
东北大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (2): 85-95.DOI: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2025.20230241
收稿日期:2023-08-18
出版日期:2025-02-15
发布日期:2025-05-20
通讯作者:
辛博
作者简介:辛 博(1988—),男, 吉林通化人,东北大学副教授,博士生导师.
基金资助:
Bo XIN( ), Gang CAO, Jia-xin QIN, Xian-li ZHAO
), Gang CAO, Jia-xin QIN, Xian-li ZHAO
Received:2023-08-18
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-05-20
Contact:
Bo XIN
摘要:
为解决激光定向能量沉积(laser-directed energy deposition, L-DED)成型工艺制备的镍钴基功能梯度材料(NiCo-FGMs)磨削后表面质量一致性较差这一问题,基于正交试验分析了磨削工艺参数对NiCo-FGMs的磨削力和表面粗糙度的影响规律,并建立相应的预测模型.针对粗加工与精加工的不同加工目标,利用第二代非支配排序遗传算法(NSGA-Ⅱ)结合熵权法与逼近理想解的排序方法即熵权TOPSIS(technique for order proference by similarity to ideal solution)法进行了多目标磨削工艺参数优化,并进行验证.结果表明:粗加工磨削参数采用ap = 53.61 μm,vs = 29.99 m/s,vw = 311.89 mm/min;精加工磨削参数采用ap = 14.96 μm,vs = 29.99 m/s,vw = 300.92 mm/min.经两道工序加工,表面粗糙度标准差从0.195 μm降至0.101 μm,有效提高NiCo-FGMs的表面粗糙度一致性.
中图分类号:
辛博, 曹刚, 秦嘉鑫, 赵显力. 激光定向能量沉积NiCo-FGMs的磨削工艺优化[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(2): 85-95.
Bo XIN, Gang CAO, Jia-xin QIN, Xian-li ZHAO. Grinding Process Optimization of Laser-Directed Energy Deposited NiCo-FGMs[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2025, 46(2): 85-95.
| 材料 | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Ti | Fe | Al | Co | Ni | W | Ta | Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K447A | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 8.69 | 0.72 | 1.16 | 0.12 | 5.58 | 10.33 | Bal. | 10.31 | 3.11 | 1.58 |
| Stellite-6 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 29.00 | 1.00 | — | 3.00 | — | Bal. | 3.00 | 4.00 | — | — |
表1 K447A和Stellite-6粉末的化学组成(质量分数) (%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of K447A and Stellite-6 powders (mass fraction)
