
东北大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 40-49.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2025.20230344
苏克箭1,2, 胡宪伟1,2, 张俊宇1,2, 王兆文1,2
收稿日期:2023-12-26
出版日期:2025-06-15
发布日期:2025-09-01
作者简介:苏克箭(1998—),男,安徽滁州人,东北大学硕士研究生基金资助:Ke-jian SU1,2, Xian-wei HU1,2, Jun-yu ZHANG1,2, Zhao-wen WANG1,2
Received:2023-12-26
Online:2025-06-15
Published:2025-09-01
摘要:
提出了碱酸浸出处理铝电解废防渗料的工艺.以某铝厂废防渗料为原料,分析其主要物相为NaF,NaAlSiO4,CaF2,α-Al2O3,Na3AlF6,Si和β-Al2O3.首先,原料水浸分离得到质量分数为98.84%的NaF.其次,采用单因素法得到碱浸处理水浸渣的最优工艺条件为温度90 ℃、液固比5 cm3/g、碱渣质量比0.25、反应时间100 min,该条件下Na3AlF6浸出率为94.04%.再次,通过单因素法得到酸浸处理碱浸渣的最优工艺条件为温度58 ℃、反应时间45 min、酸浓度0.6 mol/L、液固比12 cm3/g,该条件下NaAlSiO4和CaF2可被浸出.将碱浸液滴入酸浸液中除去酸浸液中的硅,当pH约为3时酸浸液中硅溶胶沉淀效果最好,过滤后加热硅溶胶,产物主要为SiO2·0.2Al2O3,质量分数为97.20%.将过滤去除硅溶胶后的酸浸液加入碱浸液中沉淀回收氟盐,当pH为9时,CaF2和Na3AlF6的回收率最高,分别为95.91%和92.44%,质量分数分别为48.41%和25.14%,此外,沉淀物中还含有质量分数为25.32%的Al(OH)3.
中图分类号:
苏克箭, 胡宪伟, 张俊宇, 王兆文. 碱酸法处理铝电解废防渗料[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(6): 40-49.
Ke-jian SU, Xian-wei HU, Jun-yu ZHANG, Zhao-wen WANG. Treatment of Spent Dry Barrier from Aluminum Electrolysis by Alkali-Acid Method[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2025, 46(6): 40-49.
| 仪器 | 生产厂家 | 型号 |
|---|---|---|
| X射线衍射仪 | 日本理学(Rigaku)公司 | Smartlab SE |
| 高频燃烧红外碳硫分析仪 | 美国LECO(力可)公司 | CS244 |
| 原子吸收分光光度计 | 日本日立公司 | 180-80 |
| 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪 | 美国Perkin Elmer公司 | Optima 4300D |
| 扫描电子显微镜 | 德国蔡司显微镜有限公司 | ULTRA PLUS |
表1 实验所使用的分析仪器
Table 1 Analytical instruments used in the experiment
| 仪器 | 生产厂家 | 型号 |
|---|---|---|
| X射线衍射仪 | 日本理学(Rigaku)公司 | Smartlab SE |
| 高频燃烧红外碳硫分析仪 | 美国LECO(力可)公司 | CS244 |
| 原子吸收分光光度计 | 日本日立公司 | 180-80 |
| 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪 | 美国Perkin Elmer公司 | Optima 4300D |
| 扫描电子显微镜 | 德国蔡司显微镜有限公司 | ULTRA PLUS |
| Na | F | Ca | Al | Fe | Li | C | Si | O | 余量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25.63 | 22.90 | 5.73 | 10.46 | 0.96 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 15.06 | 17.02 | 1.76 |
表2 铝电解废防渗料的元素含量(质量分数) (%)
Table 2 Element content of spent dry barrier from aluminum electrolysis (mass fraction)
| Na | F | Ca | Al | Fe | Li | C | Si | O | 余量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25.63 | 22.90 | 5.73 | 10.46 | 0.96 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 15.06 | 17.02 | 1.76 |
| 浸出步骤 | 温度/℃ | 时间/min | 碱渣质量比 | 浸出液浓度 | 液固比 | 搅拌速率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mol·L-1 | cm3·g -1 | r·min-1 | ||||
| 碱浸 | 40⁓100 | 20⁓140 | 0.1⁓0.35 | — | 2⁓6 | 300 |
| 酸浸 | 室温⁓70 | 15⁓60 | — | 0.375⁓0.675 | 8⁓14 | 300 |
| 浸出液处理 | 室温 | 实时反应 | — | — | — | 200 |
表3 碱浸、酸浸实验参数设置
Table 3 Parameter settings for alkali and acid leaching experiments
| 浸出步骤 | 温度/℃ | 时间/min | 碱渣质量比 | 浸出液浓度 | 液固比 | 搅拌速率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mol·L-1 | cm3·g -1 | r·min-1 | ||||
| 碱浸 | 40⁓100 | 20⁓140 | 0.1⁓0.35 | — | 2⁓6 | 300 |
| 酸浸 | 室温⁓70 | 15⁓60 | — | 0.375⁓0.675 | 8⁓14 | 300 |
| 浸出液处理 | 室温 | 实时反应 | — | — | — | 200 |
| pH | 2.02 | 2.29 | 2.44 | 2.58 | 2.71 | 2.83 | 2.92 | 3.03 | 3.09 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si沉淀率/% | 0 | 19.23 | 40.77 | 72.33 | 84.92 | 89.65 | 95.41 | 98.06 | 98.11 |
表4 酸浸液中硅元素的沉淀率随pH的变化
