
东北大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (11): 66-72.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2025.20240111
收稿日期:2024-05-14
出版日期:2025-11-15
发布日期:2026-02-07
通讯作者:
沈峰满
作者简介:张国鹏(1995—),男,山西运城人,东北大学博士研究生
基金资助:
Guo-peng ZHANG1, Feng-man SHEN1( ), Wei-ling ZHANG1,2, Hai-yan ZHENG1
), Wei-ling ZHANG1,2, Hai-yan ZHENG1
Received:2024-05-14
Online:2025-11-15
Published:2026-02-07
Contact:
Feng-man SHEN
摘要:
高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿过程中TiO2过度还原会严重影响高炉顺行.基于TiO2碳热还原热力学计算,并采用失重法探究温度、气氛及还原剂类型对TiO2碳热还原过程的影响.结果表明,固溶体Ti(C x,N y )的生成起始反应温度随着TiC摩尔分数的增加而升高;相同温度下,TiN在Ti(C x,N y )中的摩尔分数随N2分压增加而增大;相同反应时间内,TiO2的还原度随温度升高而增加;在Ar和N2气氛中,TiO2可与石墨发生碳热还原反应生成TiC及TiN,而在空气和CO2气氛中石墨会优先与空气中的O2及气氛中的CO2发生氧化反应;在所有还原剂中,TiO2与石墨的反应难度最大,提高入炉焦炭的石墨化程度可有效抑制高炉中TiO2的过度还原.
中图分类号:
张国鹏, 沈峰满, 章苇玲, 郑海燕. TiO2碳热还原机理及影响因素的研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(11): 66-72.