| 材料 | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Ti | Fe | Al | Co | Ni | W | Ta | Hf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K447A | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 8.69 | 0.72 | 1.16 | 0.12 | 5.58 | 10.33 | Bal. | 10.31 | 3.11 | 1.58 |
| Stellite-6 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 29.00 | 1.00 | — | 3.00 | — | Bal. | 3.00 | 4.00 | — | — |
| 变量 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 激光功率/W | 1 600 |
| 送粉速率/(g·min-1) | 15 |
| 激光扫描速度/(mm·min-1) | 600 |
| 搭接率/ % | 40 |
| 送粉/保护气体 | N2 |
| 基板预热温度,时间 | 300 ℃,10 min |
表2 NiCo-FGMs试件制备工艺参数
Table 2 Preparation process parameters of the NiCo-FGMs specimen
| 变量 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 激光功率/W | 1 600 |
| 送粉速率/(g·min-1) | 15 |
| 激光扫描速度/(mm·min-1) | 600 |
| 搭接率/ % | 40 |
| 送粉/保护气体 | N2 |
| 基板预热温度,时间 | 300 ℃,10 min |
| 序号 | ap/μm | vs/(m·s-1) | vw/(mm·min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 15 | 300 |
| 2 | 10 | 20 | 500 |
| 3 | 10 | 25 | 700 |
| 4 | 10 | 30 | 900 |
| 5 | 25 | 15 | 500 |
| 6 | 25 | 20 | 300 |
| 7 | 25 | 25 | 900 |
| 8 | 25 | 30 | 700 |
| 9 | 40 | 15 | 700 |
| 10 | 40 | 20 | 900 |
| 11 | 40 | 25 | 300 |
| 12 | 40 | 30 | 500 |
| 13 | 55 | 15 | 900 |
| 14 | 55 | 20 | 700 |
| 15 | 55 | 25 | 500 |
| 16 | 55 | 30 | 300 |
表3 正交试验表
Table 3 Orthogonal experimental table
| 序号 | ap/μm | vs/(m·s-1) | vw/(mm·min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 15 | 300 |
| 2 | 10 | 20 | 500 |
| 3 | 10 | 25 | 700 |
| 4 | 10 | 30 | 900 |
| 5 | 25 | 15 | 500 |
| 6 | 25 | 20 | 300 |
| 7 | 25 | 25 | 900 |
| 8 | 25 | 30 | 700 |
| 9 | 40 | 15 | 700 |
| 10 | 40 | 20 | 900 |
| 11 | 40 | 25 | 300 |
| 12 | 40 | 30 | 500 |
| 13 | 55 | 15 | 900 |
| 14 | 55 | 20 | 700 |
| 15 | 55 | 25 | 500 |
