
Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (8): 77-92.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2025.20250006
• Overview • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hong-liang YI, Ming-hui ZHAO, Rui-ting WANG, Yan-qi MA
Received:2025-01-16
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-11-24
Contact:
Hong-liang YI
CLC Number:
Hong-liang YI, Ming-hui ZHAO, Rui-ting WANG, Yan-qi MA. Current Status of Research on High-Strength Steel Above 1 800 MPa Grade[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2025, 46(8): 77-92.
| 钢号 | 合金成分 | 工艺 | 屈服强度/MPa | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30CrMnSiNi2A | 0.26~0.33C-0.9~1.2Si-1.0~1.3Mn- 0.9~1.2Cr-1.4~1.8Ni | 900 ℃油淬+ 250 ℃回火 | / | ≥1 600 | ≥9 |
| 35Si2Mn2MoVA | 0.32~0.38C-1.4~1.7Si-1.6~1.9Mn- 0.35~0.45Mo-0.1~0.2V | 920 ℃油淬+ 250 ℃回火 | / | ≥1 700 | ≥9 |
| 4130 | 0.28~0.33C-0.2~0.35Si-0.4~0.6Mn- 0.8~1.1Cr-0.15~0.25Mo | 860 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 340 | 1 550 | 11 |
| 4140 | 0.38~0.43C-0.2~0.35Si-0.75~1.0Mn- 0.8~1.1Cr-0.15~0.25Mo | 845 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 740 | 1 965 | 11 |
| 4340 | 0.38C~0.43C-0.2~0.35Si-0.6~0.8Mn- 0.7~0.9Cr-1.65~2.0Ni-0.2~0.3Mo | 845 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 860 | 1 980 | 11 |
| 300M | 0.41~0.46C-1.45~1.8Si-0.65~0.9Mn- 0.65~0.95Cr-1.6~2.0Ni-0.3~0.4Mo-≥0.05V | 860 ℃油淬+ 260 ℃回火 | 1 670 | 2 050 | 8 |
| D6AC | 0.42~0.48C-0.15~0.3Si-0.6~0.9Mn- 0.8~1.05Cr-0.4~0.7Ni-0.9~1.1Mo-0.05~0.1V | 880 ℃油淬+ 315 ℃回火 | 1 760 | 2 000 | 8 |
| 6150 | 0.48~0.53C-0.2~0.35Si-0.7~0.9Mn- 0.8~1.1Cr | 860 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 810 | 2 050 | 10 |
| 8640 | 0.38~0.43C-0.2~0.35Si-0.75~1.0Mn- 0.4~0.6Cr-0.4~0.7Ni-0.15~0.25Mo | 820 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 670 | 1 810 | 8 |
Table 1 Composition and mechanical properties of common low-alloyed ultra-high strength steel [16-17]
| 钢号 | 合金成分 | 工艺 | 屈服强度/MPa | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30CrMnSiNi2A | 0.26~0.33C-0.9~1.2Si-1.0~1.3Mn- 0.9~1.2Cr-1.4~1.8Ni | 900 ℃油淬+ 250 ℃回火 | / | ≥1 600 | ≥9 |
| 35Si2Mn2MoVA | 0.32~0.38C-1.4~1.7Si-1.6~1.9Mn- 0.35~0.45Mo-0.1~0.2V | 920 ℃油淬+ 250 ℃回火 | / | ≥1 700 | ≥9 |
| 4130 | 0.28~0.33C-0.2~0.35Si-0.4~0.6Mn- 0.8~1.1Cr-0.15~0.25Mo | 860 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 340 | 1 550 | 11 |
| 4140 | 0.38~0.43C-0.2~0.35Si-0.75~1.0Mn- 0.8~1.1Cr-0.15~0.25Mo | 845 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 740 | 1 965 | 11 |
| 4340 | 0.38C~0.43C-0.2~0.35Si-0.6~0.8Mn- 0.7~0.9Cr-1.65~2.0Ni-0.2~0.3Mo | 845 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 860 | 1 980 | 11 |
| 300M | 0.41~0.46C-1.45~1.8Si-0.65~0.9Mn- 0.65~0.95Cr-1.6~2.0Ni-0.3~0.4Mo-≥0.05V | 860 ℃油淬+ 260 ℃回火 | 1 670 | 2 050 | 8 |
| D6AC | 0.42~0.48C-0.15~0.3Si-0.6~0.9Mn- 0.8~1.05Cr-0.4~0.7Ni-0.9~1.1Mo-0.05~0.1V | 880 ℃油淬+ 315 ℃回火 | 1 760 | 2 000 | 8 |
| 6150 | 0.48~0.53C-0.2~0.35Si-0.7~0.9Mn- 0.8~1.1Cr | 860 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 810 | 2 050 | 10 |
| 8640 | 0.38~0.43C-0.2~0.35Si-0.75~1.0Mn- 0.4~0.6Cr-0.4~0.7Ni-0.15~0.25Mo | 820 ℃油淬+ 205 ℃回火 | 1 670 | 1 810 | 8 |
| 序号 | 合金成分 | 屈服强度/MPa | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.34C-0.25Si-1.34Mn-0.04Al-0.21V-0.04Ti-0.002B-0.24Cr | 1 353 | 2 018 | 7.5 | [ |
| 2 | 0.36C-0.22Si-1.31Mn-0.298Cr-0.005B-0.157Mo | 1 421 | 2 061 | 7 | [ |
| 3 | 0.31C-0.3Si-1.5Mn-0.03Al-1.0Cr-0.002B-0.07Ti-0.046Nb | 1 321 | 2 183 | 5.7 | [ |
| 4 | 0.38C-1.48Si-1.58Mn-0.035Al-0.91Cr-0.003 7B-0.07Ti-0.048Nb | 1 119 | 2 121 | 8.86 | [ |
| 5 | 0.354C-0.32Si-1.48Mn-0.05Al-0.042Ti-0.002 5B | 1 301 | 2 046 | 6.6 | [ |
| 6 | 0.38C-0.19Si-1.2Mn-0.28Cr-0.005Mo-0.005Ni-0.003B-0.024Ti | 1 424 | 2 045 | 5.9 | [ |
| 7 | 0.61C-1.5Cr-0.08Ni-0.05Ti-0.07Nb | 1 940 | 2 400 | 10 | [ |
| 8 | 0.66C-1.42Cr-0.4Si-0.42Mn-0.07V | 2 367 | 2 613 | 7 | [ |
| 9 | 0.46C-1.99Mn-1.53Si-1.27Cr-0.76Al-0.45Ni-0.3Mo-0.28V | 1 809 | 2 590 | 12.6 | [ |
| 10 | 0.28C-1.76Mn-0.35Si-4.4Ni-1.88Mo-0.02Al-0.06Ti-0.08Nb | 1 487 | 2 032 | 6.53 | [ |
| 11 | 0.38C-1.48Si-1.58Mn-0.035Al-0.9~1.0Cr-0.003~0.004 B-0.06~0.08Ti-0.04~0.05Nb | 1 500 | 2 080 | 8.8 | [ |
| 12 | 0.42C-0.19Si-0.80Mn-0.02Ni-1.16Cr-0.16Mo | 1 540 | 2 068 | 12.1 | [ |
| 13 | 0.56C-2.3Si-0.69Mn-0.89Cr-0.02Mo-0.1V-0.03Ti-0.2Ni-0.15Cu | 2 038 | 2 382 | 8.8 | [ |
| 14 | 0.4C-1.6Si-1.5Mn-1.4Cr-0.4Mo-0.3No-0.1W | 1 520 | 2 100 | / | [ |
| 15 | 0.48C-0.85Si-0.24Mn-0.63Cr-2.0Ni-0.42Mo-0.2V | 1 720 | 2 441 | 10 | [ |
| 16 | 0.34C-0.32Si-1.39Mn-0.03Ti-0.0025B-0.11~0.3V | 1 508 | 2 121 | 8 | [ |
