
东北大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (2): 64-75.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2025.20230232
收稿日期:2023-08-06
出版日期:2025-02-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
通讯作者:
黄建聪
作者简介:单 泉(1977—),男,江西赣州人,东北大学秦皇岛分校副教授.
Quan SHAN, Jian-cong HUANG( ), Shun ZHANG, Yan CHEN
), Shun ZHANG, Yan CHEN
Received:2023-08-06
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-05-20
Contact:
Jian-cong HUANG
摘要:
针对外骨骼康复机器人与人体之间轴线错位而导致的不兼容等问题,提出了一种冗余康复外骨骼的构型综合方法.首先,通过全局静力条件确定冗余运动副的数目,并利用几何分析减少冗余运动副类型组合的数目;其次,基于用户舒适度考虑了可能的冗余运动副轴线组合并选择了合适的组合方式;接着,结合工程约束考虑冗余运动副的可能位置排列并确定最优位置排列;最后,通过分析冗余运动副的运动,确定外骨骼和人体的位置和姿态.结果表明,在不同的轴线错位情况下,最优构型使外骨骼与人体能够实现相同的位置和姿态,有效克服了运动学不兼容性问题.
中图分类号:
单泉, 黄建聪, 张顺, 陈砚. 肘腕4-DOF冗余康复外骨骼构型综合方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(2): 64-75.
Quan SHAN, Jian-cong HUANG, Shun ZHANG, Yan CHEN. Configuration Synthesis Method of Elbow & Wrist 4-DOF Redundant Rehabilitation Exoskeleton[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2025, 46(2): 64-75.
| 运动链 | 主动转动运动副数目 | 冗余运动副数目 | 种类合成 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 4 | |
| L2 | 2 | 4 |
表1 肘、腕冗余运动副种类合成l1=4,l2=4
Table 1 Synthesis of redundant motion pair types for elbows and wrists l1=4,l2=4
| 运动链 | 主动转动运动副数目 | 冗余运动副数目 | 种类合成 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 4 | |
| L2 | 2 | 4 |
| 运动链 | 主动转动运动副数目 | 冗余运动副数目 | 种类合成 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 5 | |
| L2 | 2 | 3 |
表2 肘、腕冗余运动副种类合成l1=5,l2=3
Table 2 Synthesis of redundant motion pair types for elbows and wrists l1=5,l2=3
| 运动链 | 主动转动运动副数目 | 冗余运动副数目 | 种类合成 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 5 | |
| L2 | 2 | 3 |
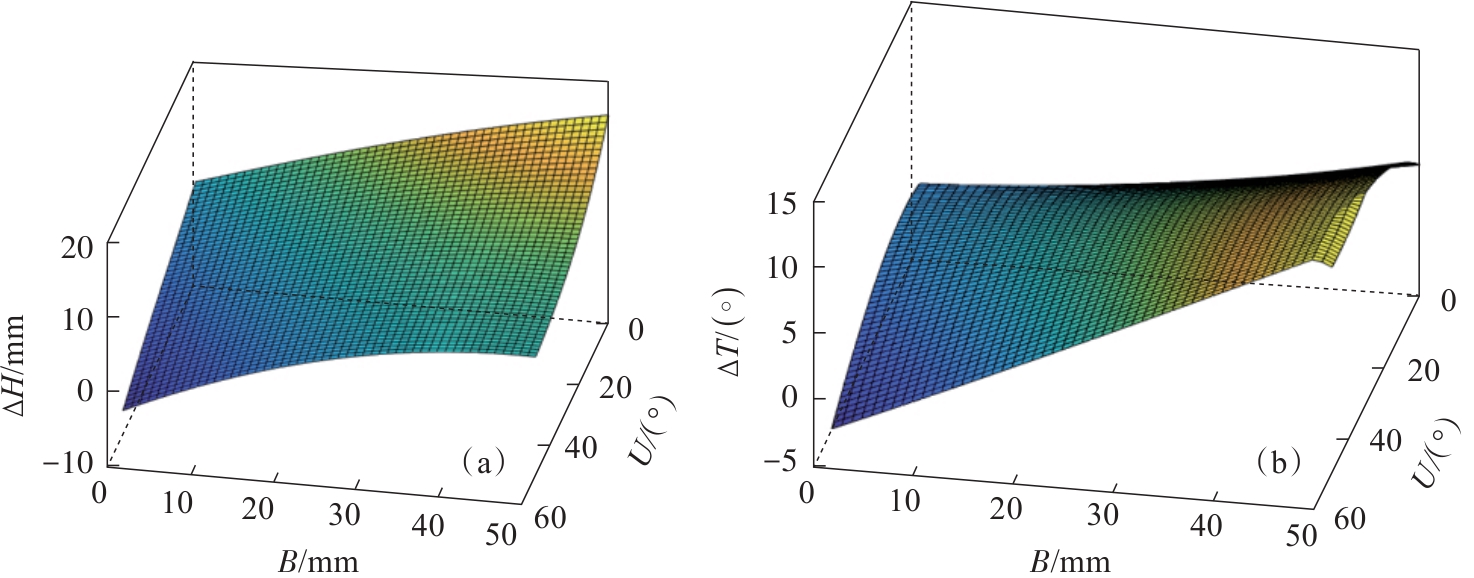
图5 外骨骼轴线与人体轴线满足平行度要求时∆H与∆T的变化(a)—∆H变化图;(b)—∆T变化图.