| 16 | 55 | 30 | 300 |
| 序号 | 0% K447A | 25% K447A | 50% K447A | 75% K447A | 100% K447A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | |
| 1 | 11.99 | 4.59 | 15.05 | 8.69 | 10.12 | 5.75 | 11.12 | 5.99 | 23.37 | 12.65 |
| 2 | 17.27 | 6.56 | 20.27 | 11.25 | 11.87 | 6.29 | 16.25 | 9.29 | 28.78 | 15.12 |
| 3 | 14.21 | 6.46 | 19.30 | 10.59 | 14.96 | 7.82 | 18.43 | 9.63 | 20.34 | 8.46 |
| 4 | 7.96 | 4.23 | 16.63 | 8.06 | 13.78 | 6.78 | 17.80 | 8.77 | 17.16 | 7.33 |
| 5 | 14.00 | 5.60 | 39.51 | 23.75 | 23.86 | 13.53 | 31.22 | 16.39 | 66.46 | 31.55 |
| 6 | 33.57 | 12.86 | 33.41 | 19.12 | 19.01 | 10.37 | 28.05 | 15.98 | 44.33 | 21.39 |
| 7 | 39.60 | 16.59 | 45.32 | 24.14 | 31.15 | 15.70 | 45.71 | 23.22 | 60.79 | 24.60 |
| 8 | 34.59 | 11.74 | 36.18 | 17.49 | 30.61 | 15.40 | 37.57 | 18.21 | 56.95 | 23.86 |
| 9 | 83.87 | 36.24 | 65.22 | 38.67 | 39.56 | 22.35 | 54.78 | 29.15 | 111.60 | 50.81 |
| 10 | 37.79 | 14.75 | 57.70 | 30.67 | 40.84 | 21.29 | 53.94 | 25.83 | 66.84 | 27.45 |
| 11 | 48.25 | 20.82 | 40.30 | 21.90 | 28.98 | 15.22 | 43.17 | 23.79 | 88.03 | 37.27 |
| 12 | 62.60 | 23.83 | 53.58 | 25.58 | 41.72 | 21.28 | 58.75 | 27.38 | 89.41 | 34.74 |
| 13 | 96.26 | 41.87 | 88.00 | 51.26 | 67.95 | 37.15 | 73.17 | 39.61 | 145.20 | 63.06 |
| 14 | 59.92 | 24.46 | 75.86 | 40.76 | 57.34 | 29.60 | 69.44 | 35.44 | 110.56 | 43.23 |
| 15 | 72.37 | 30.43 | 55.15 | 29.66 | 39.34 | 19.79 | 57.13 | 30.64 | 112.42 | 43.83 |
| 16 | 72.50 | 28.17 | 58.48 | 28.21 | 44.33 | 23.28 | 67.05 | 31.23 | 104.82 | 40.91 |
表4 磨削力结果 (N)
Table 4 Grinding force results
| 序号 | 0% K447A | 25% K447A | 50% K447A | 75% K447A | 100% K447A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | Fn | Ft | |
| 1 | 11.99 | 4.59 | 15.05 | 8.69 | 10.12 | 5.75 | 11.12 | 5.99 | 23.37 | 12.65 |
