
东北大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1244-1251.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2024.09.004
• 材料与冶金 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-08-03
出版日期:2024-09-15
发布日期:2024-12-16
通讯作者:
张德良
作者简介:冯 毅(1980-),男,重庆人,重庆大学博士研究生基金资助:
Yi FENG1,2, De-liang ZHANG2( ), Zhi-hui CAI3, Guang-jie HUANG1
), Zhi-hui CAI3, Guang-jie HUANG1
Received:2023-08-03
Online:2024-09-15
Published:2024-12-16
Contact:
De-liang ZHANG
About author:ZHANG De-liang, E-mail: zhangdeliang@caeri.com.cn摘要:
本文对比了Fe-11Mn-4Al-0.2C中锰钢变形过程中增塑机制和力学性能的演变规律.随应变速率增加(0.002~200 s-1),中锰钢屈服强度和抗拉强度的变化趋势截然相反,屈服强度从507 MPa增加到649 MPa,但抗拉强度却从1 089 MPa降低到876 MPa.准静态加载时增塑机制以强相变诱导塑性(transformation‐induced plasticity,TRIP)效应为主;动态加载初期增塑机制以弱TRIP效应为主,加载后期TRIP效应消失,转变为温升软化效应和孪晶诱导塑性(twinning‐induced plasticity,TWIP)效应.动态加载初期的位错运动速率远高于准静态的,这导致动态的屈服强度高于准静态的.随着应变的增加,动态加载逐渐累积的绝热温升抑制了马氏体相变,降低了加工硬化能力,而准静态加载则不断产生高硬度马氏体,导致准静态的抗拉强度高于动态的.
中图分类号:
冯毅, 张德良, 蔡志辉, 黄光杰. Fe-11Mn-4Al-0.2C中锰钢准静态和动态变形行为[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(9): 1244-1251.
Yi FENG, De-liang ZHANG, Zhi-hui CAI, Guang-jie HUANG. Quasi-Static and Dynamic Deformation Behavior of Fe-11Mn-4Al-0.2C Medium-Mn Steel[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(9): 1244-1251.

图8 中锰钢准静态加载不同应变的组织形貌(a)—0.10; (b)—0.25; (c)—0.35(断裂).
Fig.8 Morphologies of medium-Mn steel samples under quasi?statical loading with different strains?T=?Qρcp=gρcp∫ε2ε1σtdεt . (2)
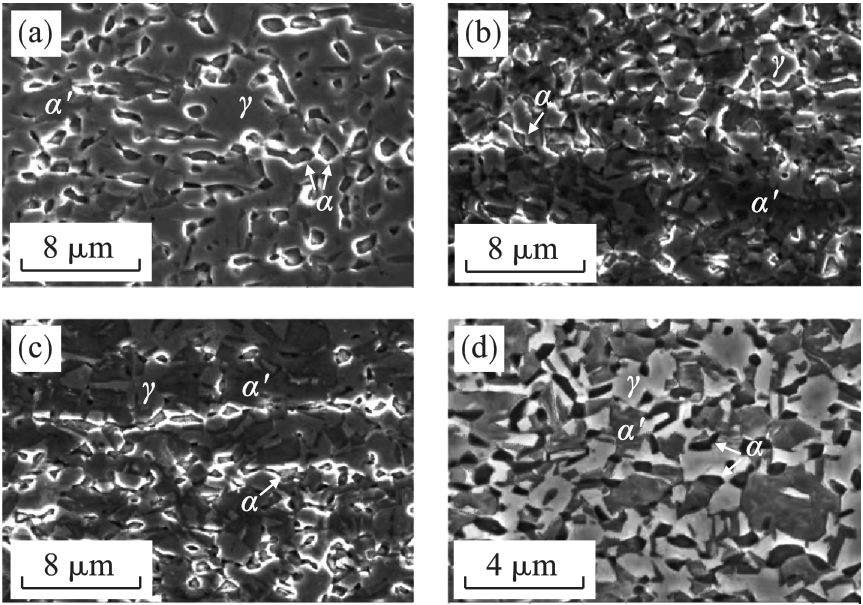
图9 中锰钢动态加载不同应变的组织形貌(a)—0.10; (b)—0.25; (c)—0.35; (d)—0.40(断裂).