Fig. 5 Variation of ∆H and ∆T when the exoskeleton axis meets the parallelism requirement with the body axis
| 运动链 | 主动转动运动副数目 | 确定冗余运动副 | 未确定冗余运动副 | 种类 合成 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 1P1R | 2 | |
| L2 | 2 | 1P1R | 2 |
表3 肘、腕部的冗余运动副种类合成l1=4,l2=4
Table 3 Synthesis of redundant motion pair types for elbows and wrists l1=4,l2=4
| 运动链 | 主动转动运动副数目 | 确定冗余运动副 | 未确定冗余运动副 | 种类 合成 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 1P1R | 2 | |
| L2 | 2 | 1P1R | 2 |
| 运动链 | 主动运动副数目 | 确定冗余运动副 | 未确定冗余运动副 | 种类合成 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 1P1R | 3 | 2 |
| L2 | 2 | 1P1R | 1 |
表4 肘、腕部的冗余运动副种类合成l1=5,l2=3
Table 4 Synthesis of redundant motion pair types for elbows and wrists l1=5,l2=3
| 运动链 | 主动运动副数目 | 确定冗余运动副 | 未确定冗余运动副 | 种类合成 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 2 | 1P1R | 3 | 2 |
| L2 | 2 | 1P1R | 1 |