Table 2 Composition and mechanical properties of hot stamping steel above 1 800 MPa grade [22-38]
| 序号 | 合金成分 | 屈服强度/MPa | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.34C-0.25Si-1.34Mn-0.04Al-0.21V-0.04Ti-0.002B-0.24Cr | 1 353 | 2 018 | 7.5 | [ |
| 2 | 0.36C-0.22Si-1.31Mn-0.298Cr-0.005B-0.157Mo | 1 421 | 2 061 | 7 | [ |
| 3 | 0.31C-0.3Si-1.5Mn-0.03Al-1.0Cr-0.002B-0.07Ti-0.046Nb | 1 321 | 2 183 | 5.7 | [ |
| 4 | 0.38C-1.48Si-1.58Mn-0.035Al-0.91Cr-0.003 7B-0.07Ti-0.048Nb | 1 119 | 2 121 | 8.86 | [ |
| 5 | 0.354C-0.32Si-1.48Mn-0.05Al-0.042Ti-0.002 5B | 1 301 | 2 046 | 6.6 | [ |
| 6 | 0.38C-0.19Si-1.2Mn-0.28Cr-0.005Mo-0.005Ni-0.003B-0.024Ti | 1 424 | 2 045 | 5.9 | [ |
| 7 | 0.61C-1.5Cr-0.08Ni-0.05Ti-0.07Nb | 1 940 | 2 400 | 10 | [ |
| 8 | 0.66C-1.42Cr-0.4Si-0.42Mn-0.07V | 2 367 | 2 613 | 7 | [ |
| 9 | 0.46C-1.99Mn-1.53Si-1.27Cr-0.76Al-0.45Ni-0.3Mo-0.28V | 1 809 | 2 590 | 12.6 | [ |
| 10 | 0.28C-1.76Mn-0.35Si-4.4Ni-1.88Mo-0.02Al-0.06Ti-0.08Nb | 1 487 | 2 032 | 6.53 | [ |
| 11 | 0.38C-1.48Si-1.58Mn-0.035Al-0.9~1.0Cr-0.003~0.004 B-0.06~0.08Ti-0.04~0.05Nb | 1 500 | 2 080 | 8.8 | [ |
| 12 | 0.42C-0.19Si-0.80Mn-0.02Ni-1.16Cr-0.16Mo | 1 540 | 2 068 | 12.1 | [ |
| 13 | 0.56C-2.3Si-0.69Mn-0.89Cr-0.02Mo-0.1V-0.03Ti-0.2Ni-0.15Cu | 2 038 | 2 382 | 8.8 | [ |
| 14 | 0.4C-1.6Si-1.5Mn-1.4Cr-0.4Mo-0.3No-0.1W | 1 520 | 2 100 | / | [ |
| 15 | 0.48C-0.85Si-0.24Mn-0.63Cr-2.0Ni-0.42Mo-0.2V | 1 720 | 2 441 | 10 | [ |
| 16 | 0.34C-0.32Si-1.39Mn-0.03Ti-0.0025B-0.11~0.3V | 1 508 | 2 121 | 8 | [ |
| 编号 | 合金成分的质量分数/% | 工艺 | 力学性能 | 参考 文献 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | Al | Cr | Ni | Nb | Mo | V | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% | |||
| 1 | 0.41 | 1.3 | 1.27 | — | 0.56 | 1.01 | — | — | — | Q&P | 2 468 | 11.6 | [ |
| 2 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 2.03 | 0.008 | 1.33 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 810~2 096 | 12~20 | [ |
| 3 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 2.6 | 0.008 | 1.33 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 965~1 975 | 12~17 | [ |
| 4 | 0.43 | 1.17 | 2.6 | 0.008 | 1.33 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 837~2 218 | 14~22 | [ |
| 5 | 0.42 | 0.59 | 2.6 | — | 1.33 | — | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 810~2 096 | 12~20 | [ |
| 6 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 1.95 | — | 0.75 | — | 0.04 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 2 100~2 251 | 16~22 | [ |
| 7 | 0.56 | 1.36 | 1.88 | — | 1.36 | — | 0.04 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 2 168~2 377 | 8~13 | [ |
| 8 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 1.78 | — | 1.08 | — | — | 0.45 | 0.21 | Q&FP | 1 942 | ~10 | [ |
Table 3 Composition, processes, and mechanical properties of high-carbon Q&P steel above 1 800 MPa
| 编号 | 合金成分的质量分数/% | 工艺 | 力学性能 | 参考 文献 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | Al | Cr | Ni | Nb | Mo | V | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% | |||
| 1 | 0.41 | 1.3 | 1.27 | — | 0.56 | 1.01 | — | — | — | Q&P | 2 468 | 11.6 | [ |
| 2 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 2.03 | 0.008 | 1.33 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 810~2 096 | 12~20 | [ |
| 3 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 2.6 | 0.008 | 1.33 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 965~1 975 | 12~17 | [ |
| 4 | 0.43 | 1.17 | 2.6 | 0.008 | 1.33 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 837~2 218 | 14~22 | [ |
| 5 | 0.42 | 0.59 | 2.6 | — | 1.33 | — | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 1 810~2 096 | 12~20 | [ |
| 6 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 1.95 | — | 0.75 | — | 0.04 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 2 100~2 251 | 16~22 | [ |
| 7 | 0.56 | 1.36 | 1.88 | — | 1.36 | — | 0.04 | 0.03 | — | Q&P | 2 168~2 377 | 8~13 | [ |
| 8 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 1.78 | — | 1.08 | — | — | 0.45 | 0.21 | Q&FP | 1 942 | ~10 | [ |
| 编号 | 合金成分的质量分数/% | 工艺 | 力学性能 | 参考 文献 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | Al | Ni | Nb | Cr | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% | |||
| 1 | 0.485 | 1.195 | 1.185 | — | 0.98 | 0.21 | — | Q-P-T(400 ℃) | 2 160 | 11 | [ |
| 2 | 0.63 | 1.52 | 1.49 | — | — | 0.036 | 0.62 | Q-P-T(400 ℃) | 1 860 | 28.9 | [ |
Table 4 Composition, processes, and mechanical properties of Q-P-T steel above 1 800 MPa grade [57,61]
| 编号 | 合金成分的质量分数/% | 工艺 | 力学性能 | 参考 文献 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | Al | Ni | Nb | Cr | 抗拉强度/MPa | 延伸率/% | |||