Fig.9 Morphologies of medium-Mn steel samples under dynamical loading with different strains
| 工程应变 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.40(断裂) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 s-1绝热温升/K | 15 | 45 | 68 | 77 |
表1 动态加载不同应变时绝热温升 (loading with different strains)
Table 1 Adiabatic temperature rise under dynamic
| 工程应变 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.40(断裂) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 s-1绝热温升/K | 15 | 45 | 68 | 77 |
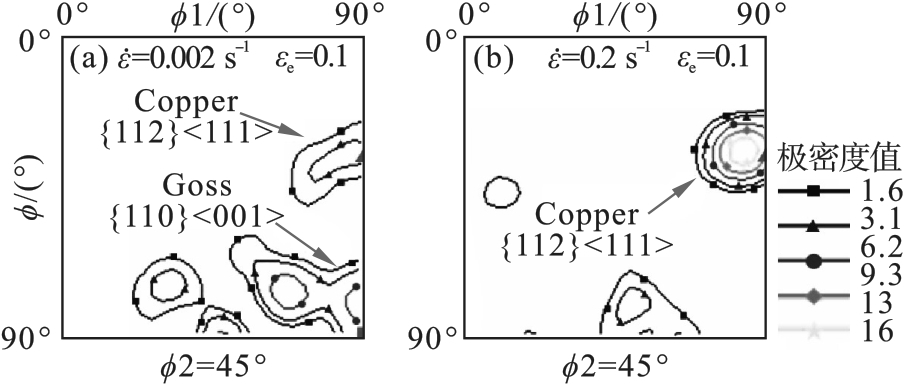
图11 εe=0.10时奥氏体?2=45°的方向分布函数(ODF)的等高线(a)—0.002 s-1; (b)—0.2 s-1.
Fig.11 Contour plots of the orientation distribution function (ODF) for austenite with ?2=45° at εe=0.10
| 工程应变 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 s-1层错能/(mJ·m-2) | 11.8 | 18.2 | 23.1 | 25.1 |
表2 动态加载不同应变下的层错能 (at the different strains)
Table 2 Stacking fault energy under dynamic loading
| 工程应变 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 s-1层错能/(mJ·m-2) | 11.8 | 18.2 | 23.1 | 25.1 |
| 应变速率/s-1 | 工程应变 | 奥氏体位错密度/m-2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 7.71e+14 |
| 0.002 | 0.10 | 21.12e+14 |
| 0.2 | 0.10 | 20.57e+14 |
表3 未变形试样和变形初期试样奥氏体位错密度
Table 3 Austenite dislocation density of the undeformed and initial deformation samples
| 应变速率/s-1 | 工程应变 | 奥氏体位错密度/m-2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 7.71e+14 |
| 0.002 | 0.10 | 21.12e+14 |
| 0.2 | 0.10 | 20.57e+14 |
| 1 | 蔡志辉,丁桦,薛鑫.新型中锰热轧TRIP钢组织演变及力学性能[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2013,34(1):62-65,70. |
| Cai Zhi‑hui, Ding Hua, Xue Xin.Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of a novel medium-Mn hot‑rolled TRIP steel[J].Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2013,34(1):62-65,70. | |
| 2 | Kalhor A, Soleimani M, Mirzadeh H,et al.A review of recent progress in mechanical and corrosion properties of dual phase steels[J].Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,2020,20(3):85-96. |
| 3 | 韦习成,符仁钰,李麟,等.不同应变率下 TRlP钢的拉伸性能[J].上海金属,2002,24(4):32-36. |
| Wei Xi‑cheng, Fu Ren‑yu, Li Lin,et al.Tensile property of TRIP steel under different strain rates[J].Shanghai Metals,2002,24(4):32-36. | |
| 4 | 史文超.TRIP780高强钢动态变形行为的宏微观研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2009. |
| Shi Wen‑chao.Macroscopic and microscopic study on dynamic deformation behavior of TRIP780 high strength steel[D].Shanghai:Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2009. | |
| 5 | Tian R, Li L, de Cooman B C,et al.Effect of temperature and strain rate on dynamic properties of low silicon TRIP steel[J].Journal of Iron and Steel Research International,2006,13(3):51-56. |
| 6 | Sahu P, Curtze S, Das A,et al.Stability of austenite and quasi‑adiabatic heating during high‑strain‑rate deformation of twinning‑induced plasticity steels[J].Scripta Materialia,2010,62(1):5-8. |
| 7 | Xu M, Yang Y G, Chen J Y,et al.Effects of strain states on stability of retained austenite in medium Mn steels[J].Journal of Iron and Steel Research International,2017,24(11):1125-1130. |
| 8 | Hwang S W, Ji J H, Park K T.Effects of Al addition on high strain rate deformation of fully austenitic high Mn steels[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2011,528(24):7267-7275. |
