
东北大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 170-178.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2024.02.003
• 材料与冶金 • 上一篇
姚文博, 刘忱, 商硕, 刘常升
收稿日期:2023-01-15
出版日期:2024-02-15
发布日期:2024-05-14
作者简介:姚文博(1997-),男,辽宁盘锦人,东北大学硕士研究生基金资助:Wen-bo YAO, Chen LIU, Shuo SHANG, Chang-sheng LIU
Received:2023-01-15
Online:2024-02-15
Published:2024-05-14
摘要:
为提高工程用高强钢的耐蚀性并降低使用材料成本,采用光纤激光器在Q960E高强钢表面以同轴送粉工艺制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层,研究不同扫描速度对组织及耐蚀性的影响.结果表明,熔覆层的晶粒形态与元素分布及含量都受到扫描速度的影响.物相主要由DO3结构的Fe3Al相和B2结构的FeAl相以共晶形式组成.熔覆层的硬度随扫描速度增加受晶粒细化的影响逐渐提高.3种扫描速度下的熔覆层自腐蚀电位随扫描速度增加先上升后下降,自腐蚀电流密度先减小后增大,经过极化后的熔覆层表面点蚀坑随扫描速度的增加先由深变浅,后点蚀坑面积扩大.
中图分类号:
姚文博, 刘忱, 商硕, 刘常升. 扫描速度对激光熔覆Fe-Al合金熔覆层组织及性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(2): 170-178.
Wen-bo YAO, Chen LIU, Shuo SHANG, Chang-sheng LIU. Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding Fe‐Al Alloy at Different Scanning Speeds[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(2): 170-178.
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | P | S | Al | B | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.20 | 0.50 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 余量 |
表1 Q960E高强钢的化学成分(质量分数) (%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of Q960E high‐strength steel(mass fraction)
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | P | S | Al | B | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.20 | 0.50 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 余量 |
| Cu | Fe | Mg | Mn | Si | Ti | Zn | Cr | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.15 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 余量 |
表2 6061铝合金粉末的化学成分(质量分数) (%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of 6061 aluminum alloy powder(mass fraction)
| Cu | Fe | Mg | Mn | Si | Ti | Zn | Cr | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.15 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 余量 |
| C | P | S | Si | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.012 | 0.0015 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 余量 |
表3 纯铁粉末的化学成分(质量分数) (%)
Table 3 Chemical composition of pure iron powder (mass fraction)
| C | P | S | Si | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.012 | 0.0015 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 余量 |
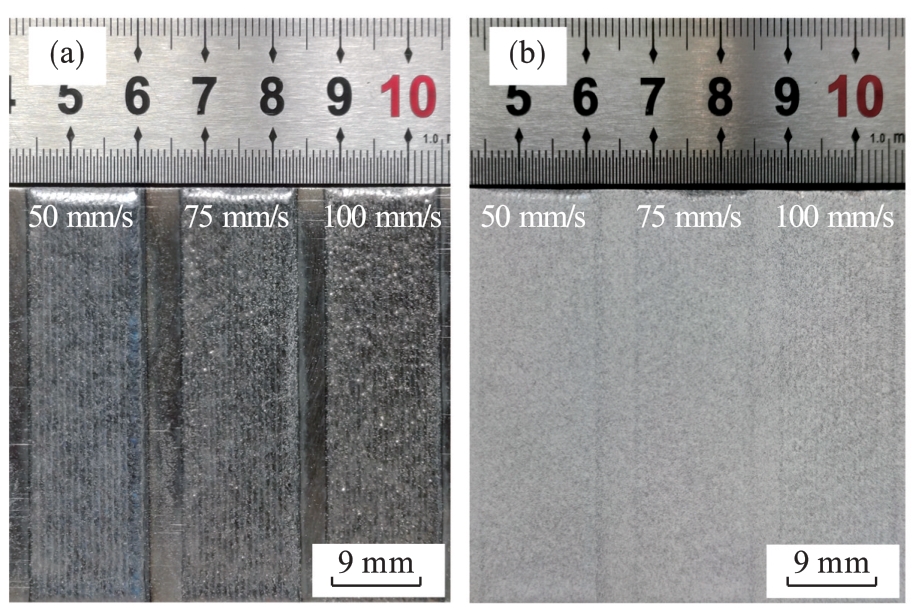
图2 不同激光扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层的宏观形貌与探伤后形貌(a)—探伤前; (b)—探伤后.