Guo-peng ZHANG, Feng-man SHEN, Wei-ling ZHANG, Hai-yan ZHENG. Research on Mechanism and Influencing Factors of TiO2 Carbothermal Reduction[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2025, 46(11): 66-72.
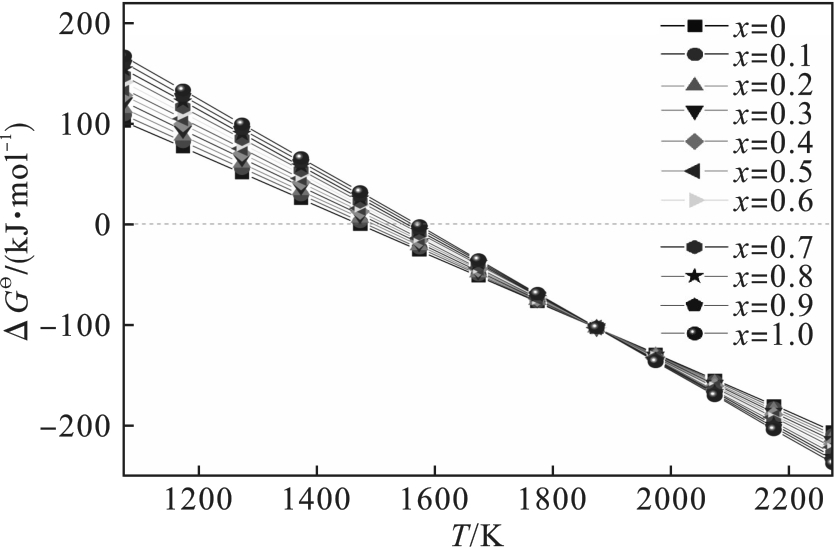
图2 不同TiC摩尔分数的Ti(C x, N y )固溶体的标准生成吉布斯自由能
Fig.2 Standard Gibbs free energy of Ti(C x, N y ) solid solution generation for different molar fractions of TiC
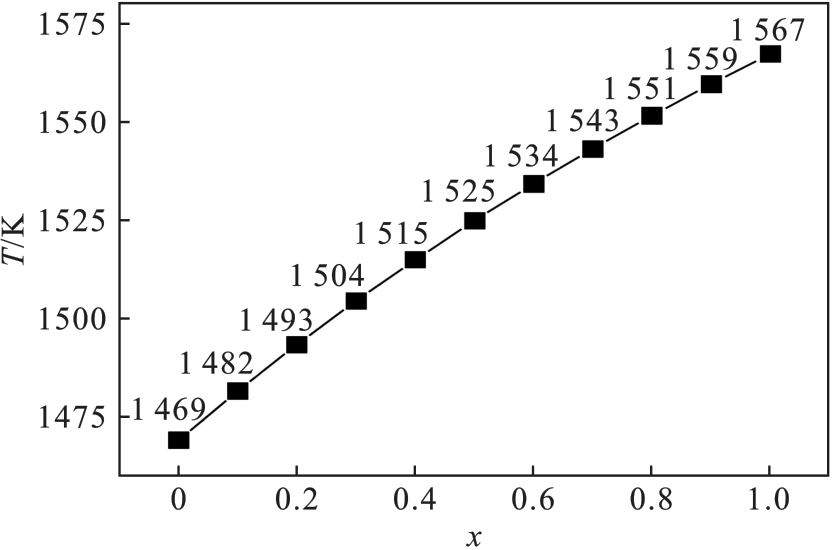
图3 不同TiC摩尔分数的Ti(C x, N y )固溶体生成的初始反应温度
Fig.3 Initial reaction temperatures for Ti(C x, N y ) solid solution generation with different molar fractions of TiC
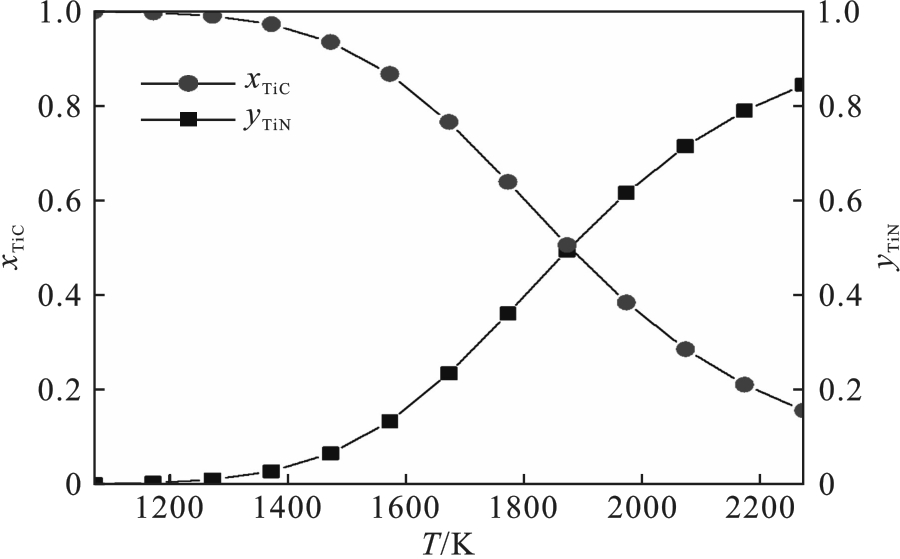
图4 N2分压为101.325 kPa时固溶体Ti(C x, N y )中TiC和TiN的摩尔分数随温度的变化
Fig.4 Variation of TiC and TiN mole fractions in Ti(C x, N y ) solid solution with temperature at N2 partial pressure of 101.325 kPa
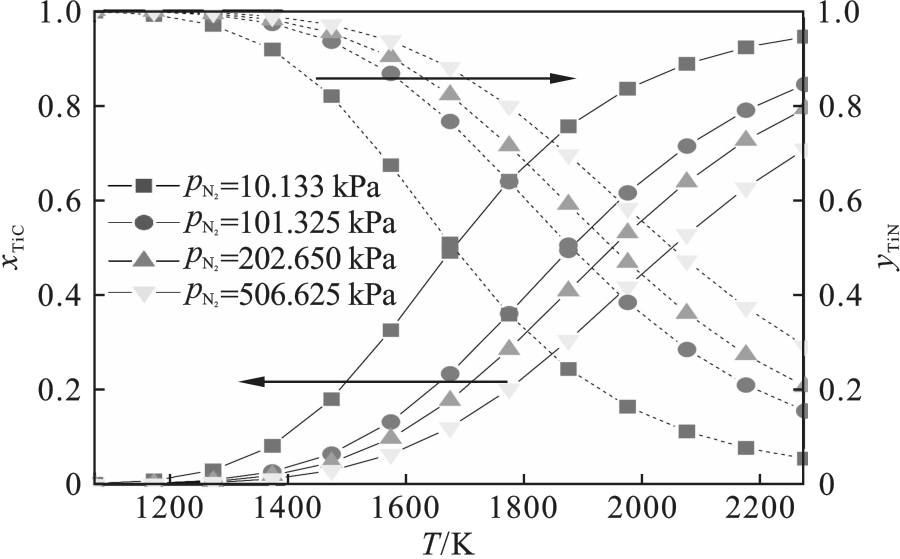
图5 不同N2分压下固溶体Ti(C x, N y )中TiC和TiN摩尔分数随温度的变化注:实线标目见左轴,虚线标目见右轴,下同.