| 9 | Lee S, Estrin Y, de Cooman B C.Effect of the strain rate on the TRIP‑TWIP transition in austenitic Fe-12pctMn-0.6pctC TWIP steel[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,2014,45(2):717-730. |
| 10 | 蔡志辉.高强塑性中锰钢的组织演变及力学性能的研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2015. |
| Cai Zhi‑hui.Study on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of medium manganese steels with superior strength and ductility[D].Shenyang:Northeastern University,2015. | |
| 11 | Cai Z H, Ding H, Misra R D K,et al.Austenite stability and deformation behavior in a cold‑rolled transformation‐induced plasticity steel with medium manganese content [J].Acta Materialia,2015,84:229-236. |
| 12 | Min J Y, Hector L G J, Zhang L,et al.Plastic instability at elevated temperatures in a TRIP-assisted steel[J].Materials & Design,2016,95:370-386. |
| 13 | Kozłowska A, Grzegorczyk B, Morawiec M,et al.Explanation of the PLC effect in advanced high‑strength medium-Mn steels:a review[J].Materials,2019,12(24):4175. |
| 14 | 王礼立,王永刚.应力波在用SHPB研究材料动态本构特性中的重要作用[J].爆炸与冲击,2005,25(1):17-25. |
| Wang Li‑li, Wang Yong‑gang.The important role of stress waves in the study on dynamic constitutive behavior of materials by SHPB[J].Explosion and Shock Waves,2005,25(1):17-25. | |
| 15 | 徐明利,张若棋,张光莹.SHPB实验中试件内早期应力平衡分析[J].爆炸与冲击,2003,23(3):235-240. |
| Xu Ming‑li, Zhang Ruo‑qi, Zhang Guang‑ying.Analysis of early stage specimen stress equilibrium in SHPB experiment[J].Explosion and Shock Waves,2003,23(3):235-240. | |
| 16 | Yen H W, Ooi S W, Eizadjou M,et al.Role of stress‑assisted martensite in the design of strong ultrafine‑grained duplex steels[J].Acta Materialia,2015,82:100-114. |
| 17 | Ma J W, Liu H T, Lu Q,et al.Transformation kinetics of retained austenite in the tensile Lüders strain range in medium Mn steel[J].Scripta Materialia,2019,169:1-5. |
| 18 | Curtze S, Kuokkala V T.Dependence of tensile deformation behavior of TWIP steels on stacking fault energy,temperature and strain rate[J].Acta Materialia,2010,58(15):5129-5141. |
| 19 | Mazancová E, Mazanec K.Stacking fault energy in high manganese alloys[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2009,16(2):26-31. |
| 20 | Gey N, Petit B, Humbert M.Electron backscattered diffraction study of ε/α’ martensitic variants induced by plastic deformation in 304 stainless steel[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,2005,36(12):3291-3299. |
| 21 | Saeed‑Akbari A, Imlau J, Prahl U,et al.Derivation and variation in composition‑dependent stacking fault energy maps based on subregular solution model in high‑manganese steels[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,2009,40(13):3076-3090. |
| 22 | 宋仁伯,霍巍丰,周乃鹏,等.Fe-Mn-Al-C系中锰钢的研究现状与发展前景[J].工程科学学报,2020,42(7):814-828. |
| Song Ren‑bo, Huo Wei‑feng, Zhou Nai‑peng,et al.Research progress and prospect of Fe-Mn-Al-C medium Mn steels[J].Chinese Journal of Engineering,2020,42(7):814-828. | |
| 23 | Allain S, Chateau J P, Bouaziz O,et al.Correlations between the calculated stacking fault energy and the plasticity mechanisms in Fe-Mn-C alloys[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2004,387/388/389:158-162. |