| 2 | 17.27 | 6.56 | 20.27 | 11.25 | 11.87 | 6.29 | 16.25 | 9.29 | 28.78 | 15.12 |
| 3 | 14.21 | 6.46 | 19.30 | 10.59 | 14.96 | 7.82 | 18.43 | 9.63 | 20.34 | 8.46 |
| 4 | 7.96 | 4.23 | 16.63 | 8.06 | 13.78 | 6.78 | 17.80 | 8.77 | 17.16 | 7.33 |
| 5 | 14.00 | 5.60 | 39.51 | 23.75 | 23.86 | 13.53 | 31.22 | 16.39 | 66.46 | 31.55 |
| 6 | 33.57 | 12.86 | 33.41 | 19.12 | 19.01 | 10.37 | 28.05 | 15.98 | 44.33 | 21.39 |
| 7 | 39.60 | 16.59 | 45.32 | 24.14 | 31.15 | 15.70 | 45.71 | 23.22 | 60.79 | 24.60 |
| 8 | 34.59 | 11.74 | 36.18 | 17.49 | 30.61 | 15.40 | 37.57 | 18.21 | 56.95 | 23.86 |
| 9 | 83.87 | 36.24 | 65.22 | 38.67 | 39.56 | 22.35 | 54.78 | 29.15 | 111.60 | 50.81 |
| 10 | 37.79 | 14.75 | 57.70 | 30.67 | 40.84 | 21.29 | 53.94 | 25.83 | 66.84 | 27.45 |
| 11 | 48.25 | 20.82 | 40.30 | 21.90 | 28.98 | 15.22 | 43.17 | 23.79 | 88.03 | 37.27 |
| 12 | 62.60 | 23.83 | 53.58 | 25.58 | 41.72 | 21.28 | 58.75 | 27.38 | 89.41 | 34.74 |
| 13 | 96.26 | 41.87 | 88.00 | 51.26 | 67.95 | 37.15 | 73.17 | 39.61 | 145.20 | 63.06 |
| 14 | 59.92 | 24.46 | 75.86 | 40.76 | 57.34 | 29.60 | 69.44 | 35.44 | 110.56 | 43.23 |
| 15 | 72.37 | 30.43 | 55.15 | 29.66 | 39.34 | 19.79 | 57.13 | 30.64 | 112.42 | 43.83 |
| 16 | 72.50 | 28.17 | 58.48 | 28.21 | 44.33 | 23.28 | 67.05 | 31.23 | 104.82 | 40.91 |
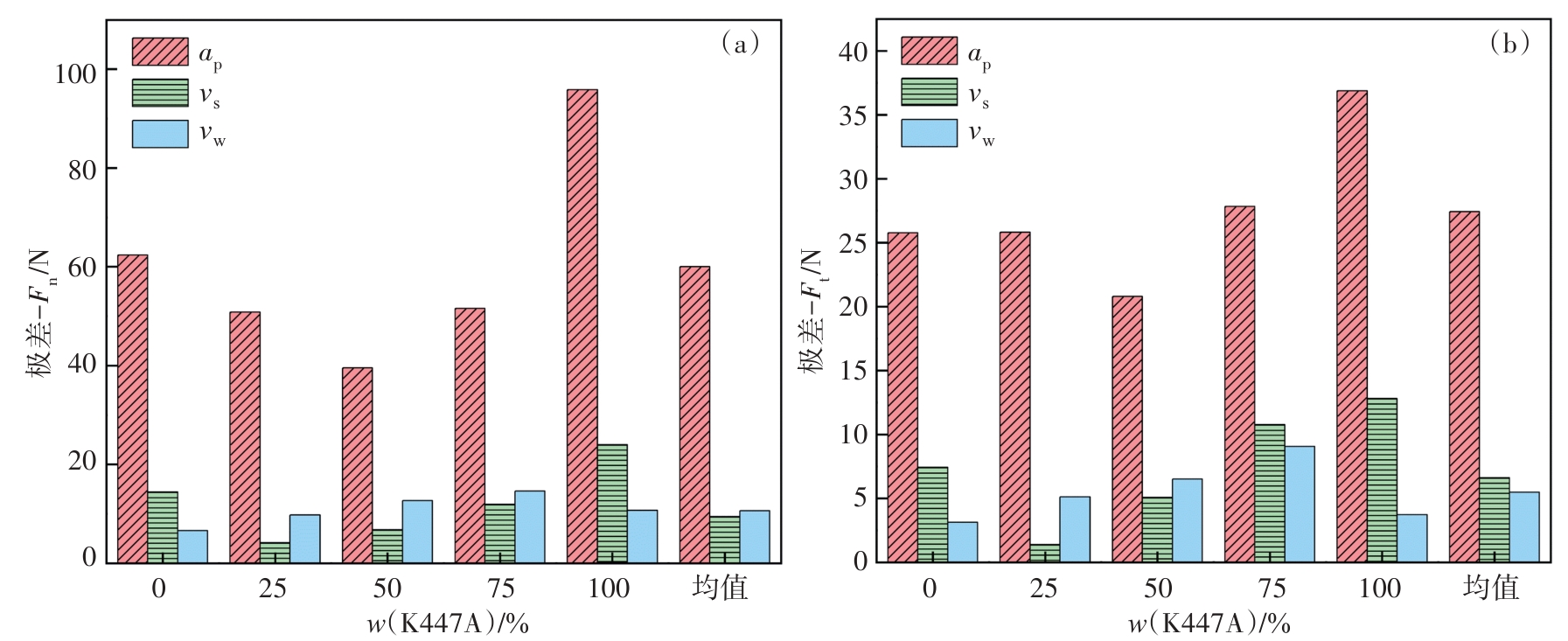
图6 磨削参数对不同梯度材料磨削力的影响极差(a)—法向磨削力;(b)—切向磨削力.
Fig.6 Range of influence of the grinding parameters on the grinding force of materials with different gradients
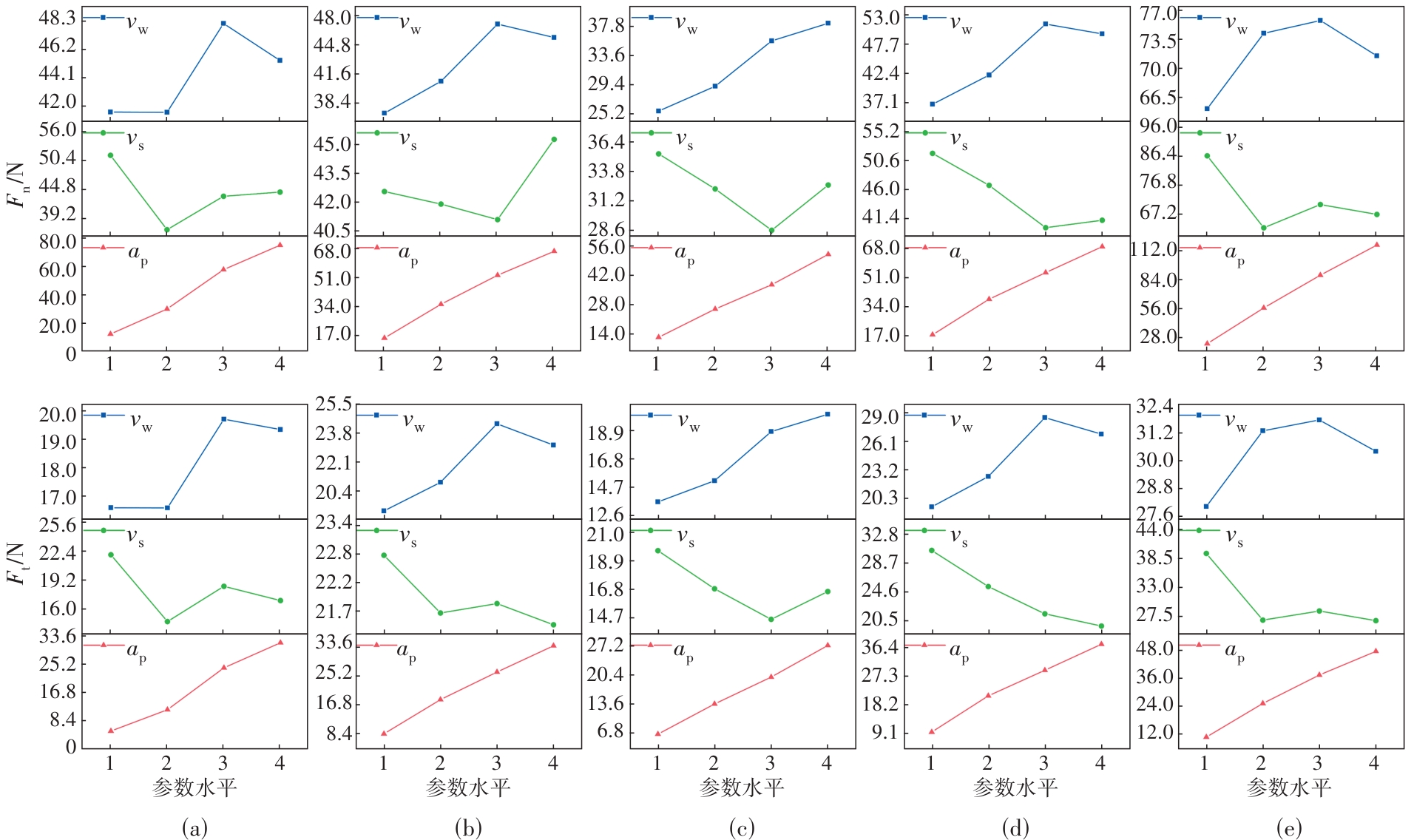
图7 不同梯度材料中磨削参数对磨削力的影响趋势(a)—0% K447A;(b)—25% K447A;(c)—50% K447A;(d)—75% K447A;(e)—100% K447A.
Fig.7 Impact trend of the grinding parameters on the grinding force in different gradient materials