| 种类合成子链 | 轴线合成 | 传递力和 力矩的方向 |
|---|---|---|
| 1P3R | ||
| 2P2R | ||
| 3P1R |
表5 肘、腕部的力与力矩情况l1=4,l2=4
Table 5 Force and torque conditions for elbows and wrists l1=4,l2=4
| 种类合成子链 | 轴线合成 | 传递力和 力矩的方向 |
|---|---|---|
| 1P3R | ||
| 2P2R | ||
| 3P1R |
| 种类合成子链 | 轴线合成 | 传递力和 力矩的方向 |
|---|---|---|
| 4P1R | ||
| 3P2R | ||
| 2P3R | ||
| 1P4R | ||
表6 肘部的力与力矩情况l1=5,l2=3 (l1=5,l2=3)
Table 6 Force and torque conditions for elbows
| 种类合成子链 | 轴线合成 | 传递力和 力矩的方向 |
|---|---|---|
| 4P1R | ||
| 3P2R | ||
| 2P3R | ||
| 1P4R | ||
| 种类合成子链 | 轴线合成 | 传递力和 力矩的方向 |
|---|---|---|
| 2P1R | ||
| 1P2R | ||
表7 腕部的力与力矩情况l1=5,l2=3 (l1=5,l2=3)
Table 7 Force and torque conditions for wrists
| 种类合成子链 | 轴线合成 | 传递力和 力矩的方向 |
|---|---|---|
| 2P1R | ||
| 1P2R | ||
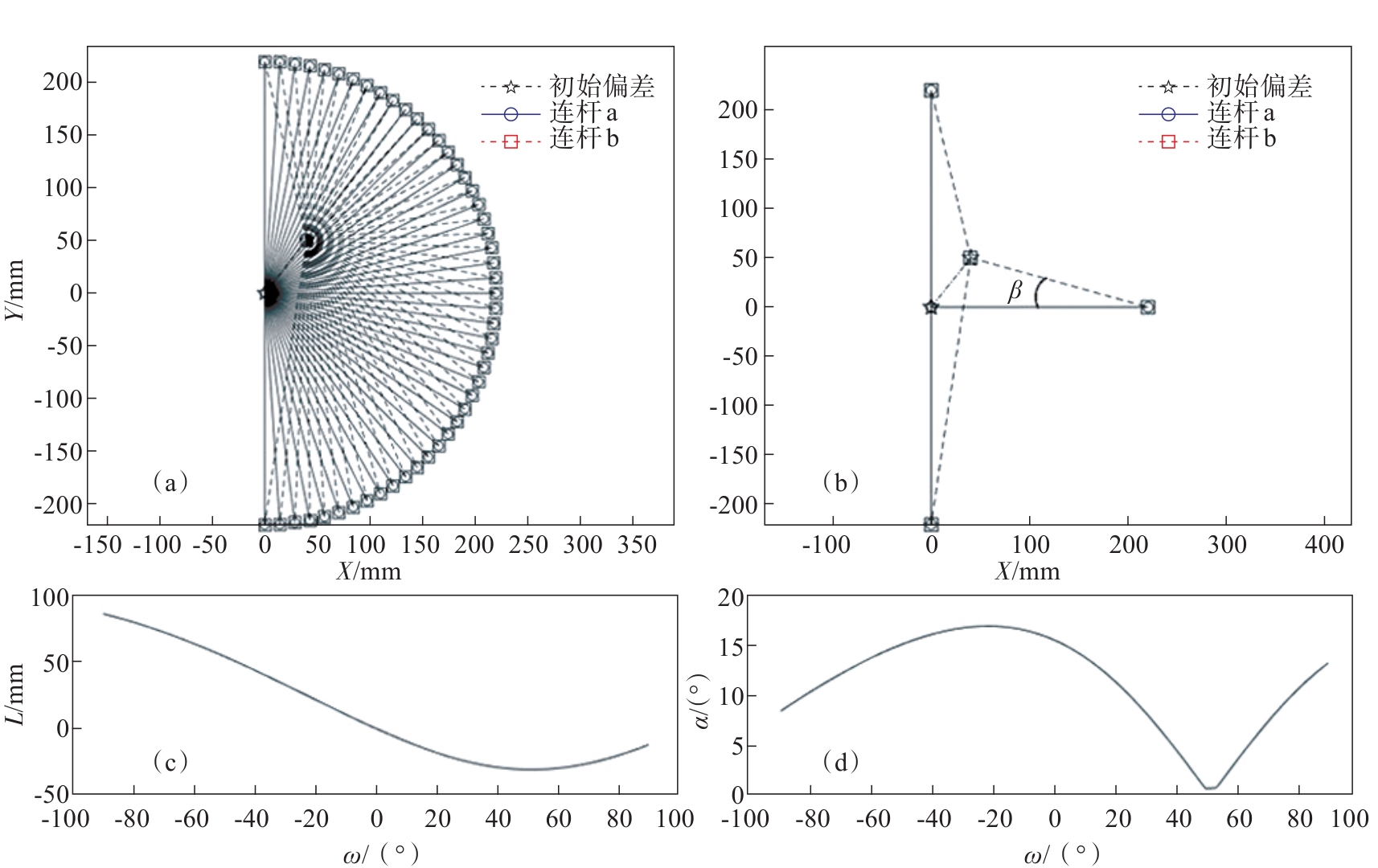
图12 当连杆b起点坐标为(40,50,0)时,外骨骼与人体的运动过程(a)—外骨骼与人体运动过程; (b)—外骨骼与人体之间的姿态偏差; (c)— 冗余移动副的运动图; (d)— 冗余转动副的运动图.