| 24 | Frommeyer G, Brüx U, Neumann P.Supra‑ductile and high‑strength manganese‑TRIP/TWIP steels for high energy absorption purposes[J].ISIJ International,2003,43(3):438-446. |
| 25 | 闫翠,李麟,符仁钰,等.TRIP钢的研究进展[J].上海金属,2008,30(4):40-44. |
| Yan Cui, Li Lin, Fu Ren‑yu,et al.A review on research progress of trip steel[J].Shanghai Metals,2008,30(4):40-44. | |
| 26 | Koyama M.Twinning‑induced plasticity (TWIP) steel[M]//Encyclopedia of Materials:Metals and Alloys.Amsterdam:Elsevier,2022:95-105. |
| 27 | 李亦庄,黄明欣.基于中子衍射和同步辐射X射线衍射的TWIP钢位错密度计算方法[J].金属学报,2020,56(4):487-493. |
| Li Yi‑zhuang, Huang Ming‑xin.A method to calculate the dislocation density of a TWIP steel based on neutron diffraction and synchrotron X-ray diffraction[J].Acta Metallurgica Sinica,2020,56(4):487-493. | |
| 28 | Gray G T.High‑strain‑rate deformation:mechanical behavior and deformation substructures induced[J].Annual Review of Materials Research,2012,42:285-303. |
| 29 | Fan H D, Wang Q Y, El‑Awady J A,et al.Strain rate dependency of dislocation plasticity[J].Nature Communications,2021,12(1):1845. |
| 30 | 李春光,张伟,刘立现,等.不同应变速率双相高强钢动态力学行为微观机理分析[J].锻压技术,2018,43(6):166-171. |
| Li Chun‑guang, Zhang Wei, Liu Li‑xian,et al.Analysis on micro‑mechanism of dynamic mechanical behavior for high‑strength steel with dual‑phase under different strain rates[J].Forging & Stamping Technology,2018,43(6):166-171. |
| [1] | 马原, 佘黎煌, 李佳蔚, 鲍喜荣. 基于注意力机制的自适应图卷积三维点云识别算法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(6): 786-792. |
| [2] | 贾蓬, 毛松泽, 钱一锦, 卢佳亮. 不同加载速率下冻融砂岩的动态劈裂特性[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(1): 111-119. |
| [3] | 赵永, 古旭升, 王述红, 高煬. 不同岩性岩石单轴压缩破坏共性前兆特征[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(9): 1309-1317. |
| [4] | 朱钊, 李源, 韩逸涛. 车致爆炸作用下装配式桥墩损伤模式及安全防护距离[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(9): 1337-1348. |
| [5] | 李海峰, 杨巧婷, 邵磊, 邹宗树. 高炉内料层结构动态追踪的技术开发[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(5): 617-625. |
| [6] | 李婵, 曲璐渲, 信俊昌, 王之琼. 基于潜在调控因子筛选的高阶动态贝叶斯建模方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(3): 323-330. |
| [7] | 苏元飞, 李慧杰, 徐晓宁, 叶其斌. 温轧对DP590钢层状超细晶双相组织与拉伸性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(3): 357-363. |
| [8] | 耿蓉, 张昭, 牛天水, 王宇飞. 基于改进蚁群算法的天基资源调度研究与仿真[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(2): 168-176. |
| [9] | 王娜, 李杨, 彭锟. 基于多角度特征提取的舵机故障诊断方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(9): 1240-1249. |
| [10] | 信俊昌, 郭恩铭, 张嘉正. 基于时序区分子图的阿尔茨海默症辅助诊断方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(8): 1089-1096. |
| [11] | 李小彭, 樊星, 李凯, 张凌越. 考虑负载时变的线路巡检机器人动态性能分析[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(5): 660-667. |
| [12] | 李奇, 于天彪, 王宛山. 光学自由曲面铣床静动态特性研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(5): 674-680. |
| [13] | 丁山, 臧仕义, 曹殿明, 佘黎煌. 基于动态ID跳变的CAN总线安全调度算法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(3): 350-358. |
| [14] | 蔡志辉, 张德良, 文光奇, 周彦君. Fe-11Mn-4Al-0.2C中锰钢动态变形行为及其本构模型[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(9): 1275-1281. |
| [15] | 张瑞友, 王超慧, 陈勇强. 基于控制思想求解非线性规划问题的李雅普诺夫方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(9): 1217-1226. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||