
Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (8): 20-31.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2025.20240217
• Overview • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ming-hui CHEN, Kai-li SONG, Yu ZHEN, Fu-hui WANG
Received:2024-11-25
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-11-24
Contact:
Ming-hui CHEN
CLC Number:
Ming-hui CHEN, Kai-li SONG, Yu ZHEN, Fu-hui WANG. Research Status and Prospects of Metal Matrix High-Temperature Self-lubricating Composites[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2025, 46(8): 20-31.
| 材料种类 | 摩擦系数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 204 ℃ | 316 ℃ | 593 ℃ | |
| 无氧化物润滑物质 | 0.46~0.78 | 0.75 | 0.60~0.80 |
PbO B2O3 CrO3 Re2O7 ReO2 Cu2O CuO CoO MoO3 WO3 Fe3O4 Fe2O3 V2O5 TiO2 Al2O3 Cr2O3 NiO | 0.19 0.64 0.14 0.35 0.64 0.30 0.60 0.46 0.51 0.41 0.60 0.46 0.53 0.68 0.77 0.41 0.70 | 0.10 0.51 — 0.23 — 0.14 0.50 0.38 0.69 0.60 — — 0.52 — — 0.64 — | 0.10 0.18 — — 0.27 0.48 0.22 0.18 0.38 0.56 0.40 0.42 0.32 — — — 0.69 |
Table 1 Friction coefficients of some metal oxides at
| 材料种类 | 摩擦系数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 204 ℃ | 316 ℃ | 593 ℃ | |
| 无氧化物润滑物质 | 0.46~0.78 | 0.75 | 0.60~0.80 |
PbO B2O3 CrO3 Re2O7 ReO2 Cu2O CuO CoO MoO3 WO3 Fe3O4 Fe2O3 V2O5 TiO2 Al2O3 Cr2O3 NiO | 0.19 0.64 0.14 0.35 0.64 0.30 0.60 0.46 0.51 0.41 0.60 0.46 0.53 0.68 0.77 0.41 0.70 | 0.10 0.51 — 0.23 — 0.14 0.50 0.38 0.69 0.60 — — 0.52 — — 0.64 — | 0.10 0.18 — — 0.27 0.48 0.22 0.18 0.38 0.56 0.40 0.42 0.32 — — — 0.69 |
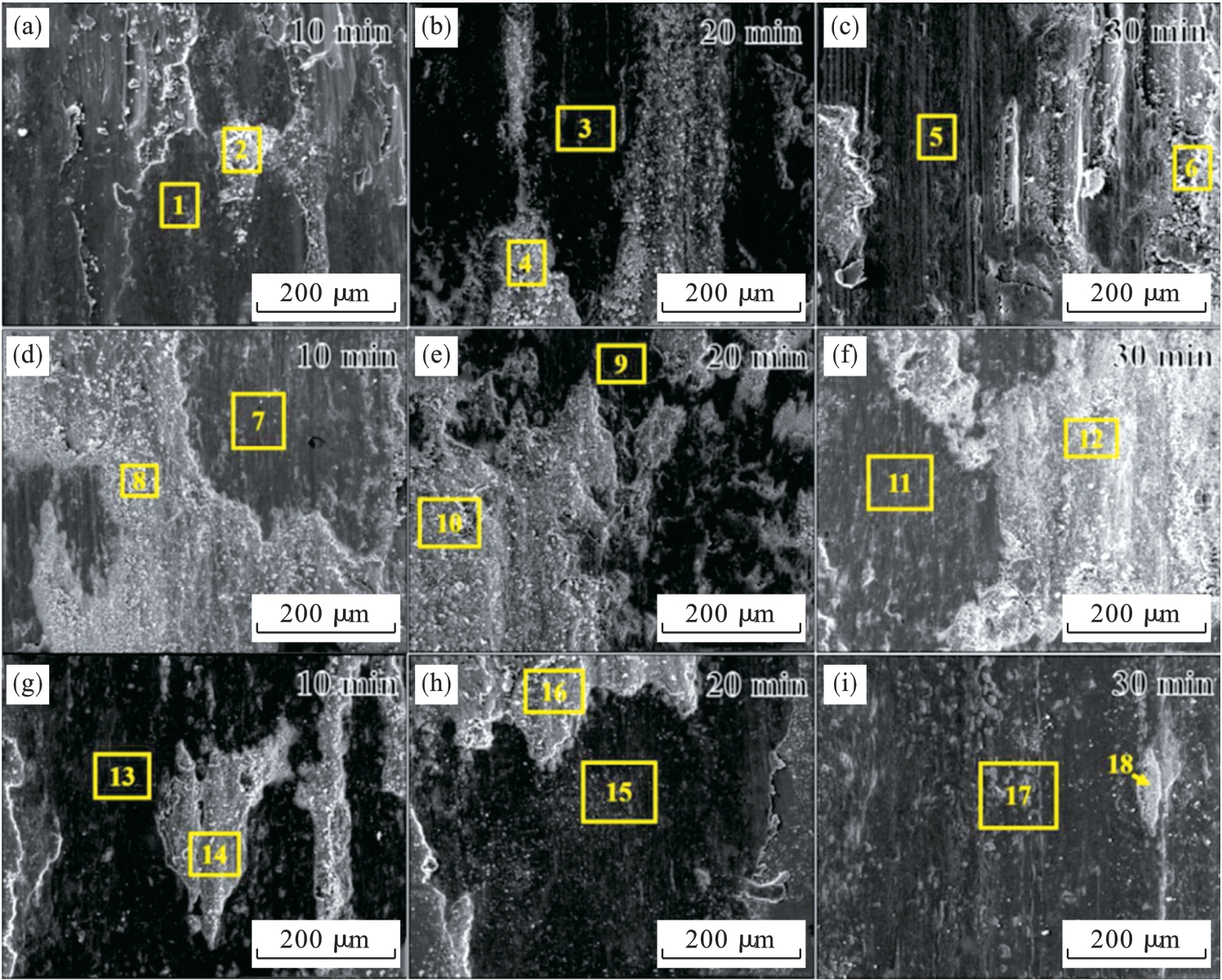
Fig.6 Wear morphologies of three high entropy alloys after friction at 400 °C for different durations[64] (a~c)—AM-Co10Cr5; (d~f)—MA-Co10Cr10; (g~i)—MA-Co15Cr5[64].
| [1] | Luo J B, Liu M, Ma L. Origin of friction and the new frictionless technology-superlubricity: advancements and future outlook [J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 86: 106092. |
| [2] | 谭国煌, 武兴华, 肖明豪, 等. TC4钛合金超疏水表面/超润滑表面的制备及防冷凝性防冰性能研究[J]. 表面技术, 2023, 52(12): 419-427,448. |
| Tan Guo-huang, Wu Xing-hua, Xiao Ming-hao, et al. The anti-condensation, anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic and SLIPS TC4 titanium alloy surfaces[J]. Surface Technology, 2023, 52(12): 419-427, 448. | |
| [3] | 郝菊文, 党兴武, 彭斌. 动静涡旋盘齿顶摩擦副摩擦力分形预测模型[J]. 计算力学学报, 2024, 42(4): 678-684. |
| Hao Ju-wen, Dang Xing-wu, Peng Bin. Fractal prediction model for friction force of tip friction pair of fixed and orbiting scroll plates [J]. Chinese Journal of computational Mechanics, 2024, 42(4): 678-684. | |
| [4] | 雒建斌. 超滑与摩擦起源的探索[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(27): 2967-2978, 2966. |
| Luo Jian-bin. Investigation on the origin of friction and superlubricity [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(27): 2967-2978, 2966. | |
| [5] | 郝恩康, 安宇龙, 赵晓琴, 等. 热喷涂高温自润滑涂层研究现状[J]. 表面技术, 2018, 47(6): 104-111. |
| Hao En-kang, An Yu-long, Zhao Xiao-qin, et al. High temperature self-lubricating coatings prepared by thermal spraying[J]. Surface Technology, 2018, 47(6): 104-111. | |
| [6] | Roy A, Patel P, Sharifi N, et al. Binary and ternary lubricious oxides for high temperature tribological applications: a review[J]. Results in Surfaces and Interfaces, 2023, 11: 100117. |
| [7] | Liu Z M, Childs T H C. The study of wear characteristics of sintered high speed steels containing CaF2, MnS and TiC additives at elevated temperature[J]. Wear, 2004, 257(3/4): 435-440. |