| 1 | 0.485 | 1.195 | 1.185 | — | 0.98 | 0.21 | — | Q-P-T(400 ℃) | 2 160 | 11 | [ |
| 2 | 0.63 | 1.52 | 1.49 | — | — | 0.036 | 0.62 | Q-P-T(400 ℃) | 1 860 | 28.9 | [ |
| 钢种 | w(Ni)/% | w(Mo)/% | w(Co)/% | w(Ti)/% | w(Al)/% | 屈服强度/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ni(200) | 18 | 3.3 | 8.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1 400 |
| 18Ni(250) | 18 | 5.0 | 8.5 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1 700 |
| 18Ni(300) | 18 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 2 000 |
| 18Ni(350) | 18 | 4.2 | 12.5 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 2 400 |
| 18Ni(铸态) | 17 | 4.6 | 10.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1 650 |
Table 5 Composition mass fraction and yield strength of early developed 18Ni martensitic aging steel[77]
| 钢种 | w(Ni)/% | w(Mo)/% | w(Co)/% | w(Ti)/% | w(Al)/% | 屈服强度/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ni(200) | 18 | 3.3 | 8.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1 400 |
| 18Ni(250) | 18 | 5.0 | 8.5 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1 700 |
| 18Ni(300) | 18 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 2 000 |
| 18Ni(350) | 18 | 4.2 | 12.5 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 2 400 |
| 18Ni(铸态) | 17 | 4.6 | 10.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1 650 |
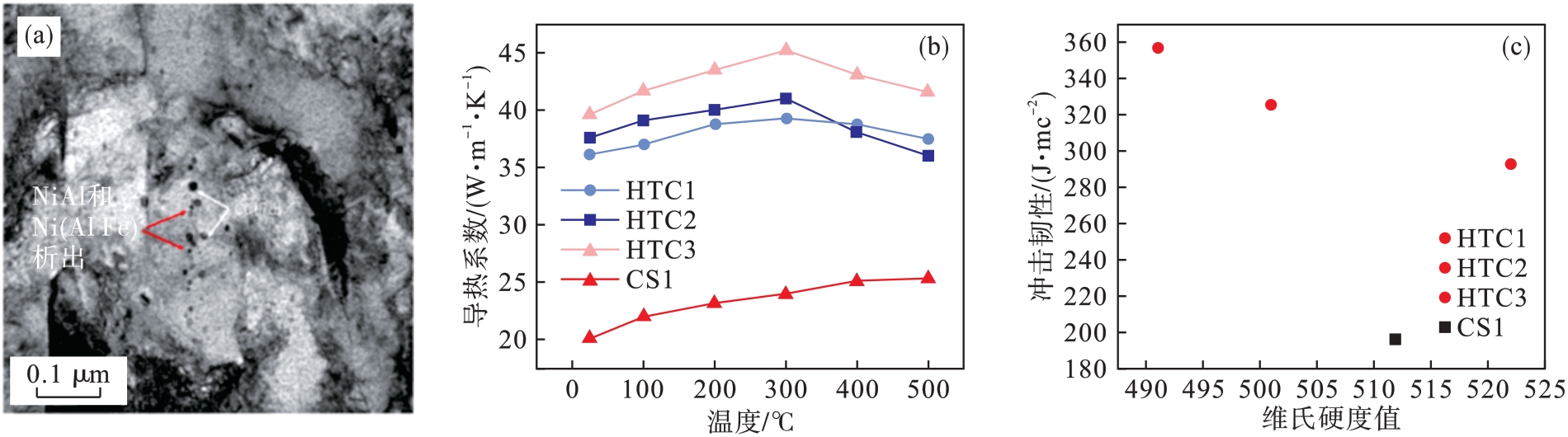
Fig.10 Comparison of thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of Cu-NiAl high thermal conductivity die steel and tempered martensitic die steel by carbide precipitation[118-119]
| [1] | 常智渊. 2 000 MPa级热冲压成形钢的组织调控及强韧化机理研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2020. |
| Chang Zhi-yuan. Study on microstructure control and strengthening-toughening mechanism of 2 000 MPa grade press hardening steel [D].Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2020. | |
| [2] | Tümer M, Schneider-Bröskamp C, Enzinger N.Fusion welding of ultra-high strength structural steels: a review[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 82: 203-229. |
| [3] | Bouaziz O, Zurob H, Huang M X. Driving force and logic of development of advanced high strength steels for automotive applications[J]. Steel Research International, 2013, 84(10): 937-947. |
| [4] | Malakondaiah G, Srinivas M, Rao P R. Ultrahigh-strength low-alloy steels with enhanced fracture toughness[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 1997, 42(1/2/3/4): 209-242. |
| [5] | 师昌绪.材料大辞典[M].北京:化学工业出版社,1994. |
| Shi Chang-xu. Materials comprehensive dictionary [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1994. | |
| [6] | 王鹏飞.真空感应冶炼AerMet100超高强度钢工艺研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2021. |
| Wang Peng-fei. Research on smelting process of AerMet100 ultra-high strength steel by vacuum induction furnace [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2021. | |
| [7] | Shao Y, Liu C X, Yan Z S, et al. Formation mechanism and control methods of acicular ferrite in HSLA steels: a review[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34(5): 737-744. |
| [8] | Speer J, Matlock D K, De Cooman B C, et al. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(9): 2611-2622. |
| [9] | Yin W J, Briffod F, Hu H Y, et al. Role of prior austenite grain boundary and retained austenite in strain localization of medium-carbon high-strength steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2024, 281: 120422. |
| [10] | 诸汇涛,王建勇,杨辉,等.马氏体时效钢的研究现状[J].机械制造,2023, 61(8): 41-46. |
| Zhu Hui-tao, Wang Jian-yong, Yang Hui, et al. Research status of martensitic aging steel [J]. Machinery, 2023, 61(8): 41-46. | |
| [11] | Tomita Y. Low-temperature improvement of mechanical properties of AISI 4340 steel through high-temperature thermomechanical treatment[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1991, 22(5): 1093-1102. |
| [12] | Dilipkumar D, Wbod W E. Acoustic-emission analysis of fracture-toughness tests[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1979, 19(11): 416-420. |
| [13] | Ryder J T, Pickel F M. Effect of temperature on stress corrosion cracking of 300M steel[J]. Joumal of Testing and Evaluation, 1978, 6(2): 129-133. |
| [14] | Bakhshi S, Mirak A. The effect of low temperature transformation time on microstructural & textural evolution, mechanical properties and fracture behavior of a low alloy, medium carbon, super strength AISI 4340 steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 831: 142247. |
| [15] | Cheng X, Gao G H, Fu C, et al. Mechanistic understanding of banded microstructure and its effect on anisotropy of toughness in low carbon-low alloy steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2025, 919: 147507. |