Fig.5 Variation of TiC and TiN mole fractions in Ti(C x, N y ) solid solution with temperature at different N2 partial pressures
| 样品编号 | 成分组成 | 配比 |
|---|---|---|
| TSM1 | TiO2+石墨 | 1∶3.3 |
| TJT2 | TiO2+焦炭 | 1∶3.3 |
| TYM3 | TiO2+烟煤 | 1∶3.3 |
| TWYM4 | TiO2+无烟煤 | 1∶3.3 |
表1 试验样品的成分配比(摩尔比) (mole ratios)
Table 1 Composition ratios of test samples
| 样品编号 | 成分组成 | 配比 |
|---|---|---|
| TSM1 | TiO2+石墨 | 1∶3.3 |
| TJT2 | TiO2+焦炭 | 1∶3.3 |
| TYM3 | TiO2+烟煤 | 1∶3.3 |
| TWYM4 | TiO2+无烟煤 | 1∶3.3 |
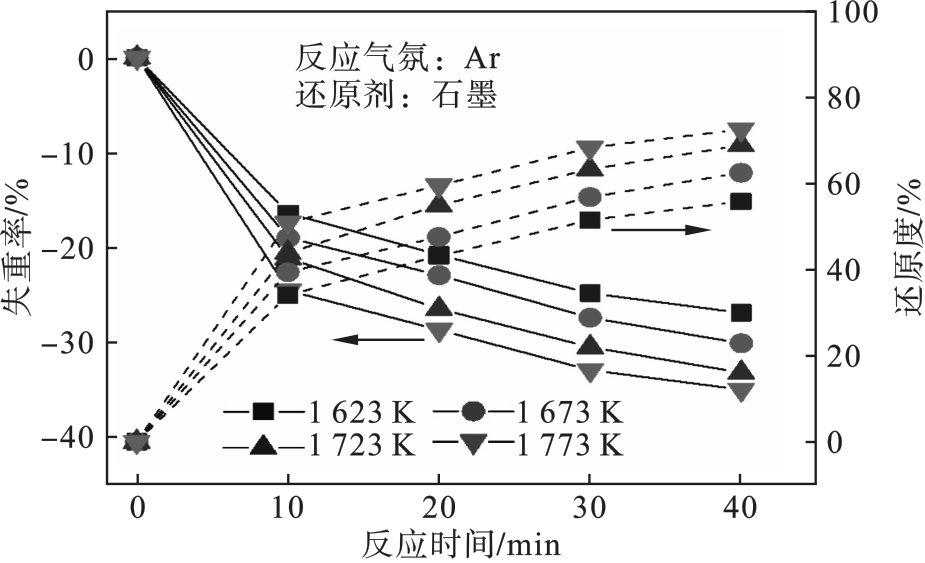
图7 不同温度条件下TiO2碳热还原后样品的失重率及还原度变化
Fig.7 Variation of weight loss rate and reduction degree of samples after carbothermal reduction of TiO2 at different temperatures
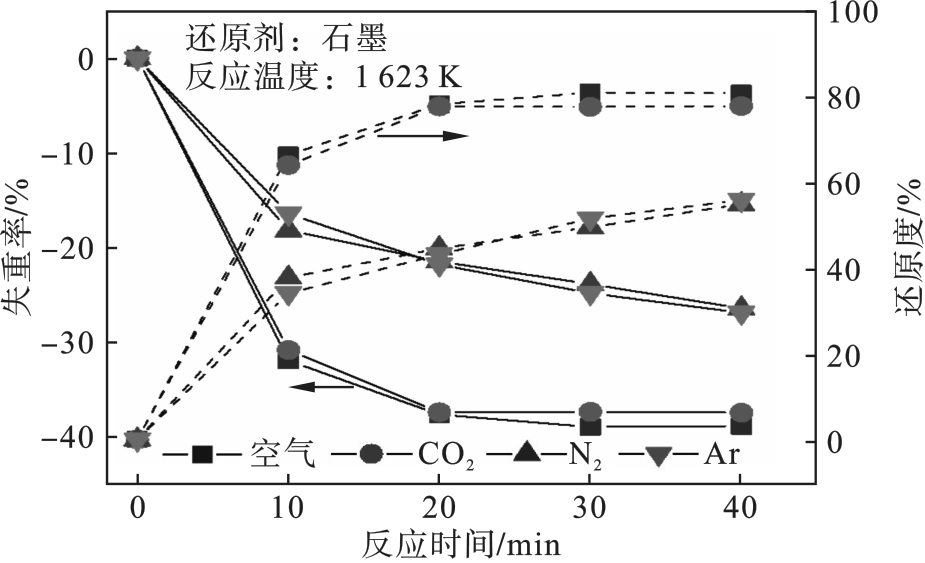
图8 不同气氛条件下TiO2碳热还原反应的失重率和还原度变化
Fig.8 Variation of weight loss rate and reduction degree in carbothermal reduction reaction of TiO2 under different atmosphere conditions
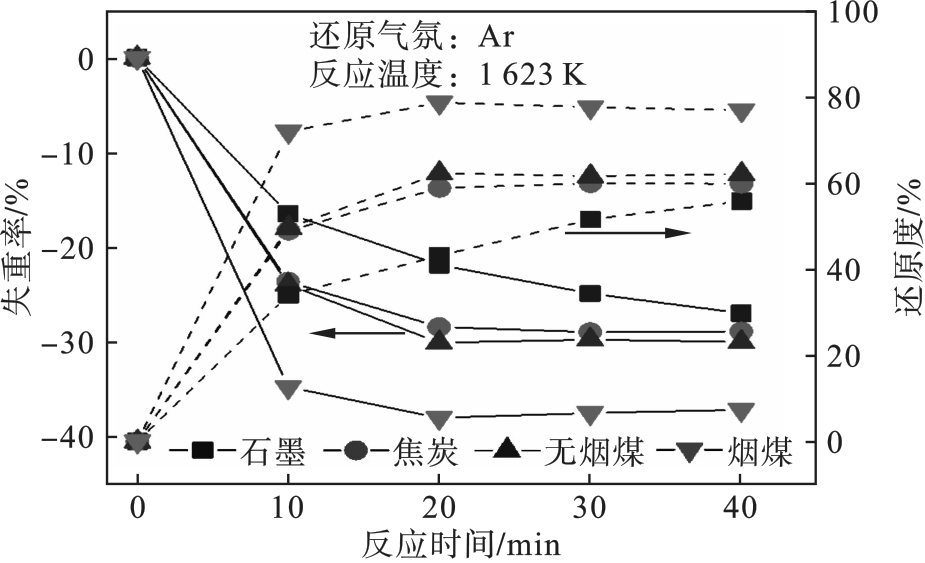
图10 不同还原剂条件下TiO2碳热还原反应的失重率和还原度变化
Fig.10 Variation of weight loss rate and reduction degree in carbothermal reduction reaction of TiO2 under different reductant conditions
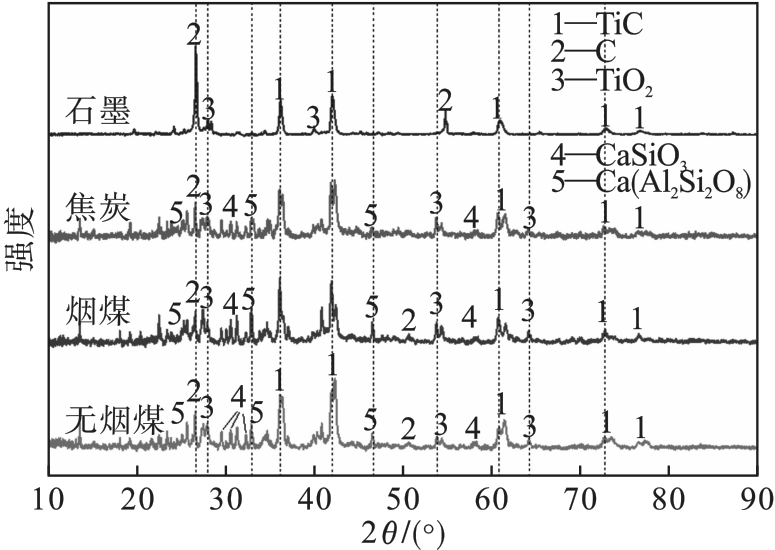
图11 不同还原剂条件下TiO2碳热还原反应后的样品物相分析
Fig.11 Physical phase analysis of samples after carbothermal reduction reaction of TiO2 under different reductant conditions
| [1] | Chen D S, Song B, Wang L N, et al. Solid state reduction of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates with pulverized coal[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(8):864-869. |
| [2] | Zhang L, Zhang L N, Wang M Y, et al. Precipitation selectivity of perovskite phase from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag under dynamic oxidation conditions[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2007, 353(22/23):2214-2220. |
| [3] | Pang Z D, Jiang Y Y, Ling J W, et al. Blast furnace ironmaking process with super high TiO2 in the slag: density and surface tension of the slag[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2022,29(6):1170-1178. |
| [4] | Valighazvini F, Rashchi F, Khayyam Nekouei R. Recovery of titanium from blast furnace slag[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(4):1723-1730. |