| [8] | 徐笑笑, 梁斐, 张亚平, 等. 梯度纳米结构轴承钢的高温摩擦磨损行为[J]. 中国表面工程, 2024, 37(5): 77-87. |
| Xu Xiao-xiao, Liang Fei, Zhang Ya-ping, et al. Tribological behavior of gradient nanostructured bearing steel at elevated temperatures [J]. China Surface Engineering, 2024, 37(5): 77-87. | |
| [9] | 甄金明, 李斐, 朱圣宇, 等. Ti对镍基高温自润滑复合材料力学和摩擦学性能的影响[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2014, 34(5): 586-591. |
| Zhen Jin-ming, Li Fei, Zhu Sheng-yu, et al. The influence of Ti on the mechanical and tribological properties of nickel-based high-temperature self-lubricating composites[J]. Tribology, 2014, 34(5): 586-591. | |
| [10] | Sliney H E. Wide temperature spectrum self-lubricating coatings prepared by plasma spraying[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1979, 64(2): 211-217. |
| [11] | Dellacorte C, Fellenstein J A. The effect of compositional tailoring on the thermal expansion and tribological properties of PS300: a solid lubricant composite coating[J]. Tribology Transactions, 1997, 40(4): 639-642. |
| [12] | Dellacorte C. The evaluation of a modified chrome oxide based high temperature solid lubricant coating for foil gas bearings[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2000, 43(2): 257-262. |
| [13] | Balić E E, Blanchet T A. Thrust-washer tribological evaluation of PS304 coatings against Rene 41 [J]. Wear, 2005,259(7): 876-881. |
| [14] | Ding C H, Li P L, Ran G, et al. Tribological property of self-lubricating PM304 composite[J]. Wear, 2007, 262(5/6): 575-581. |
| [15] | Dellacorte C. The effect of counterface on the tribological performance of a high temperature solid lubricant composite from 25 to 650℃[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 1996, 86/87(2): 486-492. |
| [16] | Wang W C. Application of a high temperature self-lubricating composite coating on steam turbine components[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 177/178: 12-17. |
| [17] | Zhang A J, Han J S, Su B, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and tribological performance of CoCrFeNi high entropy entropy alloy matrix self-lubricating composite[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 114: 253-263. |
| [18] | 燕松山, 谢鹏, 解芳. Ag-Cu-Sn/金属陶瓷润滑层高温摩擦配副特性研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2018, 43(5): 7-12, 18. |
| Yan Song-shan, Xie Peng, Xie Fang. Wear behaviors of Ag-Cu-Sn cermet lubricating coatings with different materials at high temperature[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2018, 43(5): 7-18. | |
| [19] | 李超. 高温自补偿润滑的热力耦合驱动模型及成膜机理研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2017. |
| Li Chao. Research on thermo-mechanical coupled driven model and film-formating mechanisms of high temperature self-compensation lubricating composites [D]. Jinan: Jinan University, 2017. | |
| [20] | Liu Z X, Shen Y, Liu J, et al. Effects of double-sided textures matching on friction and wear performance in reciprocating contact interface[J]. Wear, 2024, 556: 205522. |
| [21] | Li B, Gao Y M, Jia J H, et al. Influence of heat treatments on the microstructure as well as mechanical and tribological properties of NiCrAlY-Mo-Ag coatings[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 686: 503-510. |