| [16] | 万翛如,许昌淦.高强度及超高强度钢[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1988:25-71. |
| Wan Xiao-ru, Xu Chang-gan. High strength and ultra-high strength steel[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1988: 25-71. | |
| [17] | 王瑞.超高强度钢制备工艺的关键技术研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2017. |
| Wang Rui. Key process technologies for manufacture of ultra high strength steels [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2017. | |
| [18] | 张国英.新型无钴高强高韧钢的微观结构与强韧性机理研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2000. |
| Zhang Guo-ying. Investigation on microstructure and strength-toughening mechanism of a noval cobalt-free ultra-high tensile steel with high fracture toughness [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2000. | |
| [19] | Taylor T, Clough A. Critical review of automotive hot-stamped sheet steel from an industrial perspective[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 34(7): 809-861. |
| [20] | Karbasian H, Tekkaya A E. A review on hot stamping[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210(15): 2103-2118. |
| [21] | Honeycombe R W K, Arnold E. Steels: microstructure and properties[M]. London: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1981. |
| [22] | 田秀刚,王朝,孙旭,等.加热温度对34MnB5热成形钢组织性能的影响[J].金属热处理,2023, 48(3): 135-139. |
| Tian Xiu-gang, Wang Chao, Sun Xu, et al. Effect of heating temperature on microstructure and properties of 34MnB5 hot forming steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023, 48(3): 135-139. | |
| [23] | 郝亮,朱国明,闻玉辉,等.超高强度硼钢38MnB5的热冲压工艺研究[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(4): 817-823. |
| Hao Liang, Zhu Guo-ming, Wen Yu-hui, et al. Study on hot stamping process of 38MnB5 ultra high strength boron steel [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(4): 817-823. | |
| [24] | Chen W J, Gao P F, Wang S, et al. Strengthening mechanisms of Nb and V microalloying high strength hot-stamped steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 797: 140115. |
| [25] | Liang J T, Zhao Z Z, Sun B H, et al.A novel ultra-strong hot stamping steel treated by quenching and partitioning process[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 34(18): 2241-2249. |
| [26] | Chang Z Y, Liu Z Y, Yu Q, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a 2000 MPa grade ultrahigh strength boron steel[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2022, 1270: 012055. |
| [27] | Taylor T, Fourlaris G, Evans P, et al. New generation ultrahigh strength boron steel for automotive hot stamping technologies[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 30(7): 818-826. |
| [28] | Sun J J, Liu Y N, Zhu Y T, et al. Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 6596. |
| [29] | Wang Y J, Sun J J, Jiang T, et al. A low-alloy high-carbon martensite steel with 2.6 GPa tensile strength and good ductility[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 158: 247-256. |
| [30] | Li J K, Yang Z N, Ma H, et al. A medium-C martensite steel with 2.6 GPa tensile strength and large ductility[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2023, 228: 115327. |
| [31] | Mandal G, Roy C, Ghosh S K, et al. Structure-property relationship in a 2 GPa grade micro-alloyed ultrahigh strength steel[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 705: 817-827. |
| [32] | Liang J T, Lu H Z, Zhang L L, et al. A 2000 MPa grade Nb bearing hot stamping steel with ultra-high yield strength[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 801: 140419. |
| [33] | Furuya Y, Matsuoka S. Improvement of gigacycle fatigue properties by modified ausforming in 1600 and 2000 MPA-class low-alloy steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33(11): 3421-3431. |
| [34] | Kim B, Boucard E, Sourmail T, et al. The influence of silicon in tempered martensite: understanding the microstructure-properties relationship in 0.5~0.6wt% C steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 68: 169-178. |
| [35] | 于林然,杨卓越,苏杰,等.一种新型2 GPa级低合金超高强度钢及热处理工艺[J].金属热处理,2024, 49(3): 164-168. |
| Yu Lin-ran, Yang Zhuo-yue, Su Jie, et al. A novel 2 GPa grade low alloy ultra-high strength steel and heat treatment process[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2024, 49(3): 164-168. | |
| [36] | 谢地荣,薛彦均,尉文超,等.回火温度对2 300 MPa 级低合金超高强度钢组织及力学性能的影响[J].钢铁研究学报,2024, 36(5): 660-668. |