Fig.2 Macroscopic morphology and flawed morphology of Fe-Al alloy cladding layer prepared at different laser scanning speeds
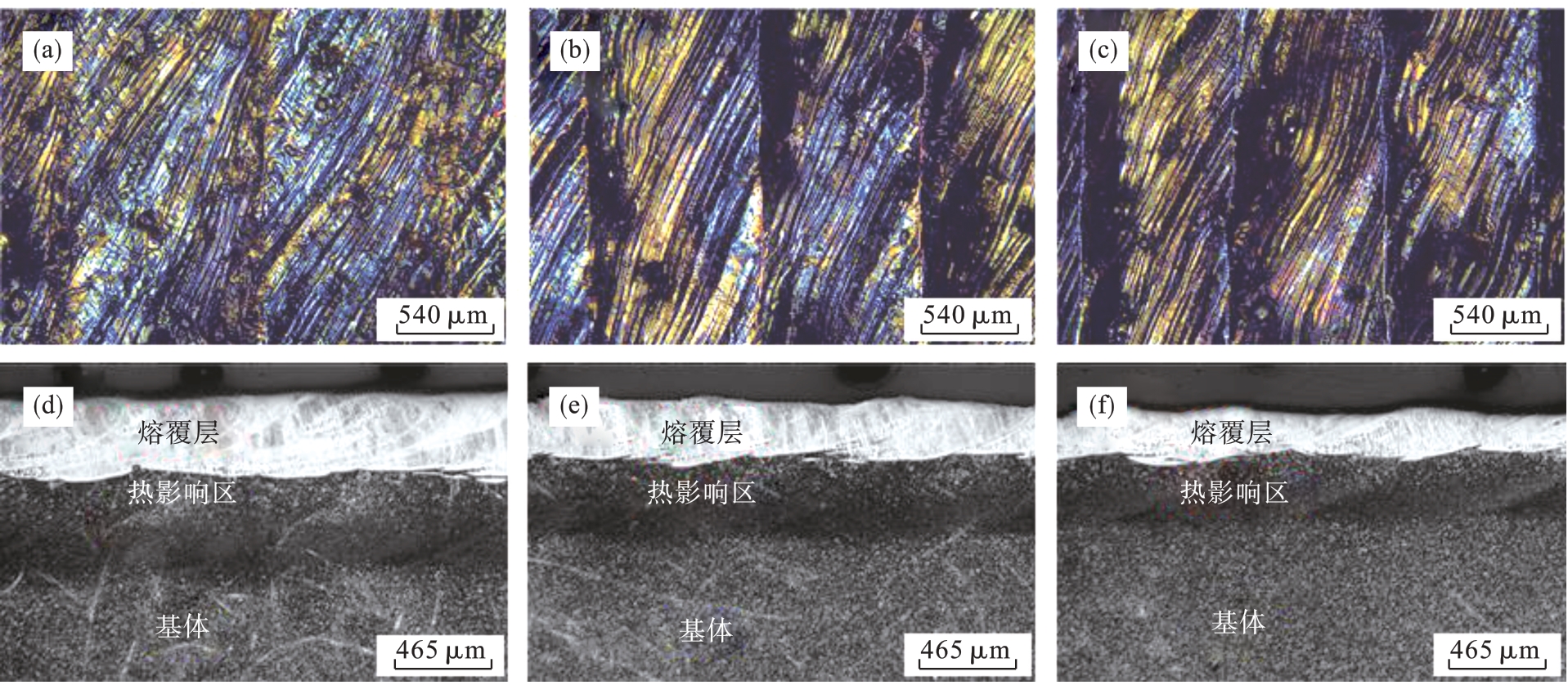
图3 不同扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层表面光学形貌及横截面金相组织(a)(d)—50 mm/s; (b)(e)—75 mm/s; (c)(f)—100 mm/s.
