满足:
‖u1‖=r1⇒α1(A1(u))≤α1(u1),
‖u1‖=R1⇒α1(A1(u))≥α1(u1),
‖u2‖=r2⇒α2(A2(u))≤α2(u2),
‖u2‖=R2⇒α2(A2(u))≥α2(u2),
其中u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R,那么A在Kr,R中存在不动点.
证明 因为∀u1∈(K1)r1,R1,
([R1]+[r1]-1)u1∈(K1)r1,R1,
∀u2∈(K2)r2,R2,
([R2]+[r2]-1)u2∈(K2)r2,R2,
所以可设A1* * *:Kr,R→K1×K2为
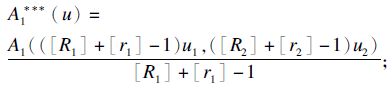
可设A2* * *:Kr,R→K1×K2为
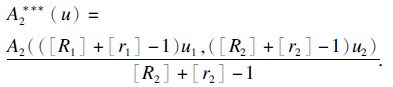
因此算子A* * *=(A1* * *,A2* * *)满足定理1的条件,从而A* * *存在不动点v=(v1,v2)∈Kr,R.
令u=(u1,u2)为
u1=(R1/‖v1‖+r1/‖v1‖-1)v1,
u2=(R2/‖v2‖+r2/‖v2‖-1)v2,
易见u=(u1,u2)∈Kr,R是A的不动点.
2 结 语设E=C(G)为N维欧氏空间RN中非空有界闭集G上的连续函数空间,令
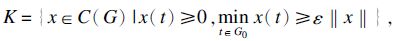
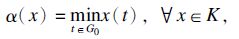
| [1] | 郭大钧.非线性泛函分析[M].2版.济南:山东科学技术出版社,2001. (Guo Da-jun.Nonlinear functional analysis [M].2nd ed.Jinan:Shandong Science and Technology Press,2001.)( 2) 2) |
| [2] | Precup R. A vector version of Krasnoselskii fixed point theorem in cones and positive periodic solutions of nonlinear systems[J].Journal of Fixed Point Theory and Applications, 2007,2(1):141-151. ( 1) 1) |
| [3] | Avery R,Henderson J,O’Regan D.Four functionals fixed point theorem[J].Mathematical and Computer Modelling,2008,48(7/8):1081-1089.( 1) 1) |
| [4] | Anderson D R,Zhai C.Positive solutions to semi-positone second-order three-point problems on time scales[J].Applied Mathematics and Computation,2010,215(10):3713-3720.( 1) 1) |
| [5] | Cabada A, Cid J A.Existence of a non-zero fixed point for nondecreasing operators via Krasnoselskii’s fixed point theorem[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Theory,Method & Applications,2009,71(5/6):2114-2118.( 1) 1) |
| [6] | 费祥历,王峰,陈云.关于一个新泛函的锥拉伸与压缩不动点定理及应用[J].纯粹数学与应用数学,2010,26(4):547-553. (Fei Xiang-li,Wang Feng,Chen Yun.A cone expansion and compression fixed point theorem about a new functional and its applications[J].Pure and Applied Mathematics,2010,26(4): 547-553.)( 1) 1) |
| [7] | Han W,Jin Z,Kang S.Existence of positive solutions of nonlinear m-point BVP for an increasing homeomorphism and positive homomorphism on time scales[J].Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics,2009,233(2):188-196.( 1) 1) |
| [8] | Sun D D, Zhang G W.Computing the topological degree via semi-concave functionals[J].Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis,2012,39(1):107-117.( 1) 1) |
| [9] | Wong J S W.Existence of positive solutions for second order multi-point boundary value problems[J].Differential Equations & Applications,2012,4(2):197-219.( 1) 1) |
| [10] | Wang F,Zhang F,Yu Y.Existence of positive solutions of Neumann boundary value problem via a convex functional compression-expansion fixed point theorem[J].Fixed Point Theory,2010,11(2):395-400.( 1) 1) |
| [11] | Zhai C. Positive solutions for semi-positone three-point boundary value problems[J].Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics,2009,228(1):279-286.( 1) 1) |
| [12] | Zhang H, Sun J.Existence of positive solution to singular systems of second-order four-point BVPs[J].Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computation,2009,29(1/2):325-339.( 1) 1) |
| [13] | Zhang G W, Sun J X.A generalization of the cone expansion and compression fixed point theorem and applications[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Theory,Method & Applications,2007,67(2):579-586.( 1) 1) |