| Xie Di-rong, Xue Yan-jun, Wei Wen-chao, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2 300 MPa grade low alloy ultra-high strength steel [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2024, 36(5): 660-668. | |
| [37] | 易红亮,常智渊,才贺龙,等.热冲压成形钢的强度与塑性及断裂应变[J].金属学报,2020, 56(4): 429-443. |
| Yi Hong-liang, Chang Zhi-yuan, Cai He-long, et al. Strength, ductility and fracture strain of press-hardening steels [J]. Acta Metallica Sinica, 2020, 56(4): 429-443. | |
| [38] | 易红亮,刘宏亮,常智渊,等.热冲压成形用钢材、热冲压成形工艺及热冲压成形构件:201610535069.3[P]. 2017-02-15. |
| Yi Hong-liang, Liu Hong-liang, Chang Zhi-yuan, et al. Steel for hot stamping forming, hot stamping forming process and hot stamping forming member: 201610535069.3[P]. 2017-02-15. | |
| [39] | Jimenez-Melero E, van Dijk N H, Zhao L, et al. In situ synchrotron study on the interplay between martensite formation, texture evolution and load partitioning in low-alloyed TRIP steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(21): 6407-6416. |
| [40] | Yang D P, Wang T, Miao Z T, et al. Effect of grain size on the intrinsic mechanical stability of austenite in transformation-induced plasticity steels: the competition between martensite transformation and dislocation slip[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 162: 38-43. |
| [41] | An X L, Zhang R M, Wu Y X, et al. The role of retained austenite on the stress-strain behaviour of chemically patterned steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 831: 142286. |
| [42] | Seo E J, Cho L, Estrin Y, et al. Microstructure-mechanical properties relationships for quenching and partitioning (Q&P) processed steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 113: 124-139. |
| [43] | Soleimani M, Kalhor A, Mirzadeh H. Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) in advanced steels: a review[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 795: 140023. |
| [44] | Clarke A J, Speer J G, Miller M K, et al. Carbon partitioning to austenite from martensite or bainite during the quench and partition (Q&P) process: a critical assessment[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(1): 16-22. |
| [45] | Santofimia M J, Zhao L, Petrov R, et al. Characterization of the microstructure obtained by the quenching and partitioning process in a low-carbon steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(12): 1758-1764. |
| [46] | Yan S, Liu X H, Liu W J, et al. Comparison on mechanical properties and microstructure of a C-Mn-Si steel treated by quenching and partitioning (Q&P) and quenching and tempering (Q&T) processes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 620: 58-66. |
| [47] | HajyAkbary F, Sietsma J, Miyamoto G, et al. Analysis of the mechanical behavior of a 0.3C-1.6Si-3.5Mn(wt%) quenching and partitioning steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 677: 505-514. |
| [48] | Thomas G A, Speer J G. Interface migration during partitioning of Q&P steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 30(9): 998-1007. |
| [49] | Wang H S, Shen F H, Wang Y, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on the microstructure, deformation and fracture properties of an ultrahigh strength medium-Mn steel processed by quenching and tempering[J]. Steel Research International, 2023, 94(11): 2200902. |
| [50] | Kim B, Celada C, San Martín D, et al. The effect of silicon on the nanoprecipitation of cementite[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(18): 6983-6992. |
| [51] | Yi H L, Lee K Y, Bhadeshia H K D H. Mechanical stabilisation of retained austenite in δ-TRIP steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528: 5900-5903. |
| [52] | Yi H L, Ryu J H, Bhadeshia H K D H, et al. Low-alloy duplex, directly quenched transformation-induced plasticity steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(7): 604-607. |
| [53] | Li H Y, Lu X W, Li W J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of an ultrahigh-strength 40SiMnNiCr steel during the one-step quenching and partitioning process[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2010, 41(5): 1284-1300. |
| [54] | Jirková H, Kučerová L, Mašek B. Effect of quenching and partitioning temperatures in the Q-P process on the properties of AHSS with various amounts of manganese and silicon[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2012, 706-709: 2734-2739. |
| [55] | Jirkova H, Kucerova L. Q-P process on steels with various carbon and chromium contents[C]// Proceedings of the 8th Pacific Rim International Congress on Advanced Materials and Processing. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2013: 819-824. |