Fig.3 Surface optical morphology and cross-sectional metallographic microstructure of Fe-Al alloy cladding layer prepared at different scanning speeds
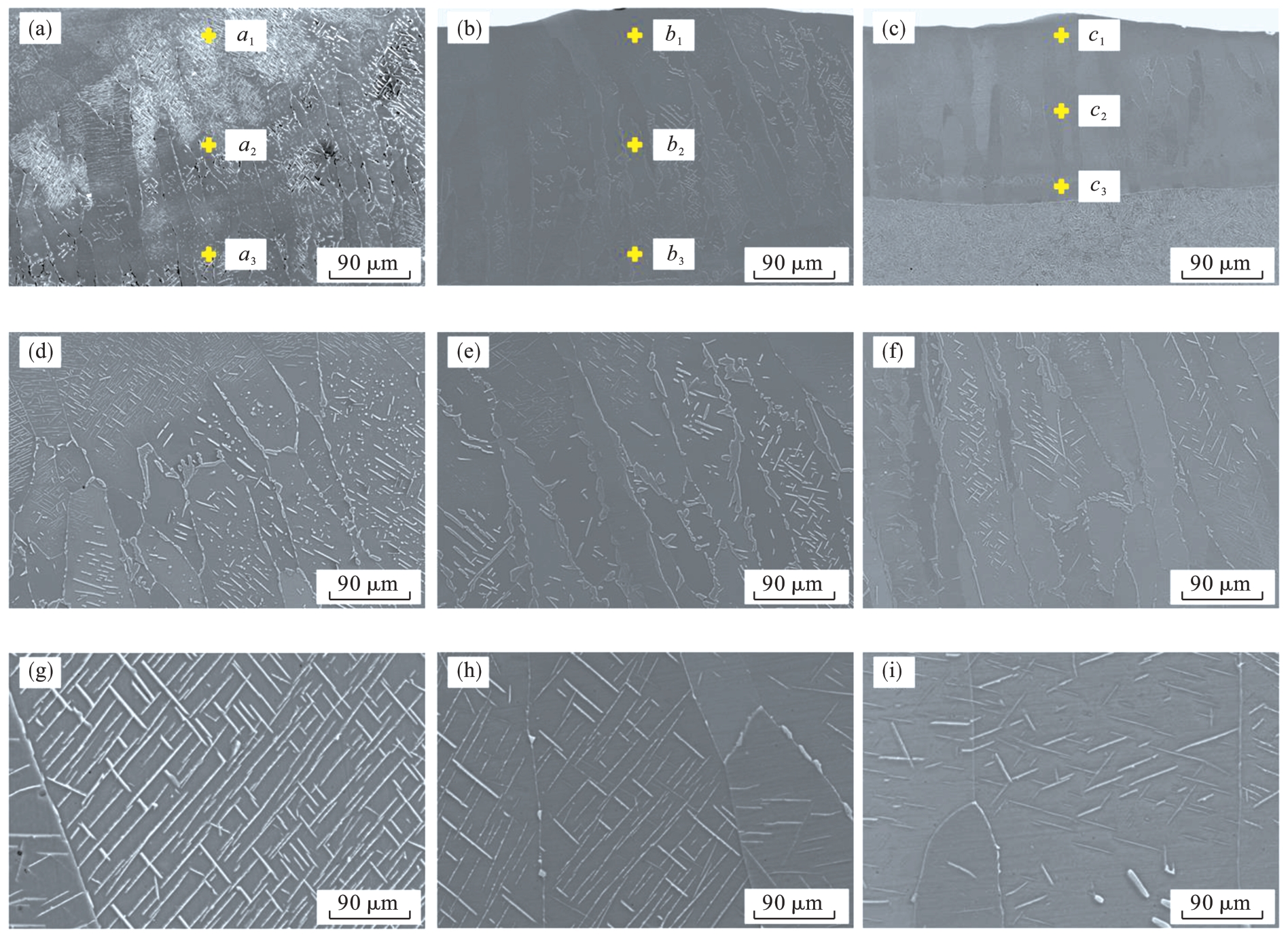
图4 不同扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层截面的SEM图(a)(d)(g)—50 mm/s; (b)(e)(h)—75 mm/s; (c)(f)(i)—100 mm/s.