Fig. 12 Motion process of the exoskeleton and the human body when the coordinates of the starting point of the connecting rod b are (40,50,0)
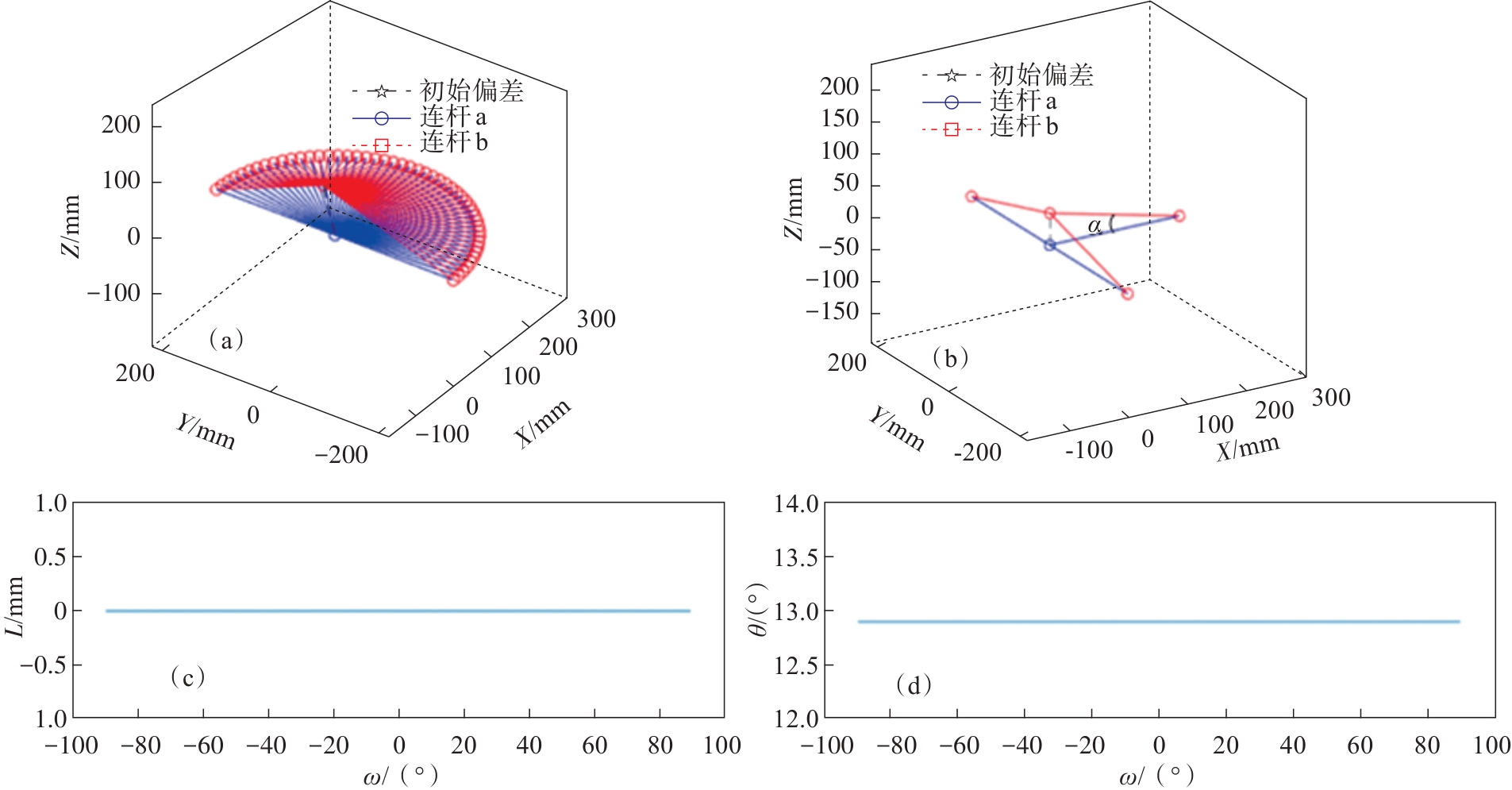
图13 当连杆b起点坐标为(0,0,50)时,外骨骼与人体的运动过程(a)—外骨骼与人体的运动过程; (b)—外骨骼与人体之间的姿态偏差;(c)—冗余移动副的运动图;(d)—冗余转动副的运动图.