Table 4 Variation of precipitation rate of silicon element in acid leaching solution with pH
| pH | 2.02 | 2.29 | 2.44 | 2.58 | 2.71 | 2.83 | 2.92 | 3.03 | 3.09 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si沉淀率/% | 0 | 19.23 | 40.77 | 72.33 | 84.92 | 89.65 | 95.41 | 98.06 | 98.11 |
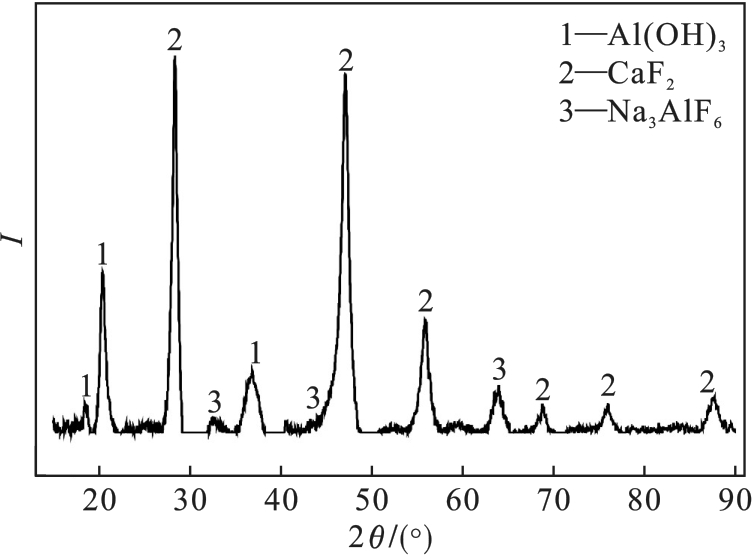
图17 去除硅溶胶的酸浸液加入碱浸液后所得沉淀物的XRD图谱
Fig.17 XRD pattern of precipitate obtained by adding alkali leaching solution to acid leaching solution after silica sol removal
| 元素 | EDS | ICP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 点1 | 点2 | ||
| Al | 8.44 | 9.06 | 8.76 |
| Si | 38.95 | 37.45 | 37.69 |
表5 EDS和ICP测得酸浸液中硅凝沉淀产物中Si和Al的质量分数
Table 5 Mass fraction of Si and Al in silica coagulation precipitation products in acid leaching solution measured by EDS and ICP %
| 元素 | EDS | ICP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 点1 | 点2 | ||
| Al | 8.44 | 9.06 | 8.76 |
| Si | 38.95 | 37.45 | 37.69 |
| 种类 | 溶度积 |
|---|---|
| CaF2 | 3.90×10-10 |
| Na3AlF6 | 4.22×10-10 |
| Al(OH)3 | 1.30×10-33 |
表6 25 ℃下CaF2,Na3AlF6,Al(OH)3的溶度积[29] (Al(OH)3 at 25 ℃[29])
Table 6 Solubility products of CaF2, Na3AlF6 and
| 种类 | 溶度积 |
|---|---|
| CaF2 | 3.90×10-10 |
| Na3AlF6 | 4.22×10-10 |
| Al(OH)3 | 1.30×10-33 |
| [1] | Yurkov A. Refractories and carbon cathode materials for aluminium reduction cells[M]// Yurkov A. Refractories for Aluminium. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 65-208. |
| [2] | 王耀武, 彭建平, 狄跃忠, 等. 铝电解槽干式防渗料在电解过程中的反应机理探讨[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 1035-1041. |
| Wang Yao-wu, Peng Jian-ping, Di Yue-zhong, et al. Mechanism of deterioration for dry barrier material in aluminum electrolysis cells[J].CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(3): 1035-1041. | |
| [3] | 王耀武, 桓书星, 狄跃忠, 等. 铝电解槽废耐火材料的危害与处理方法的研究现状[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(3): 42-47. |
| Wang Yao-wu, Huan Shu-xing, Di Yue-zhong, et al. The harmless of spent refractory in aluminum electrolysis cells and summary of its treatment [J].Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 39(3): 42-47. | |
| [4] | Kruger J, Thome R, Moritz D, et al. Rotating apparatus for manufacturing hydrogen fluoride:US4362701[P]. 1982-12-07. |
| [5] | Brooks D G, Cutshall E R, Banker D B, et al. Thermal treatment of spent pot liner in a rotary kiln[M]//Tomsett A, Johnson J. Essential Readings in Light Metals. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 1044-1048. |
| [6] | 宋云霞, 薛济来, 朱骏,等. 电热碳还原铝电解槽废旧防渗料制备粗铝硅合金的研究[C]//中国有色金属协会第八届冶金工程科学论坛论文集. 北京:北京科技大学出版社, 2009: 199-202. |
| Song Yun-xia, Xue Ji-lai, Zhu Jun, et al. Study on carbon-thermal reduction process of producing aluminum-silicon alloy from aluminum reduction pot linings[C]//Proceedings of the 8th Metallurgical Engineering Science Forum of China Nonferrous Metals Association(CNMA). Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing Press, 2009: 199-202.) | |
| [7] | 刘佳智, 王耀武, 张立达, 等. 真空热还原处理铝电解槽废防渗料的研究[J]. 轻金属, 2021(4): 19-23. |
| Liu Jia-zhi, Wang Yao-wu, Zhang Li-da, et al. Study on disposal process for spent dry barrier of aluminum pots by vacuum thermal reduction[J]. Light Metals, 2021(4): 19-23. | |
| [8] | 王天, 王耀武, 张立达, 等. 真空热还原石灰固化法处理铝电解槽废耐火材料的研究[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2020, 19(3): 185-189,195. |