Fig.4 SEM images of the cross section of Fe-Al alloy cladding layer prepared at different scanning speeds
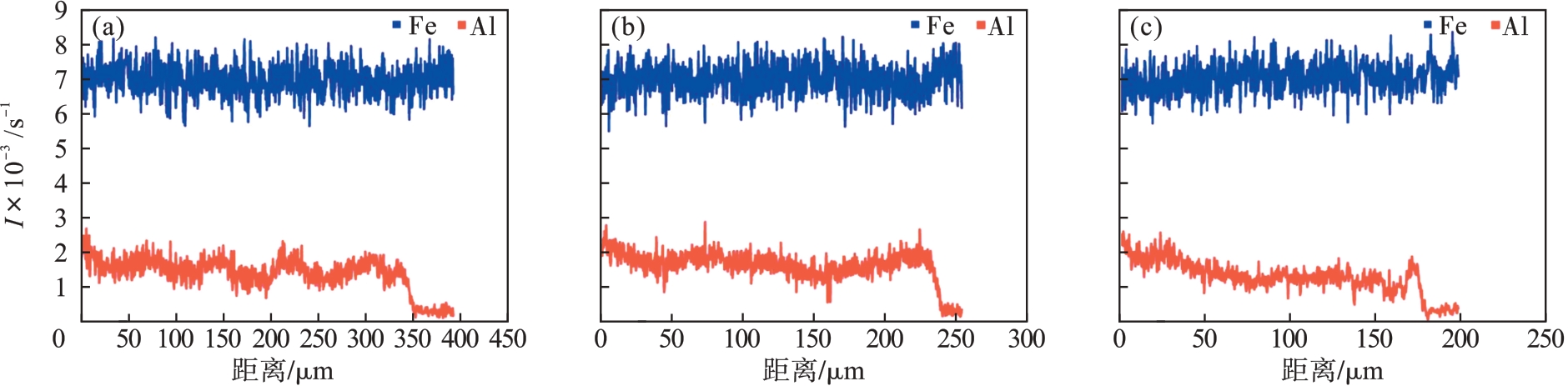
图5 不同扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层截面的EDS图(a)—50 mm/s; (b)—75 mm/s; (c)—100 mm/s.