| [5] | Yuan Z F, Wang X Q, Xu C, et al. A new process for comprehensive utilization of complex titania ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19(9):975-978. |
| [6] | Saito N, Hori N, Nakashima K, et al. Viscosity of blast furnace type slags[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2003, 34(5):509-516. |
| [7] | Zheng H Y, Zhou S F, Zhang S, et al. Viscosity estimation of TiO2-bearing blast furnace slag with high Al2O3 at 1 500 oC[J]. Metals, 2023, 13(3):573. |
| [8] | Shankar A, Görnerup M, Seetharaman S, et al. Sulfide capacity of high alumina blast furnace slags[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2006, 37(6):941-947. |
| [9] | Sohn I, Wang W L, Matsuura H, et al. Influence of TiO2 on the viscous behavior of calcium silicate melts containing 17 mass% Al2O3 and 10 mass% MgO[J]. ISIJ International, 2012, 52(1):158-160. |
| [10] | Zheng H Y, Zhou X R, Hu X G, et al. Desulphurisation behaviour of blast furnace slag with high Al2O3 content at 1823 K[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2022,49(6):596-603. |
| [11] | Gao K, Jiao K X, Zhang J L, et al. Dissection investigation of forming process of titanium compounds layer in the blast furnace hearth[J]. ISIJ International, 2020, 60(11): 2385-2391. |
| [12] | Qiu G B, Ma S W, Deng Q Y, et al. Study on the formation of Ti(C,N) between blast furnace hot metal and slag bearing high TiO2 [J]. Metalurgia International, 2012, 17(4): 94-99. |
| [13] | Narita K, Maekawa M, Onoye T, et al. Formation of titanium compounds, so-called titanium bear, in the blast furnace hearth[J]. Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1977, 17(8):459-468. |
| [14] | Zhen Y L, Zhang G H, Chou K C. Carbothermic reduction of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2016, 35(3): 309-319. |
| [15] | 张建良,焦克新,刘征建,等.长寿高炉炉缸保护层综合调控技术[J].钢铁,2017, 52(12):1-7. |
| Zhang Jian-liang, Jiao Ke-xin, Liu Zheng-jian, et al. Comprehensive regulation technology for hearth protective layer of blast furnace longevity[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017, 52(12):1-7. | |
| [16] | 赵永彬,张建良,宁晓钧,等.低钛高炉渣中Ti(C,N)形成的研究[J].钢铁钒钛,2014, 35(1):79-84. |
| Zhao Yong-bin, Zhang Jian-liang, Ning Xiao-jun, et al. Study on the formation of Ti(C,N) in low TiO2 content blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(1):79-84. | |