| [56] | Hsu T Y, Xu Z Y. Design of structure, composition and heat treatment process for high strength steel[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, 561/565: 2283-2286. |
| [57] | Wang X D, Zhong N, Rong Y H, et al. Novel ultrahigh-strength nanolath martensitic steel by quenching-partitioning-tempering process[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2009, 24(1): 260-267. |
| [58] | Zhong N, Wang X D, Wang L, et al. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of a Nb-microalloyed advanced high-strength steel treated by quenching-partitioning-tempering process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2009, 506(1/2): 111-116. |
| [59] | Peng F, Xu Y B, Gu X L, et al. The relationships of microstructure-mechanical properties in quenching and partitioning (Q&P) steel accompanied with microalloyed carbide precipitation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 723: 247-258. |
| [60] | Krauss G. Deformation and fracture in martensitic carbon steels tempered at low temperatures[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B: Process Metallurgy and Materials Processing Science, 2001, 32(2): 205-221. |
| [61] | Wang Y, Li R B, Zuo X W, et al. The twice softening of martensitic matrix in Q-P-T steels and its effect on ductility[J]. Heat Treatment and Surface Engineering, 2019, 1(1/2): 2-10. |
| [62] | Yi H L, Chen P, Hou Z Y, et al. A novel design: Partitioning achieved by quenching and tempering (Q-T & P) in an aluminium-added low-density steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 68(6): 370-374. |
| [63] | Du P J, Chen P, Misra D K, et al. Transformation-induced ductility of reverse austenite evolved by low-temperature tempering of martensite[J]. Metals, 2020, 10(10): 1343. |
| [64] | He B B, Pan S, Huang M X. Extra work hardening in room-temperature quenching and partitioning medium Mn steel enabled by intercritical annealing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 797: 140106. |
| [65] | He B B, Liu L, Huang M X. Room-temperature quenching and partitioning steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2018, 49(8): 3167-3172. |
| [66] | Li S S, Wen P Y, Li S L, et al. A novel medium-Mn steel with superior mechanical properties and marginal oxidization after press hardening[J]. Acta Materialia, 2021, 205: 116567. |
| [67] | Gu G Y, Kim J H, Lee H H, et al. Room temperature quenching and partitioning (RT-Q&P) processed steel with chemically heterogeneous initial microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 851: 143651. |
| [68] | Hou Z R, Opitz T, Xiong X C, et al. Bake-partitioning in a press-hardening steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 162: 492-496. |
| [69] | He B B, Hu B, Yen H W, et al. High dislocation density-induced large ductility in deformed and partitioned steels[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6355): 1029-1032. |
| [70] | Liu L, Yu Q, Wang Z, et al. Making ultrastrong steel tough by grain-boundary delamination[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6497): 1347-1352. |
| [71] | Li Y J, Yuan G, Li L L, et al. Ductile 2-GPa steels with hierarchical substructure[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6628): 168-173. |
| [72] | Xu Y S, Gong Y, Du H, et al. A newly-designed hot stamping plus non-isothermal Q&P process to improve mechanical properties of commercial QP980 steel[J]. International Journal of Lightweight Materials and Manufacture, 2020, 3(1): 26-35. |
| [73] | Sun W W, Wu Y X, Yang S C, et al. Advanced high strength steel (AHSS) development through chemical patterning of austenite[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 146: 60-63. |
| [74] | Zhang C, Xiong Z P, Yang D Z, et al. Heterogeneous quenching and partitioning from manganese-partitioned pearlite: retained austenite modification and formability improvement[J]. Acta Materialia, 2022, 235: 118060. |
| [75] | Gao G H, Zhang H, Gui X L, et al. Enhanced ductility and toughness in an ultrahigh-strength Mn-Si-Cr-C steel: the great potential of ultrafine filmy retained austenite[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 76: 425-433. |
| [76] | Rao M N. Progress in understanding the metallurgy of 18% Nickel-Maraging Steel[J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2006, 97(11): 1594-1607. |
| [77] | Sha W, Guo Z L. Maraging steels modelling of microstructure, properties and applications[M]. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2009. |