| 序号 | Ra | 标准差 | 平均值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0% K447A | 25% K447A | 50% K447A | 75% K447A | 100% K447A | |||
| 1 | 1.38 | 0.75 | 2.01 | 1.24 | 1.09 | 0.464 | 1.29 |
| 2 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 1.68 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.349 | 1.12 |
| 3 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 1.34 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.272 | 0.93 |
| 4 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.177 | 0.81 |
| 5 | 1.26 | 0.80 | 2.09 | 1.14 | 1.11 | 0.484 | 1.28 |
| 6 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 1.68 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 0.343 | 1.10 |
| 7 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 1.17 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.207 | 0.84 |
| 8 | 0.46 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.96 | 0.195 | 0.72 |
| 9 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 2.04 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.483 | 1.23 |
| 10 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 2.01 | 1.16 | 1.18 | 0.523 | 1.16 |
| 11 | 0.63 | 0.77 | 1.07 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.178 | 0.88 |
| 12 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 0.179 | 0.75 |
| 13 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 2.20 | 1.58 | 1.16 | 0.567 | 1.34 |
| 14 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 1.47 | 0.95 | 1.04 | 0.274 | 1.02 |
| 15 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 1.01 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.148 | 0.83 |
| 16 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.183 | 0.77 |
表5 粗糙度测量结果 (μm)
Table 5 Roughness measurement results