| [17] | 高运明,李慈颖,李亚伟,等.TiO2碳热还原与高炉钛渣提取碳氮化钛分析[J].武汉科技大学学报(自然科学版),2007, 30(1):5-9. |
| Gao Yun-ming, Li Ci-ying, Li Ya-wei, et al. Analysis of carbothermal reduction of TiO2 and extraction of titanium carbonitride from the blast furnace slag bearing titania[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition),2007, 30(1):5-9. | |
| [18] | Wang Y Z, Zhang J L, Liu Z J, et al. Carbothermic reduction reactions at the metal-slag interface in Ti-bearing slag from a blast furnace[J]. JOM, 2017, 69(11):2397-2403. |
| [19] | Jiao K X, Zhang J L, Hou Q F, et al. Analysis of the relationship between productivity and hearth wall temperature of a commercial blast furnace and model prediction[J]. Steel Research International, 2017,88(9): 1600475. |
| [20] | Jiao K X, Zhang J L, Liu Z J, et al. Dissection investigation of Ti(C, N) behavior in blast furnace hearth during vanadium titano-magnetite smelting[J]. ISIJ International, 2017, 57(1): 48-54. |
| [21] | 詹星.小高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿解剖研究[J].钢铁钒钛,1984, 5(2):3-15. |
| Zhan Xing. Anatomical study on smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite in small blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1984, 5(2):3-15. | |
| [22] | 郑常乐,邵球军,张建良,等.富氧率对钒钛磁铁矿球团还原行为的影响[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2016, 37(2): 198-202, 212. |
| Zheng Chang-le, Shao Qiu-jun, Zhang Jian-liang, et al. Influence of oxygen enrichment rate on reduction behavior of titanomagnetite pellets[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2016, 37(2): 198-202, 212. | |
| [23] | 焦克新,张建良,刘征建,等.高炉炉缸含钛保护层物相及TiC0.3N0.7形成机理[J].工程科学学报,2019, 41(2):190-198. |
| Jiao Ke-xin, Zhang Jian-liang, Liu Zheng-jian, et al. Mineralogical phase and formation mechanism of titanium-bearing protective layers in a blast furnace hearth[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2019, 41(2):190-198. | |
| [24] | 焦克新,张建良,左海滨,等.高炉炉缸黏滞层物相及形成机理[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2014, 35(7):987-991. |
| Jiao Ke-xin, Zhang Jian-liang, Zuo Hai-bin, et al. Composition and formation mechanism of viscous layers in blast furnace hearth[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2014, 35(7):987-991. | |