| Wang Tian, Wang Yao-wu, Zhang Li-da, et al. A study on the treatment of spent refractory materials of aluminum electrolytic cell by vacuum thermal reduction and lime solidification process[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2020, 19(3): 185-189,195. | |
| [9] | Hou W Y, Li H S, Li M, et al. Recycling of spent refractory materials to produce Al-Si master alloys via the aluminum reduction cell[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 289: 125162. |
| [10] | Liu F Q, Xie M Z, Liu W, et al. Footprint of harmful substances in spent pot lining of aluminum reduction cell[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(7): 1956-1963. |
| [11] | Chen Y R, Li P, Bu X N, et al. Resource utilization strategies for spent pot lining: a review of the current state [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 300: 121816. |
| [12] | Nie Y F, Guo X Y, Guo Z H, et al. Defluorination of spent pot lining from aluminum electrolysis using acidic iron-containing solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 194: 105319. |
| [13] | Yang K, Li J, Huang W L, et al. A closed-circuit cycle process for recovery of carbon and valuable components from spent carbon cathode by hydrothermal acid-leaching method[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 318: 115503. |
| [14] | Yuan J, Xiao J, Li F C, et al. Co-treatment of spent cathode carbon in caustic and acid leaching process under ultrasonic assisted for preparation of SiC[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2018, 41: 608-618. |
| [15] | Xu Z B, Xu L, Han Z H, et al. Research on microwave hydrothermal alkaline leaching defluorination of spent cathode carbon from aluminum electrolysis[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2023, 201: 108168. |
| [16] | Xiao J, Yuan J, Tian Z L, et al. Comparison of ultrasound-assisted and traditional caustic leaching of spent cathode carbon (SCC) from aluminum electrolysis[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2018, 40: 21-29. |
| [17] | Bonadia P, Valenzuela F A O, Bittencourt L R, et al. Aluminosilicate refractories for aluminum cell linings[J]. American Ceramic Society Bulletin, 2005, 84(2): 26-31. |
| [18] | Allaire C. Refractory lining for alumina electrolytic cells[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1992, 75(8): 2308-2311. |
| [19] | Schøning C, Grande T, Siljan O J. Cathode refractory materials for aluminium reduction cells[M]//Tomsett A, Johnson J. Essential Readings in Light Metals. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 849-856. |
| [20] | Murata K J. Internal structure of silicate minerals that gelatinize with acid[J]. American Mineralogist, 1943, 28(11/12): 545-562. |
| [21] | 张爱芬, 马慧侠, 白万里. 熔融制样-X射线荧光光谱法测定铝电解槽用干式防渗料中主次成分[J]. 冶金分析, 2014, 34(5): 25-29. |
| Zhang Ai-fen, Ma Hui-Xia, Bai Wan-li, et al. Determination of major and minor components in dry barrier of aluminum electrolytic cell by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with sample fusion preparation[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(5): 25-29. | |
| [22] | 朱新伟, 刘双, 熊毅. 铝电解槽用新型干式防渗料性能的研究[J]. 轻金属, 2009(10): 26-30. |