| [78] | Lombardo S, Ferreira N R, de Souza Santos L A, et al. Microstructural characterization of joints of maraging 300 steel welded by laser and subjected to plasma nitriding treatment [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2016, 869: 479-483. |
| [79] | Fanton L, Abdalla A J, de Lima M S F. Heat treatment and Yb-fiber laser welding of a maraging steel[J]. Welding Journal, 2014, 93(9): 362-368. |
| [80] | Rajkumar V, Arivazhagan N, Ramkumar K D. Studies on welding of maraging steels [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 75: 83-87. |
| [81] | Raabe D, Ponge D, Dmitrieva O. Designing ultrahigh strength steels with good ductility by combining transformation induced plasticity and martensite aging [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2009, 11(7): 547-555. |
| [82] | Seede R, Shoukr D, Zhang B, et al. An ultra-high strength martensitic steel fabricated using selective laser melting additive manufacturing: densification, microstructure, and mechanical properties [J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 186: 199-214. |
| [83] | Anil Kumar V, Karthikeyan M K, Gupta R K, et al. Aging behavior in 15-5 pH precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2012, 710: 483-488. |
| [84] | Zou X D, Niu B, Pan L L, et al. Wire+arc additive manufacturing and heat treatment of super martensitic stainless steel with a refined microstructure and excellent mechanical properties [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(7): 2624. |
| [85] | Samei J, Asgari H, Pelligra C, et al. A hybrid additively manufactured martensitic-maraging stainless steel with superior strength and corrosion resistance for plastic injection molding dies [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 45: 102068. |
| [86] | Karabeyoglu S S, Yaman P. An experimental investigation of martensitic stainless steel in aircraft and aerospace industry for thermal wear performance and corrosion potential [J]. Practical Metallography, 2022, 59(4): 199-215. |
| [87] | Li X D, Yin Z D. A computer-simulated electron diffraction analysis of precipitates in 18Ni(350) maraging steel [J]. Materials Letters, 1995, 23(4/6): 269-272. |
| [88] | Pardal J M, Tavares S S M, Terra V F, et al. Modeling of precipitation hardening during the aging and overaging of 18Ni-Co-Mo-Ti maraging 300 steel [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 393(1/2): 109-113. |
| [89] | Viswanathan U K, Dey G K, Asundi M K. Precipitation hardening in 350 grade maraging steel [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1993, 24(11): 2429-2442. |
| [90] | Li X D, Yin Z D, Li H B, et al. Mössbauer study of the early stages of aging in 18Ni(350) maraging steel [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 1993, 33(3/4): 277-280. |
| [91] | Cerra F M A, Pereira Ú C, Cardoso J L, et al. Microstructural characterization of grade 300 and grade 350 maraging steels and electrochemical study in hydrofluoric solution [J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2021, 243: 109738. |
| [92] | Marcisz J, Adamczyk M, Garbarz B. Optimisation of mechanical properties of 18%Ni350 grade maraging steel using novel heat treatment [J]. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 2017, 62(1): 73-84. |
| [93] | Ahmed M, Salam I, Nasim I, et al. Reclamation and additional alloying of 18Ni(350) maraging steel [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 1994, 3(3): 386-392. |
| [94] | Kalish D, Rack H J. Thermal embrittlement of 18 Ni(350) maraging steel [J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 2(9): 2665-2672. |
| [95] | Rack H J, Kalish D. The strength and fracture toughness of 18 Ni (350) maraging steel[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 11(2): 3011-3020. |
| [96] | Becker T H, Dimitrov D. The achievable mechanical properties of SLM produced maraging steel 300 components[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2016, 22(3): 487-494. |
| [97] | Song J, Tang Q, Feng Q X, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical behaviors of 18Ni-300 maraging steel manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 120: 105725. |
| [98] | Kempen K, Yasa E, Thijs L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted 18Ni-300 steel [J]. Physics Procedia, 2011, 12: 255-263. |
| [99] | Wu W P, Wang X, Wang Q, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of maraging 18Ni-300 steel obtained by powder bed based selective laser melting process[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2020, 26(8): 1379-1387. |