Fig.5 EDS plots of the cross section of Fe-Al alloy cladding layer prepared at different scanning speeds
| 元素 | a1 | a2 | a3 | b1 | b2 | b3 | c1 | c2 | c3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 14.64 | 10.48 | 11.16 | 14.84 | 11.70 | 13.34 | 13.20 | 9.20 | 8.08 |
| Fe | 85.36 | 89.52 | 88.84 | 85.16 | 88.30 | 86.66 | 86.80 | 90.80 | 91.92 |
表4 不同扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层截面沿表面至基底的点扫描元素含量(原子数分数) (%)
Table 4 Point scan of cross section from surface to substrate of Fe Al alloy cladding layer prepared at different scanning speeds(atom fraction)
| 元素 | a1 | a2 | a3 | b1 | b2 | b3 | c1 | c2 | c3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 14.64 | 10.48 | 11.16 | 14.84 | 11.70 | 13.34 | 13.20 | 9.20 | 8.08 |
| Fe | 85.36 | 89.52 | 88.84 | 85.16 | 88.30 | 86.66 | 86.80 | 90.80 | 91.92 |
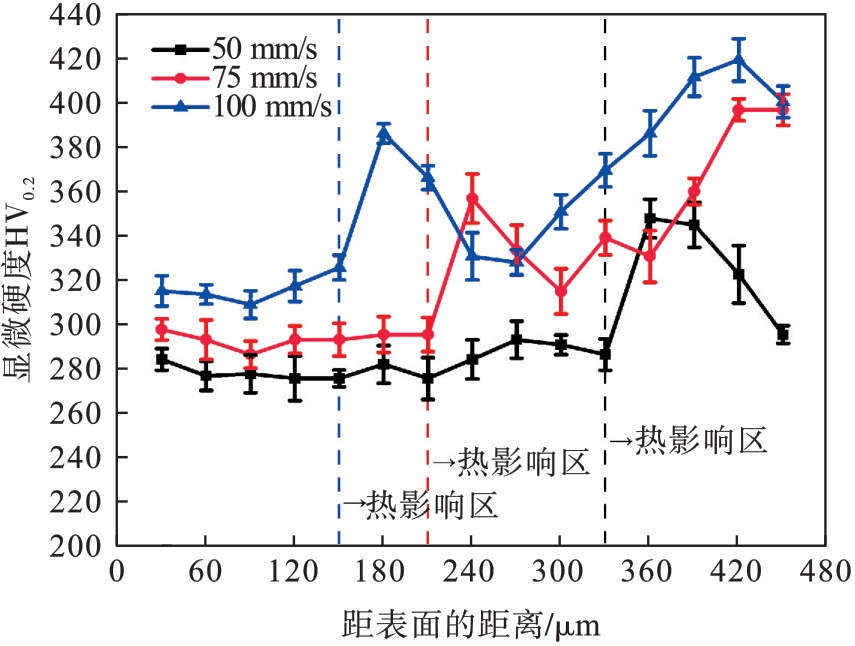
图8 不同扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层表面至 基底方向的硬度
Fig.8 Hardness of Fe-Al alloy cladding layer from surface to substrate direction prepared at different scanning speeds
| 扫描速度/(mm·s-1) | 自腐蚀电位/V | 自腐蚀电流密度 |
|---|---|---|
| A·cm-2 | ||
| 50 | -0.937 | 2.158×10-6 |
| 75 | -0.887 | 1.119×10-6 |
| 100 | -0.939 | 2.104×10-6 |
表5 不同扫描速度下所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层的自腐蚀电位与自腐蚀电流密度