| [22] | Wang X P, Feng X C, Lu C, et al. Mechanical and tribological properties of plasma sprayed NiAl composite coatings with addition of nanostructured TiO2/Bi2O3 [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 349: 157-165. |
| [23] | Wang J Y, Wang W Z, Jia J H. The oxidation resistance and tribological properties of Ni-based composites with in situ/ex situ Al2O3 and TiC ceramic phases at high temperatures[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2016, 31(20): 3262-3271. |
| [24] | Feng X C, Jia J H, Wang W Z, et al. Mechanical and tribological properties of NiAl-NbC-Ag composites prepared by hot-pressing sintering[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 32(12): 2361-2372. |
| [25] | Li B, Jia J H, Gao Y M, et al. Microstructural and tribological characterization of NiAl matrix self-lubricating composite coatings by atmospheric plasma spraying[J]. Tribology International, 2017, 109: 563-570. |
| [26] | Feng X C, Lu C, Jia J H, et al. High temperature tribological behaviors and wear mechanisms of NiAl-NbC-Ag composites formed by in-situ decomposition of AgNbO3 [J]. Tribology International, 2020, 141: 105898. |
| [27] | 丁春华, 丁永超, 李亚云. 采用粉末冶金法制备Ag2MoO4/Ag自润滑涂层及其性能研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2019, 36(5): 1082-1087, |
| ⅵ. | |
| Ding Chun-hua, Ding Yong-chao, Li Ya-yun. Preparation and properties of Ag2MoO4/Ag self-lubricating coatings by powder metallurgy[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2019, 36(5): 1082-1087,ⅵ. | |
| [28] | 李建, 李长生, 段昭宇. MoS2-Ag-V2O5对镍基材料摩擦磨损性能的影响[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2021, 39(2): 141-146. |
| Li Jian, Li Chang-sheng, Duan Zhao-yu. Effect of MoS2-Ag-V2O5 on friction and wear properties of nickel-based composites [J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2021, 39(2): 141-146. | |
| [29] | 李建. NiCrW基高温合金自润滑复合材料的制备及摩擦学性能研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2020. |
| Li Jian. Preparation and tribological properties of NiCrW-based superalloy self-lubricating composites[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2020. | |
| [30] | 程书帅, 崔功军, 李方舟, 等. 纳米SiC增强CoCrMo高温抗磨复合材料及摩擦学性能[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2022, 42(6): 1127-1137. |
| Cheng Shu-shuai, Cui Gong-jun, Li Fang-zhou, et al. High-temperature wear resistant CoCrMo matrix composites reinforced by nano-SiC and tribological properties [J]. Tribology, 2022, 42(6): 1127-1137. | |
| [31] | Cui G J, Liu Y P, Li S, et al. Nano-TiO2 reinforced CoCr matrix wear resistant composites and high-temperature tribological behaviors under unlubricated condition[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 6816. |
| [32] | Cui G J, Qian Y, Bian C X, et al. CoCrNi matrix high-temperature wear resistant composites with micro- and nano-Al2O3 reinforcement[J]. Composites Communications, 2020, 22: 100461. |
| [33] | 钱钰, 李赛, 崔功军, 等. 纳米ZrO2增强CoCrW基复合材料的制备及高温摩擦学性能研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2021, 46(9): 29-31. |
| Qian Yu, Li Sai, Cui Gong-jun, et al. Preparation and high-temperature tribological properties of nano-ZrO2 reinforced CoCrW matrix composites[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2021, 46(9): 40-46. | |
| [34] | 程书帅. SiC(纳米)/CoCrMo 高温抗磨复合材料的设计及摩擦学性能研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2022. |
| Cheng Shu-shuai.Design and tribological properties of high-temperature wear resistant CoCrMo matrixcomposites reinforced by nano-SiC [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022. | |