| [25] | Wada H, Pehlke R D. Nitrogen solubility and nitride formation in austenitic Fe-Ti alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1985, 16(4): 815-822. |
| [26] | Ozturk B, Fruehan R J. Thermodynamics of inclusion formation in Fe-Ti-C-N alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1990, 21(5): 879-884. |
| [27] | Li Y, Li Y Q, Fruehan R J. Formation of titanium carbonitride from hot metal[J]. ISIJ International, 2001,41(12):1417-1422. |
| [28] | Xiang D W, Shen F M, Jiang X, et al. Pyrolysis characteristics of industrial lignin for use as a reductant and an energy source for future iron making[J]. ACS Omega, 2021,6(5): 3578-3586. |
| [29] | Lyu T T, Hu T, Tian F. Hydrogen-enhanced carbothermal reduction for the synthesis of TiC from TiO2 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1039: 183002. |
| [30] | Tang S Y, Song G Q, Guo J J, et al. Oxidation behavior of TiC and TiCN and their potential photocatalytic activity in semi-oxidized state[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2025,7(16): 5031-5041. |
| [31] | Chen M, Chen B X, Jiang Y, et al. Study of Ti(C,N) formations in TiO2-containing slags[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2025, 56(1): 1018-1028. |
| [32] | Sui J H, Yang S T, Wang Q, et al. Influence of blast furnace burden with different TiO2 contents on the process of reduction and slag formation in cohesive zone[J]. ISIJ International, 2025,65(4): 521-532. |
| [33] | Zhang S S, Zhang J L, Wang Z Y, et al. Advancements in oxygen blast furnace technology and its application in the smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite: a comprehensive review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2024, 212: 108732. |
| [34] | Huang Y, Zhang Z D, Tang J, et al. Mathematical simulation on smelting vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite by oxygen blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 2025,65(11): 1690-1700. |
| [35] | Chen B X, Chen M, Zhang K X, et al. Metallurgical properties of vanadium titanomagnetite sinter in the cohesive zone of H2-rich oxygen blast furnace[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2025: 1-12. |