Table 5 Corrosion potential and corrosion current of the molten cladding layer at different scanning speeds
| 扫描速度/(mm·s-1) | 自腐蚀电位/V | 自腐蚀电流密度 |
|---|---|---|
| A·cm-2 | ||
| 50 | -0.937 | 2.158×10-6 |
| 75 | -0.887 | 1.119×10-6 |
| 100 | -0.939 | 2.104×10-6 |
| 扫描速度/(mm·s-1) | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | CCPE1/(μF·cm-2) | n1 | CCPE2/(μF·cm-2) | n2 | Rc/(Ω·cm2) | Rct/(Ω·cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 6.271 | 3.527 2×10-4 | 0.814 94 | 48.939×10-4 | 0.813 93 | 1 556 | 383.9 |
| 75 | 4.586 | 6.551 6×10-4 | 0.765 18 | 10.511×10-4 | 0.500 51 | 876 | 1 022 |
| 100 | 5.629 | 3.797 9×10-4 | 0.812 86 | 15.81×10-4 | 0.597 15 | 1 009 | 600.1 |
表6 不同扫描速度下的EIS拟合结果
Table 6 EIS fitting results at different scanning speeds
| 扫描速度/(mm·s-1) | Rs/(Ω·cm2) | CCPE1/(μF·cm-2) | n1 | CCPE2/(μF·cm-2) | n2 | Rc/(Ω·cm2) | Rct/(Ω·cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 6.271 | 3.527 2×10-4 | 0.814 94 | 48.939×10-4 | 0.813 93 | 1 556 | 383.9 |
| 75 | 4.586 | 6.551 6×10-4 | 0.765 18 | 10.511×10-4 | 0.500 51 | 876 | 1 022 |
| 100 | 5.629 | 3.797 9×10-4 | 0.812 86 | 15.81×10-4 | 0.597 15 | 1 009 | 600.1 |
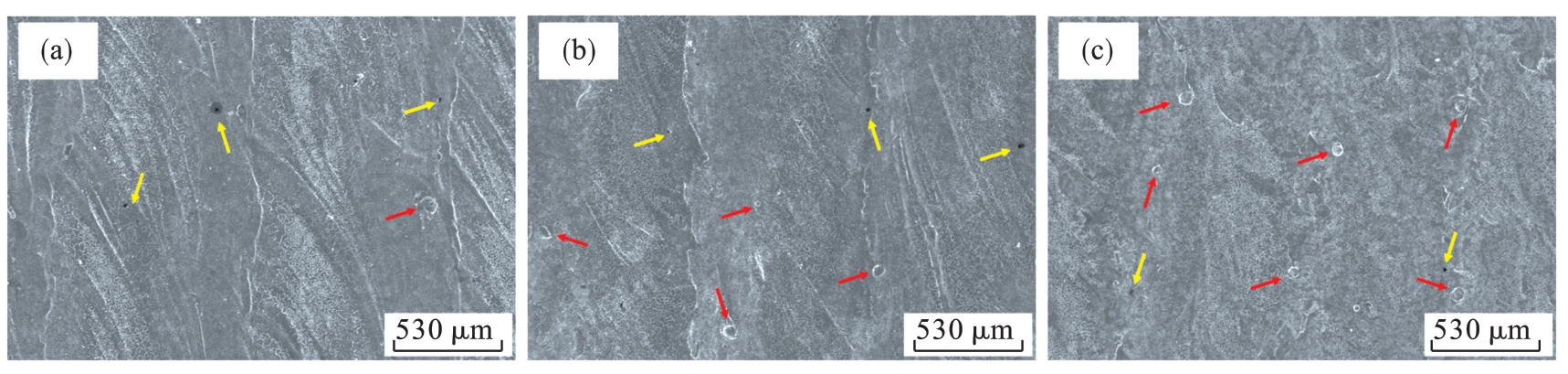
图13 不同扫描速度所制备Fe-Al合金熔覆层极化后的表面形貌(a)—50 mm/s; (b)—75 mm/s; (c)—100 mm/s.