| [35] | Liu H Q, Cui G J, Shi R B, et al. MoS2/CoCrNi self-lubricating composite coating and its high-temperature tribological properties[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(12): 4280-4289. |
| [36] | 钱钰, 崔功军, 卞灿星, 等. WS2增强CoCrTi复合材料的制备及高温摩擦学性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2021, 46(12): 94-99. |
| Qian Yu, Cui Gong-jun, Bian Can-xing, et al. Preparation and high-temperature tribological properties of WS2 reinforced CoCrTi composites[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021, 46(12): 94-99. | |
| [37] | Cui G J, Liu H Q, Li S, et al. Design and high-temperature tribological properties of CoCrW with rare earth fluoride composites[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 2402-2411. |
| [38] | Ren Q C, Cui G J, Li T Y, et al. High-temperature wear behavior of cobalt matrix composites reinforced by LaF3 and CeO2 [J]. Tribology Letters, 2021, 69(4): 149. |
| [39] | Nguyen C, Tieu A K, Su L H, et al. Microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of Al0.3CrFeNiTi0.3-CaF2/BaF2 self-lubricating composite fabricated by spark plasma sintering[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 188: 108855. |
| [40] | 熊党生, 李建亮. 高温摩擦磨损与润滑[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2013. |
| (Xiong Dang-sheng, Li Jian-liang [M]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, 2013.) | |
| [41] | Finkin E F. A theory for the effects of film thickness and normal load in the friction of thin films[J]. Journal of Lubrication Technology, 1969, 91(3): 551-556. |
| [42] | Aouadi S M, Gao H, Martini A, Scharf T W, Muratore C. Lubricious oxide coatings for extreme temperature applications: a review [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2014, 257: 266-277. |
| [43] | Stone D, Liu J, Singh D P, et al. Layered atomic structures of double oxides for low shear strength at high temperatures[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 62(10): 735-738. |
| [44] | Erdemir A. A crystal chemical approach to the formulation of self-lubricating nanocomposite coatings [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 200(5/6): 1792-1796. |
| [45] | Finkin E F. Theoretical analysis of factors controlling the wear of solid-film-lubricated ball-bearings [J]. Wear, 1984, 94(2): 211-217. |
| [46] | Aouadi S M, Singh D P, Stone D S, et al. Adaptive VN/Ag nanocomposite coatings with lubricious behavior from 25 to 1 000 °C [J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(16): 5326-5331. |
| [47] | Albrecht T A, Stern C L, Poeppelmeier K R. The Ag2O-V2O5-HF(aq) system and crystal structure of α-Ag3VO4 [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2007, 46(5): 1704-1708. |
| [48] | Murakami T, Ouyang J H, Umeda K, et al. High-temperature friction properties of BaSO4 and SrSO4 powder films formed on Al2O3 and stainless steel substrates[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 432(1/2): 52-58. |
| [49] | Liu C, Zou J M, Yang J Z, et al. Boosting sodium-ion storage performance by tailoring intragranular porous WS2/C nanocomposites anode[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 616: 156532. |
| [50] | Kong X, Sun W Y, Wang Q C, et al. Improving high-temperature wear resistance of NiCr matrix self-lubricating composites by controlling oxidation and surface texturing[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 131: 253-263. |