Fig. 13 Motion process of the exoskeleton and the human body when the coordinates of the starting point of the connecting rod b are (0,0,50)
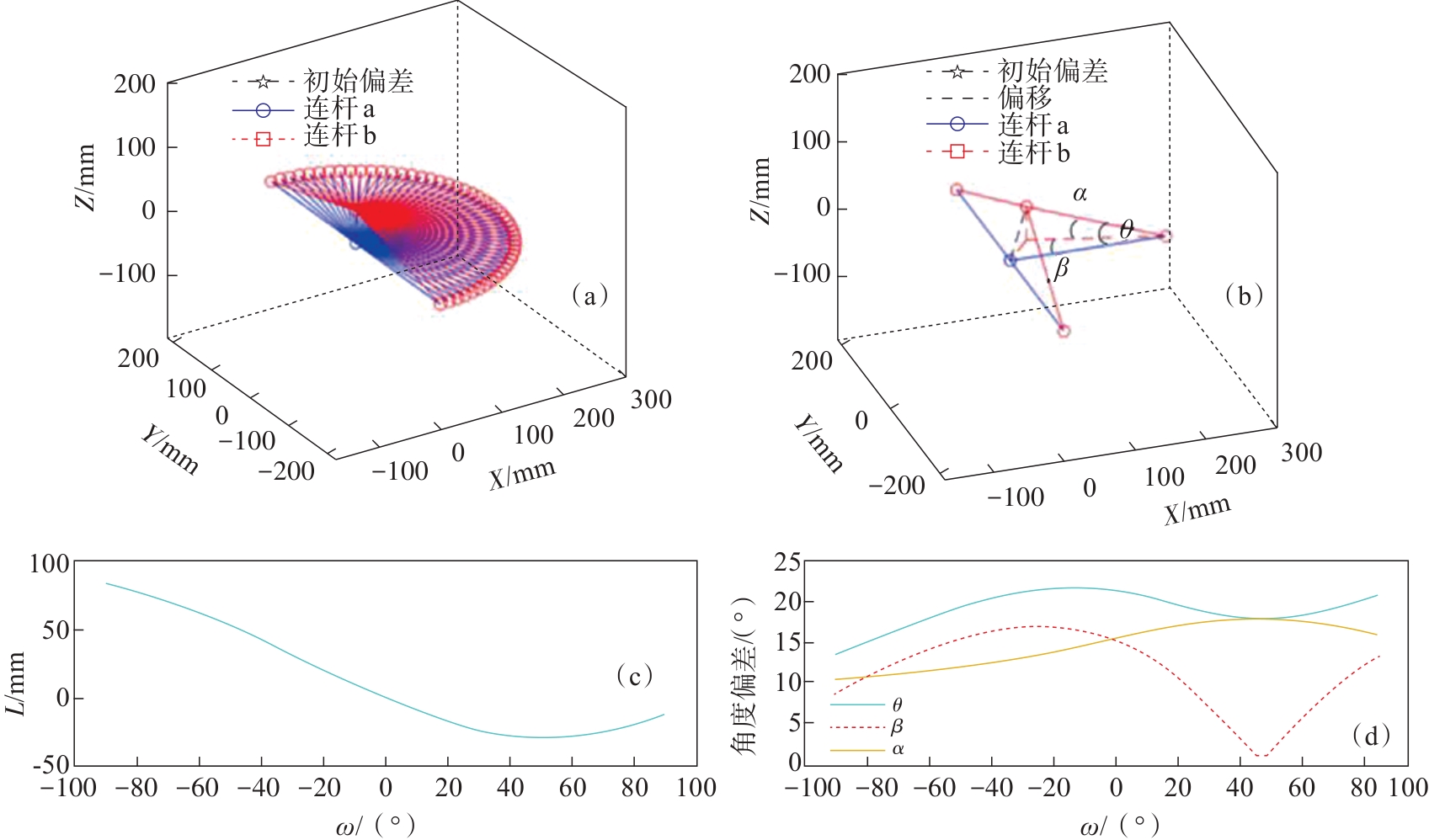
图14 当连杆b起点坐标为(40,50,50)时,外骨骼与人体的运动过程(a)—外骨骼与人体的运动过程;(b)—外骨骼与人体之间的姿态偏差;(c)—冗余移动副的运动图;(d)—冗余转动副的运动图.