| Zhu Xin-wei, Liu Shuang, Xiong Yi, et al. Studies on a new phase plate dry barrier for aluminium electrolytic cell [J]. Light Metals, 2009(10): 26-30. | |
| [23] | 抚顺铝业有限责任公司. 氟化钠化学分析方法第2部分: [S]. 北京:中华人民共和国工业和信息化部,2010. |
| Fushun Aluminum Co. Method of chemical analysis for sodium fluoride, part 2: [S]. Beijing: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China, 2010. | |
| [24] | 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 氟化钠: [S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2009. |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Sodium fluoride: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China,2009. | |
| [25] | Hench L L, West J K. The sol-gel process[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1990, 90(1): 33-72. |
| [26] | Wen L Y, Xu J C, Yang Q, et al. Gelation process of nanosilica sol and its mechanism: molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 216: 115538. |
| [27] | Terry B. The acid decomposition of silicate minerals, part II: hydrometallurgical applications[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1983, 10(2): 151-171. |
| [28] | Moqadam M, Riccardi E, Trinh T T, et al. Rare event simulations reveal subtle key steps in aqueous silicate condensation[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(20): 13361-13371. |
| [29] | 马荔, 陈虹锦. 基础化学[M]. 2版. 北京:化学工业出版社,2011:462. |
| Ma Li, Chen Hong-jin. Basic chemistry[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press,2011:462. |
| [1] | 林清扬, 陈晓方, 谢永芳. 基于残差卷积自注意力神经网络的铝电解过热度识别方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(1): 8-17. |
| [2] | 李雪娇, 杨洪英, 赵鹤飞, 胡红胜. 铝电解槽集气结构的数值模拟研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(7): 966-972. |
| [3] | 李雪娇, 杨洪英, 胡红胜, 宋海琛. 残极集气系统对无组织烟气减排的作用[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(6): 844-849. |
| [4] | 邵安林, 苏兴国, 韩跃新, 李艳军. 东鞍山浮选尾矿预富集精矿悬浮磁化焙烧试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(5): 703-708. |
| [5] | 杨酉坚, 齐俊峰, 庞小娟, 王兆文. 冶金级氧化铝颗粒磨损指数分析[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(6): 801-806. |
| [6] | 王耀武, 尤晶, 彭建平, 狄跃忠. 铝电解过程中锂元素的阴极渗透机理[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(1): 62-67. |
| [7] | 李拓夫, 陶文举, 王兆文, 刘小珍. 磷生铁和钢爪尺寸对铝电解槽阳极物理场的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(6): 828-834. |
| [8] | 李拓夫, 陶文举, 王兆文, 孔令宇. 预焙炭阳极环形槽炭碗设计的仿真研究[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(12): 1715-1720. |
| [9] | 黄义鹏, 王兆文, 杨酉坚, 石忠宁. 铝电解槽阳极形状对气泡排出的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(2): 228-233. |
| [10] | 侯剑峰, 王兆文, 李拓夫, 石忠宁. 椰壳类活性炭高温改性及吸附铝电解质熔盐中K+的性能[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 37(12): 1740-1744. |
| [11] | 毛瑞, 张建良, 刘征建, 王飞. 钢铁厂含铁尘泥球团自还原实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 36(6): 790-795. |
| [12] | 曹晓舟, 时园园, 赵爽, 薛向欣. 铝电解槽废旧阴极炭块中有价组分的回收[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 35(12): 1746-1749. |
| [13] | 齐凤升;杨柳;李宝宽;冯乃祥;. 铝电解阳极碳块析出气体引起的电解质/铝液界面波动[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(7): 1009-1012. |
| [14] | 贺铸;李宝宽;王芳;冯乃祥;. 电解槽内异型凸台对电解质/铝液界面波动的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 32(5): 704-707. |
| [15] | 李丽匣;王亚琴;韩跃新;包士雷;. 陶瓷废料生产建筑材料的试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 32(3): 419-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||