| [51] | Liu S S, Chen Y H, An Z B, et al. Microstructure and oxidation of NiCr alloys studied by analytical in situ environmental TEM[J]. Corrosion Science, 2023, 224: 111525. |
| [52] | 彭玉春, 陈泷, 张祥雷, 等. 高温滑动摩擦中釉质层的综述研究[J]. 材料保护, 2022, 55(6): 147-153. |
| Peng Yu-chun, Chen Long, Zhang Xiang-lei, et al. A review on glaze layers in high temperature sliding friction[J]. Material Protection, 2022, 55(6): 147-153. | |
| [53] | Stott F H, Wood G C. The influence of oxides on the friction and wear of alloys[J]. Tribology International, 1978, 11(4): 211-218. |
| [54] | Barnes D J, Wilson J E, Stott F H, et al. The influence of oxide films on the friction and wear of Fe-5% Cr alloy in controlled environments[J]. Wear, 1977, 45(2): 161-176. |
| [55] | Jiang J R, Stott F H, Stack M M. A generic model for dry sliding wear of metals at elevated temperatures[J]. Wear, 2004, 256(9/10): 973-985. |
| [56] | Inman I A, Datta P K, Du H L, et al. Studies of high temperature sliding wear of metallic dissimilar interfaces[J]. Tribology International, 2005, 38(9): 812-823. |
| [57] | Lepesant P, Boher C, Berthier Y, et al. A phenomenological model of the third body particles circulation in a high temperature contact[J]. Wear, 2013, 298: 66-79. |
| [58] | Zhao Z K, Shen Y, Liu Y, et al. Low and high temperature effects on friction and wear performance of Cr-plated cylinder liner[J]. Wear, 2024, 546: 205329. |
| [59] | Motallebzadeh A, Atar E, Cimenoglu H. Sliding wear characteristics of molybdenum containing Stellite 12 coating at elevated temperatures[J]. Tribology International, 2015, 91: 40-47. |
| [60] | Jiang J J, Xin B B, Zhang A J, et al. Investigation of mechanical properties and high temperature wear resistance of CoFeNi1.5VZr0.4Si x high entropy alloys optimized by Si alloying[J]. Tribology International, 2024, 200: 110165. |
| [61] | Chen W, Peng Y C, Wang Y F, et al. Research on high-temperature friction and wear performances of Stellite 12 laser cladding layer against coated boron steels[J]. Wear, 2023, 520: 204665. |
| [62] | Ouyang J, Liang X S, Liu Z G, et al. Friction and wear properties of hot-pressed NiCr-BaCr2O4 high temperature self-lubricating composites[J]. Wear, 2013, 301(1/2): 820-827. |
| [63] | Li J L, Xiong D S, Huang Z J, et al. Effect of Ag and CeO2 on friction and wear properties of Ni-base composite at high temperature[J]. Wear, 2009, 267(1/2/3/4): 576-584. |
| [64] | Xu J, Kong X, Chen M H, et al. High-entropy FeNiCoCr alloys with improved mechanical and tribological properties by tailoring composition and controlling oxidation[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 82: 207-213. |
| [65] | Kato H. Severe-mild wear transition by supply of oxide particles on sliding surface[J]. Wear, 2003, 255: 426-429. |
| [66] | Dreano A, Fouvry S, Sao-Joao S, et al. The formation of a cobalt-based glaze layer at high temperature: a layered structure[J]. Wear, 2019, 440: 203101. |
| [67] | Dreano A, Baydoun S, Fouvry S, et al. Influence of a pre-existing glaze layer on the fretting-wear response of HS25 cobalt-based alloy subjected to various temperature conditions[J]. Wear, 2022, 488: 204144. |
| [68] | Viat A, Dreano A, Fouvry S, et al. Fretting wear of pure cobalt chromium and nickel to identify the distinct roles of HS25 alloying elements in high temperature glaze layer formation[J]. Wear, 2017, 376: 1043-1054. |