| 序号 | Ra | 标准差 | 平均值 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0% K447A | 25% K447A | 50% K447A | 75% K447A | 100% K447A | |||
| 1 | 1.38 | 0.75 | 2.01 | 1.24 | 1.09 | 0.464 | 1.29 |
| 2 | 1.17 | 0.74 | 1.68 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.349 | 1.12 |
| 3 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 1.34 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.272 | 0.93 |
| 4 | 0.57 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.177 | 0.81 |
| 5 | 1.26 | 0.80 | 2.09 | 1.14 | 1.11 | 0.484 | 1.28 |
| 6 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 1.68 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 0.343 | 1.10 |
| 7 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 1.17 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.207 | 0.84 |
| 8 | 0.46 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.96 | 0.195 | 0.72 |
| 9 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 2.04 | 1.24 | 1.15 | 0.483 | 1.23 |
| 10 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 2.01 | 1.16 | 1.18 | 0.523 | 1.16 |
| 11 | 0.63 | 0.77 | 1.07 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.178 | 0.88 |
| 12 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 0.179 | 0.75 |
| 13 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 2.20 | 1.58 | 1.16 | 0.567 | 1.34 |
| 14 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 1.47 | 0.95 | 1.04 | 0.274 | 1.02 |
| 15 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 1.01 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.148 | 0.83 |
| 16 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.183 | 0.77 |
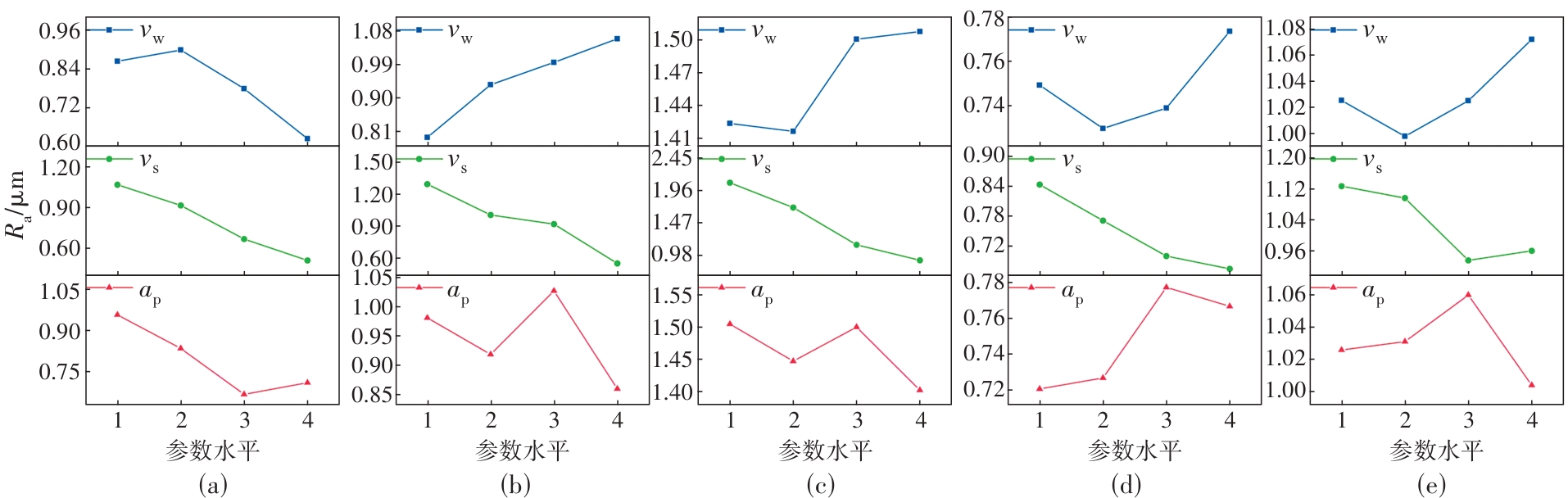
图9 磨削参数对不同梯度材料表面粗糙度的影响趋势(a)—0% K447A;(b)—25% K447A;(c)—50% K447A;(d)—75% K447A;(e)—100% K447A.