| [36] | Qu Y X, Xing L, Gao M L, et al. Progress and prospects for titanium extraction from titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Materials, 2024, 17(24): 6291. |
| [37] | Zheng K, Wang W, Huang T, et al. Influence of temperature and slag composition on wetting behavior of titanium-containing blast furnace slag and tuyere coke[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2025,32(10): 3298-3307. |
| [1] | 曹晓舟, 邵胜琦, 岳宏瑞. 铁酸钙与TiO2的扩散反应特征[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(2): 193-200. |
| [2] | 于宏东, 王丽娜, 曲景奎, 齐涛. 中国典型钒钛磁铁矿的工艺矿物学特征与矿石价值[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(2): 275-281. |
| [3] | 张立恒, 高子先, 汤卫东, 薛向欣. w(TiO2)对高铬型钒钛磁铁矿烧结矿冶金性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 41(11): 1667-1672. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 姜涛, 刘亚静, 薛向欣. 微波预处理对钒钛磁铁矿磨矿动力学的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(5): 663-667. |
| [5] | 何占伟, 薛向欣. 不同钒钛磁铁矿炉料冶金性能的对比研究[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(2): 207-211. |
| [6] | 边雪, 胡吕, 彭朋, 刘思洋. xCeO2-yWO3-TiO2脱硝催化剂的制备与性能[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(12): 1716-1720. |
| [7] | 骆旭峰, 张晟, 孙用军, 董辉. 钒钛磁铁矿焙烧竖炉操作参数对传热过程的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(1): 53-58. |
| [8] | 姜婷婷, 石勇, 柯军, 许开立. 基于碳量子点的TiO2改性及降解污染物性能[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 39(1): 138-142. |
| [9] | 李尉, 付贵勤, 储满生, 朱苗勇. 红格钒钛磁铁矿氧化物相转变及非等温氧化动力学[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 38(4): 517-521. |
| [10] | 唐志东, 李文博, 高鹏, 韩跃新. 朝阳钒钛磁铁矿工艺矿物学研究[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 38(12): 1769-1774. |
| [11] | 王俊鹏, 姜涛, 刘亚静, 薛向欣. 钒钛磁铁矿微波助磨实验[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 38(11): 1559-1563. |
| [12] | 李峰, 储满生, 唐珏, 冯聪. 用综合加权评分法优化高铬型钒钛矿电热熔分工艺[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 37(9): 1327-1331. |
| [13] | 郑常乐, 邵球军, 张建良, 王广伟. 富氧率对钒钛磁铁矿球团还原行为的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 37(2): 198-203. |
| [14] | 姜鑫, 王琳, 柳明旭, 沈峰满. 还原时间对高料层碳热还原金属化率的影响[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 37(12): 1720-1725. |
| [15] | 储满生, 冯聪, 唐珏, 柳政根. 中性气氛下钒钛磁铁矿高炉渣系研究[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 36(9): 1283-1287. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||