Fig. 14 Motion process of the exoskeleton and the human body when the coordinates of the starting point of the connecting rod b are (40,50,50)
| 1 | Hwang S H, Sun D I, Han J, et al. Gait pattern generation algorithm for lower-extremity rehabilitation–exoskeleton robot considering wearer’s condition[J]. Intelligent Service Robotics, 2021, 14(3): 345-355. |
| 2 | Valdez S I, Gutierrez-Carmona I, Keshtkar S, et al. Kinematic and dynamic design and optimization of a parallel rehabilitation robot[J]. Intelligent Service Robotics, 2020, 13(3): 365-378. |
| 3 | Xu P P, Xia D, Li J C, et al. Execution and perception of upper limb exoskeleton for stroke patients: a systematic review[J]. Intelligent Service Robotics, 2022, 15(4): 557-578. |
| 4 | Shi D, Zhang W X, Zhang W, et al. A review on lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robots[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 32(1): 74-84. |
| 5 | Hu M W, Wang H G, Pan X N. Optimal configuration selection for stiffness identification of 7-DOF collaborative robots[J]. Intelligent Service Robotics, 2020, 13(3): 379-391. |
| 6 | Ruiz-Olaya A F, Lopez-Delis A, da Rocha A F. Upper and lower extremity exoskeletons[M]//Handbook of Biomechatronics. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 283-317. |
| 7 | Louie D R, Eng J J. Powered robotic exoskeletons in post-stroke rehabilitation of gait: a scoping review[J]. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 2016, 13(1): 53-57. |
| 8 | Wang X, Song Q Z, Wang X G, et al. Kinematics and dynamics analysis of a 3-DOF upper-limb exoskeleton with an internally rotated elbow joint[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(3): 464. |
| 9 | Esmaeili M, Jarrassé N, Dailey W, et al. Hyperstaticity for ergonomie design of a wrist exoskeleton[C]// IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR). Seattle, WA:IEEE, 2013: 1-6. |
| 10 | Schiele A. An explicit model to predict and interpret constraint force creation in pHRI with exoskeletons[C]//2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Pasadena:IEEE, 2008: 1324-1330. |
| 11 | Yan H, Wang H B, Chen P, et al. Configuration design of an upper limb rehabilitation robot with a generalized shoulder joint[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(5): 2080. |
| 12 | Jarrasse N, Morel G. Connecting a human limb to an exoskeleton[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2011, 28(3): 697-709. |
| 13 | Fang Y F, Tsai L W. Enumeration of a class of overconstrained mechanisms using the theory of reciprocal screws[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2004, 39(11): 1175-1187. |
| 14 | Perry J C, Rosen J, Burns S. Upper-limb powered exoskeleton design[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2007, 12(4): 408-417. |
| 15 | Schiele A, van der Helm F C T. Kinematic design to improve ergonomics in human machine interaction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2006, 14(4): 456-469. |
| 16 | Schiele A, van der Helm F C T. Influence of attachment pressure and kinematic configuration on pHRI with wearable robots[J]. Applied Bionics and Biomechanics, 2009, 6(2): 157-173. |
| 17 | Jamwal P K, Hussain S, Ghayesh M H, et al. Impedance control of an intrinsically compliant parallel ankle rehabilitation robot[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(6): 3638-3647. |
| 18 | Näf M B, Junius K, Rossini M, et al. Misalignment compensation for full human-exoskeleton kinematic compatibility: state of the art and evaluation[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2018, 70(5): 050802. |
| 19 | 李剑锋, 黄相强, 陶春静, 等. 膝关节康复外骨骼构型综合与结构设计[J].哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2017, 38(4): 625-632. |
| Li Jian-feng, Huang Xiang-qiang, Tao Chun-jing, et al. Configuration synthesis and structure design of knee rehabilitation exoskeleton[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2017, 38(4): 625-632. | |
| 20 | Chao E Y, An K N, Askew L J, et al. Electrogoniometer for the measurement of human elbow joint rotation[J].Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 1980, 102(4): 301-310. |
| [1] | 徐红丽, 贾本卿, 栾阔. 基于改进人工势场的多UUV编队避障方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(11): 1547-1556. |
| [2] | 陈晓明, 陈大川, 赵玉倩, 李程. 面向海滩环境监测的绳驱柔性骨骼仿生蟹机器人[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(10): 1443-1451. |
| [3] | 单泉, 张顺, 黄建聪, 陈砚. 上肢康复机器人模糊自适应交互控制研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(7): 974-983. |
| [4] | 吴昊, 梁忠超, 王文成, 王永富. 具有不确定滑转的轮式移动机器人轨迹跟踪控制方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(6): 858-865. |
| [5] | 陆志国, 王逍. 基于B样条与鲸鱼优化算法的机械臂轨迹规划[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(5): 683-689. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||