Fig.13 Surface morphology after polarization of Fe-Al alloy cladding layer prepared at different scanning speeds
| 1 | Zhu X X, Shen Y F, Ge Y P,et al.Effect of hot dip plating process parameters on microstructure and properties of zinc‐10% aluminum‐mischmetal alloy coated for bridge cable steel wire[J].Metals,2022,12(8):1257. |
| 2 | Zhao J, Gao Q W, Wang H Q,et al.Microstructure and mechanical properties of Co‐based alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding and plasma arc spray welding[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,785:846-854. |
| 3 | 顾剑锋,李沛,钟庆东.物理气相沉积在耐腐蚀涂层中的应用[J].材料导报,2016,30(9):75-80. |
| Gu Jian‑feng, Li Pei, Zhong Qing‑dong.Application of physical vapor deposition in corrosion resistant coatings[J].Materials Reports,2016,30(9):75-80. | |
| 4 | Wang Q Y, Zhang Y F, Bai S L,et al.Microstructures,mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Hastelloy C22 coating produced by laser cladding[J].Journal of alloys and compounds,2013,553:253-258. |
| 5 | Liu J, Liu H, Tian X H,et al.Microstructural evolution and corrosion properties of Ni‐based alloy coatings fabricated by multi‐layer laser cladding on cast iron[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,822:153708. |
| 6 | 任超,李铸国,疏达,等.17-4PH 不锈钢表面激光熔覆 Stellite6 涂层组织及耐水蚀性能[J].中国激光,2017,44(4):107-114. |
| Ren Chao, Li Zhu‑guo, Shu Da,et al.Microstructure and water erosion resistance property of Stellite6 coating by laser cladding on 17-4PH stainless steel surface[J].Chinese Journal of Lasers,2017,44(4):107-114. | |
| 7 | Li Y Z, Shi Y.Microhardness,wear resistance,and corrosion resistance of AlxCrFeCoNiCu high‑entropy alloy coatings on aluminum by laser cladding[J].Optics & Laser Technology,2021,134:106632. |
| 8 | 高帅龙,孙德福,谷臻,等.机械合金化粉末激光熔化沉积制备Fe-Cr-Mn-N奥氏体不锈钢厚熔覆涂层的性能[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2022,51(1):321-326. |
| Gao Shuai‐long, Sun De‐fu, Gu Zhen,et al.Properties of Fe-Cr-Mn-N austenitic stainless steel thick cladding coating prepared by laser melting deposition using mechanical alloyed powders[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2022,51(1):321-326. | |
| 9 | Liu J, Liu H, Chen P J,et al.Microstructural characterization and corrosion behaviour of AlCoCrFeNiTix high‐entropy alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding[J].Surface and Coatings Technology,2019,361:63-74. |
| 10 | Rao V S.A review of the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of iron aluminides[J].Electrochimica Acta,2004,49(26):4533-4542. |
| 11 | Totemeier T C, Wright R N, Swank W D.FeAl and Mo-Si-B intermetallic coatings prepared by thermal spraying[J].Intermetallics,2004,12(12):1335-1344. |
| 12 | Luo X X, Cao J, Meng G H,et al.Systematical investigation on the microstructures and tribological properties of Fe-Al laser cladding coatings[J].Applied Surface Science,2020,516:146121. |
| 13 | Luo X X, Yao Z J, Zhang P Z,et al.Laser cladding Fe-Al-Cr coating with enhanced mechanical properties[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology:Materials Science Edition,2019,34(5):1197-1204. |
| 14 | Nunobiki M, Harada Y, Okuda K.Production of Fe‐Al alloy coat on steel block by scanning laser beam[J].Advanced Materials Research,2014,1017:794-799. |
| 15 | Sharma G, Awasthi R, Chandra K.A facile route to produce Fe-Al intermetallic coatings by laser surface alloying[J].Intermetallics,2010,18(11):2124-2127. |
| 16 | 徐瀚宗,葛鸿浩,王杰锋,等.工艺参数对316L不锈钢激光熔覆层中Cr元素分布的影响[J].中国激光,2020,47(12):94-103. |
| Xu Han‐zong, Ge Hong‐hao, Wang Jie‐feng,et al.Effects of process parameters upon chromium element distribution in laser‐cladded 316L stainless steel[J].Chinese Journal of Lasers,2020,47(12):94-103. | |