| [100] | Yin S, Chen C Y, Yan X C, et al. The influence of aging temperature and aging time on the mechanical and tribological properties of selective laser melted maraging 18Ni-300 steel[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 22: 592-600. |
| [101] | He Y, Yang K, Sha W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a 2000 MPa grade Co-free maraging steel after aging at 753K[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36(9): 2273-2287. |
| [102] | He Y, Yang K, Sha W, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a 2000 MPa Co-free maraging steel after aging at 753 K[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004, 35(9): 2747-2755. |
| [103] | Niu M C, Yin L C, Yang K, et al. Synergistic alloying effects on nanoscale precipitation and mechanical properties of ultrahigh-strength steels strengthened by Ni3Ti, Mo-enriched, and Cr-rich co-precipitates[J]. Acta Materialia, 2021, 209: 116788. |
| [104] | 尹炎祺,伍翠兰,谢盼,等.冷轧及退火制备的超细晶粒双相Mn12Ni2MoTi(Al)[J].金属学报,2016, 52(12): 1527-1535. |
| Yin Yan-qi, Wu Cui-lan, Xie Pan, et al. An ultrafine grained duplex Mn12Ni2MoTi(Al) steel fabricated by cold rolling and annealing [J]. Acta Metallica Sinica, 2016, 52(12): 1527-1535. | |
| [105] | Stallybrass C, Schneider A, Sauthoff G. The strengthening effect of (Ni,Fe)Al precipitates on the mechanical properties at high temperatures of ferritic Fe-Al-Ni-Cr alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13(12): 1263-1268. |
| [106] | Sun L, Simm T H, Martin T L, et al. A novel ultra-high strength maraging steel with balanced ductility and creep resistance achieved by nanoscale β-NiAl and Laves phase precipitates[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 149: 285-301. |
| [107] | Simm T H, Sun L, Galvin D R, et al. A SANS and APT study of precipitate evolution and strengthening in a maraging steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 702: 414–424. |
| [108] | Jiang S H, Wang H, Wu Y, et al. Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation[J]. Nature, 2017, 544(7651): 460-464. |
| [109] | Galindo N E I, Rainforth W M, Rivera P E J. Predicting microstructure and strength of maraging steels: elemental optimization[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 117: 270-285. |
| [110] | Wang J, Wu D J, Zhu C Y, et al. Thermal stability enhancement of hybrid Ni2Al3/Ni coatings on creep-resistant ferritic steels by a mechanism of thermodynamically constrained interdiffusion[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 232: 489-496. |
| [111] | Wang M, Sun H Y, Zheng W Y, et al. Creep behavior of an alumina-forming austenitic steel with simple alloy design[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2020, 25: 101303. |
| [112] | Yamamoto Y, Santella M L, Brady M P, et al. Effect of alloying additions on phase equilibria and creep resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, 40(8): 1868-1880. |
| [113] | Jiao Z B, Luan J H, Miller M K, et al. Co-precipitation of nanoscale particles in steels with ultra-high strength for a new era[J]. Materials Today, 2017, 20(3): 142-154. |
| [114] | Jiao Z B, Luan J H, Miller M K, et al. Precipitation mechanism and mechanical properties of an ultra-high strength steel hardened by nanoscale NiAl and Cu particles[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 97: 58-67. |
| [115] | Liu Z K, Jie X H, Wu H S, et al. The preparation and properties of Ni2Al3 intermetallic compound coating[J]. Coatings, 2023, 13(11): 1900. |
| [116] | Polvani R S, Tzeng W S, Strutt P R. High temperature creep in a semi-coherent NiAl-Ni2AlTi alloy[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1976, 7: 33-40. |
| [117] | Baik S, Wang S Y, Liaw P K, et al. Increasing the creep resistance of Fe-Ni-Al-Cr superalloys via Ti additions by optimizing the B2/L21 ratio in composite nano-precipitates[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 157(15): 142-154. |
| [118] | 易红亮,刘连骞,芦富敏,等.热作模具钢、其热处理方法及热作模具: 202210703843.2[P]. 2022-07-29. |
| Yi Hong-liang, Liu Lian-qian, Lu Fu-min, et al. Hot work die steel, heat treatment method thereof and hot work die: 202210703843.2[P]. 2022-07-29. | |
| [119] | 易红亮,刘连骞,王国栋,等.热作模具钢、其热处理方法及热作模具: 201910156108.2[P]. 2020-09-18. |
| Yi Hong-liang, Liu Lian-qian, Wang Guo-dong, et al. Hot work die steel, heat treatment method thereof and hot work die: 201910156108.2[P]. 2020-09-18. |
| [1] | YANG Sen-yu, FU Tian-liang, ZHU Mei-jun, WANG Zhao-dong. Experimental Study and Application of Temperature-Controlled Quenching for Q960E Ultra High Strength Steel Plates [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2022, 43(11): 1570-1574. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||