| [69] | 李甜甜, 孙耀宁, 张丽, 等. 表面织构化对摩擦学性能影响的研究进展[J]. 机械工程材料, 2020, 44(5): 44-48. |
| Li Tian-tian, Sun Yao-ning, Zhang Li, et al. Research progress on effect of surface texturing on tribological properties[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 44(5): 44-48. | |
| [70] | Grabon W, Koszela W, Pawlus P, et al. Improving tribological behaviour of piston ring-cylinder liner frictional pair by liner surface texturing[J]. Tribology International, 2013, 61: 102-108. |
| [71] | 魏晓凤. 激光干涉制备人工髋关节仿生微纳结构表面技术的研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2016. |
| Wei Xiao-feng. Fabrication of bionic micro and nano surface structures of artificial hip joints by laser interference[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2016. | |
| [72] | 孔轩. NiCr基核壳结构自润滑复合材料的设计与摩擦学性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2023. |
| Kong Xuan. Design and tribological properties of the NiCr based self-lubricating composites with core-shell structure [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2023. | |
| [73] | Kong X, Liu Y, Chen M H, et al. Heterostructured NiCr matrix composites with high strength and wear resistance[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 105: 142-152. |
| [74] | Hoagland R G, Kurtz R J, Henager C H. Slip resistance of interfaces and the strength of metallic multilayer composites[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(6): 775-779. |
| [75] | Gouveia A F, Sczancoski J C, Ferrer M M, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigations of electronic structure and photoluminescence properties of β-Ag2MoO4 microcrystals[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2014, 53(11): 5589-5599. |
| [76] | Hao E K, An Y L, Chen J, et al. In-situ formation of layer-like Ag2MoO4 induced by high-temperature oxidation and its effect on the self-lubricating properties of NiCoCrAlYTa/Ag/Mo coatings[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 75: 164-173. |
| [77] | Zhen Y, Chen M H, Yu C T, et al. High temperature self-lubricating Ti-Mo-Ag composites with exceptional high mechanical strength and wear resistance[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 180: 80-90. |
| [78] | Shi X L, Yao J, Xu Z S, et al. Tribological performance of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites containing Ag, Ti3SiC2 and BaF2/CaF2 tested from room temperature to 600℃[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 53: 620-633. |
| [79] | Wang L, Liu Z Q, Li S F, et al. Few-layered Ti3C2 MXene-coated Ti-6Al-4V composite powder for high-performance Ti matrix composite [J]. Composites Communications, 2022, 33: 101238. |
| [80] | Shi X L, Xu Z S, Wang M, et al. Tribological behavior of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites containing silver from 25 to 800 ℃ [J]. Wear, 2013, 303(1/2): 486-494. |
| [81] | Xu Z S, Shi X L, Wang M, et al. Effect of Ag and Ti3SiC2 on tribological properties of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites at room and increased temperatures [J]. Tribology Letters, 2014, 53(3): 617-629. |
| [82] | Shen Q, Shi X L, Yang K, et al. Tribological performance of TiAl matrix composites containing silver and V2O5 nanowires at elevated temperatures [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(61): 56294-56302. |