| 17 | Qiao Y X, Huang J, Huang D,et al.Effects of laser scanning speed on microstructure,microhardness,and corrosion behavior of laser cladding Ni45 coatings[J].Journal of Chemistry,2020,2020:1-11. |
| 18 | Li L Q, Shen F M, Zhou Y D,et al.Comparative study of stainless steel AISI 431 coatings prepared by extreme‐high‐speed and conventional laser cladding[J].Journal of Laser Applications,2019,31(4):042009. |
| 19 | Figueredo E W A, Apolinario L H R, Santos M V,et al.Influence of laser beam power and scanning speed on the macrostructural characteristics of AISI 316L and AISI 431 stainless steel depositions produced by laser cladding process[J].Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance,2021,30(5):3298-3312. |
| 20 | Xu X, Lu H F, Su Y Y,et al.Comparing corrosion behavior of additively manufactured Cr‐rich stainless steel coating between conventional and extreme high‐speed laser metal deposition[J].Corrosion Science,2022,195:109976. |
| 21 | Gaberšček M, Pejovnik S.Impedance spectroscopy as a technique for studying the spontaneous passivation of metals in electrolytes[J].Electrochimica Acta,1996,41(7/8):1137-1142. |
| 22 | Yang D C, Kan X F, Gao P F,et al.Influence of porosity on mechanical and corrosion properties of SLM 316L stainless steel[J].Applied Physics A,2022,128(1):1-9. |
| 23 | Parakh A, Vaidya M, Kumar N,et al.Effect of crystal structure and grain size on corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,863:158056. |
| 24 | Aghuy A A, Zakeri M, Moayed M H,et al.Effect of grain size on pitting corrosion of 304L austenitic stainless steel[J].Corrosion Science,2015,94:368-376. |
| 25 | Wang P J, Ma L W, Cheng X Q,et al.Influence of grain refinement on the corrosion behavior of metallic materials:a review[J].International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials,2021,28(7):1112-1126. |
| [1] | 温雪龙, 王承宝, 刘文博, 任海洋. 选区激光熔化FeCoNiCr系高熵合金微观组织的实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(4): 536-543. |
| [2] | 李慧杰, 韦浩, 徐晓宁, 叶其斌. 梯度结构中间坯制备超细晶低碳钢的组织特性与强化机理[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(11): 1578-1584. |
| [3] | 支卫军, 姚赞, 姜周华. 高碳镀锌钢丝的组织演变及对扭转性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(1): 49-54. |
| [4] | 赵宇辉, 高孟秋, 赵吉宾, 贺晨. 增减材复合制造WC颗粒增强316L不锈钢材料组织性能[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(2): 197-205. |
| [5] | 王胤, 李勇, 钱晓明, 张博四. 真空离心铸造冷却速率对7055铝合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(12): 1769-1776. |
| [6] | 姚云龙, 修世超, 孙聪, 洪远. 基于40Cr高温动态力学性能的磨削表面动态再结晶行为[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(8): 1120-1126. |
| [7] | 郗文超, 宋博学, 梁赢东, 于天彪. 原位生成NbC增强YCF102熔覆层热力学与耐磨性研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(4): 538-543. |
| [8] | 蔡志辉 , 文光奇, 韩阿康, 张开华. 调质工艺对V微合金油井管用钢力学性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(10): 1414-1420. |
| [9] | 辛博, 程光, 姚俊, 巩亚东. 自适应FGM激光熔覆成形的粉体快速混合机理[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(8): 1123-1128. |
| [10] | 辛博, 周显新, 巩亚东. 变厚度熔覆层沉积成形工艺与性能研究[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(3): 374-379. |
| [11] | 宋博学, 于天彪, 姜兴宇, 郗文超. 激光熔覆产生的熔池温度与对流分析[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(10): 1427-1431. |
| [12] | 刘后龙, 刘玲玲, 李兴, 陈礼清. 冷轧工艺对铁素体不锈钢成形性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(8): 1099-1104. |
| [13] | 许妮君, 刘常升, 冯欣俣, 孙挺. 激光工艺对45钢表面梯度熔覆层组织性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(4): 495-499. |
| [14] | 于天彪, 宋博学, 郗文超, 马哲伦. 激光熔覆工艺参数对熔覆层形貌的影响及优化[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(4): 537-542. |
| [15] | 黄慧强, 邸洪双, 张天宇, 闫宁. 两相区退火温度对高铝低硅TRIP钢组织性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(12): 1700-1706. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||