| [1] | Yu XIA, Jing LIU, Xu-wen HE, Hong-ying YANG. Removal Effect of Organics in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate of Municipal Wastewater by Ozone Catalytic Oxidation [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(9): 1342-1351. |
| [2] | Shang-wu YANG, Hai-xia QU, Heng-jun LI, Chang-sheng LIU. Properties of (Ti,W)C Particles Reinforced Ni-based Coating by Laser Cladding [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(7): 953-959. |
| [3] | Hang SUN, Wei CHEN, Chang LUO, Chang-sheng LIU. Microstructure and Properties of Tempered High Vanadium Semi High Speed Steel Alloy Cladding Layer [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(5): 636-642. |
| [4] | Jin-zhe JIANG, Yue LIU, Chun-ming LIU. Regulation of Secondary Carbide Characteristics and Its Effect on Wear Resistance of High Carbon High Alloy Martensitic Steel [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(4): 490-498. |
| [5] | Meng CHEN, Yu HONG. Test Study on Drying Shrinkage Properties of Engineered Cementitious Composites with RTP‐PVA Hybrid Fibre [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2024, 45(3): 407-414. |
| [6] | ZHANG Sheng-nan, SUN Zhi-li, GUO Fan-yi, WANG Jian. Study on Tooth Surface Wear and Pitting Corrosion of Carbon Steel Gears Under Different Lubrication Conditions [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(7): 972-981. |
| [7] | YAN Yu-tao, JIANG Cheng, GAO Lian-qi. Life Analysis of Coupling Damage Between Sliding Wear and Contact Fatigue Based on Morris Method [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(7): 964-971. |
| [8] | HUANG Xian-zhen, SUN Liang-shi, GAO Wei, LI Yu-xiong. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Cutting Tools Based on SFS-SVR in High Speed Milling Operations [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(6): 824-831. |
| [9] | SUN Yao, TANG Ben-jia, GONG Ya-dong, LI Si-hui. Preparation Method and Experimental Study of Array Microholes on the Surface of Nickel-Based Single Crystal Superalloy [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(12): 1719-1725. |
| [10] | LIANG Ying-dong, NIU Jun-kai, ZHANG Chao, YU Tian-biao. Wear Behavior of Polyurethane Polishing Pads Used in BK7 Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Polishing [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(1): 82-88. |
| [11] | HUANG Xue-chi, LI Bao-kuan, LIU Cheng-jun, LIU Zhong-qiu. Effect of Low Vacuum on Electroslag Remelting Process and Ingot Quality [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(1): 55-62. |
| [12] | WANG Hong-min, CHAN Liang. Early Wear Diagnosis of Gears Based on Spectrum Correlation Analysis [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2023, 44(1): 18-25. |
| [13] | YIN Guo-qiang, WANG Dong, GUAN Yun-yun, WANG Jia-hui. Grinding Wheel Wear Experiment Based on Acoustic Emission Monitoring [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2022, 43(8): 1127-1133. |
| [14] | FU Yue-chun, WEI Ze-qi, YANG Li-na, WANG Yu-min. Interfacial Reaction and Thermal Stability of SiCf/Ti2AlNb Composites [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2022, 43(8): 1105-1112. |
| [15] | HUANG Xian-zhen, SUN Liang-shi, DING Peng-fei, ZHU Hui-bin. Optimization of Turning Parameters of GH4169 Based on Reliability [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2022, 43(5): 696-702. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||