Fig.9 Impact trend of the grinding parameters on the surface roughness of materials with different gradients
| 变量 | 自由度 | 平方和 | 均方 | F值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回归 | 3 | 1.044 187 | 0.348 062 | 126.117 6 |
| 残差 | 12 | 0.033 118 | 0.002 760 | — |
| 总计 | 15 | 1.077 305 | — | — |
表6 粗糙度标准差预测模型方差分析
Table 7 ANOVA of the roughness standard deviation prediction model
| 变量 | 自由度 | 平方和 | 均方 | F值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回归 | 3 | 1.044 187 | 0.348 062 | 126.117 6 |
| 残差 | 12 | 0.033 118 | 0.002 760 | — |
| 总计 | 15 | 1.077 305 | — | — |
| 变量 | 自由度 | 平方和 | 均方 | F值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回归 | 3 | 0.517 136 | 0.172 379 | 21.542 84 |
| 残差 | 12 | 0.096 020 | 0.008 002 | — |
| 总计 | 15 | 0.613 156 | — | — |
表7 粗糙度标准差预测模型方差分析
Table 7 ANOVA of the roughness standard deviation prediction model
| 变量 | 自由度 | 平方和 | 均方 | F值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回归 | 3 | 0.517 136 | 0.172 379 | 21.542 84 |
| 残差 | 12 | 0.096 020 | 0.008 002 | — |
| 总计 | 15 | 0.613 156 | — | — |
| 方案 | 正理想解距离 | 负理想解距离 | 相对贴近度 | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 0.383 065 | 0.538 008 | 0.584 110 | 1 |
| 121 | 0.383 110 | 0.537 717 | 0.583 950 | 2 |
| 9 | 0.389 791 | 0.545 486 | 0.583 235 | 3 |
| ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ |
| 43 | 0.460 695 | 0.291 348 | 0.387 408 | 200 |
表8 粗加工各方案与理想解之间的相对贴近度
Table 8 Relative closeness between each scheme and ideal solution in rough machining
| 方案 | 正理想解距离 | 负理想解距离 | 相对贴近度 | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 0.383 065 | 0.538 008 | 0.584 110 | 1 |
| 121 | 0.383 110 | 0.537 717 | 0.583 950 | 2 |
| 9 | 0.389 791 | 0.545 486 | 0.583 235 | 3 |
| ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ |
| 43 | 0.460 695 | 0.291 348 | 0.387 408 | 200 |
| 方案 | 正理想解距离 | 负理想解距离 | 相对贴近度 | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | 0.229 899 | 0.612 230 | 0.727 003 | 1 |
| 126 | 0.235 464 | 0.621 043 | 0.725 088 | 2 |
| 15 | 0.230 347 | 0.602 385 | 0.723 384 | 3 |
| ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ |
| 190 | 0.616 914 | 0.267 685 | 0.302 606 | 200 |
表9 精加工各方案与理想解之间的相对贴近度
Table 9 Relative closeness between each scheme and ideal solution in finish machining
| 方案 | 正理想解距离 | 负理想解距离 | 相对贴近度 | 排序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | 0.229 899 | 0.612 230 | 0.727 003 | 1 |
| 126 | 0.235 464 | 0.621 043 | 0.725 088 | 2 |
| 15 | 0.230 347 | 0.602 385 | 0.723 384 | 3 |
| ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ |
| 190 | 0.616 914 | 0.267 685 | 0.302 606 | 200 |
| 工序 | ap/μm | vs/(m·s-1) | vw/(mm·min-1) | Fn/N | σ/μm | Zw/(mm3·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粗加工 | 54 | 30 | 311.89 | 59.78 | 0.195 | 1 979.6 |
| 精加工 | 15 | 30 | 300.92 | 20.58 | 0.101 | 173.17 |
表10 磨削试验结果
Table 10 Grinding experiment results
| 工序 | ap/μm | vs/(m·s-1) | vw/(mm·min-1) | Fn/N | σ/μm | Zw/(mm3·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粗加工 | 54 | 30 | 311.89 | 59.78 | 0.195 | 1 979.6 |
| 精加工 | 15 | 30 | 300.92 | 20.58 | 0.101 | 173.17 |
| 1 | Tyagi S A, Manjaiah M. Laser additive manufacturing of titanium-based functionally graded materials: a review[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2022, 31(8): 6131-6148. |
| 2 | Zhang R Y, Nagaraja K M, Bian N, et al. Experimental studies on fabricating functionally gradient material of stainless steel 316L-Inconel 718 through hybrid manufacturing: directed energy deposition and machining[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 120(11): 7815-7826. |
| 3 | Su Y, Chen B, Tan C W, et al. Influence of composition gradient variation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 316 L/Inconel 718 functionally graded material fabricated by laser additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 283: 116702. |
| 4 | Zhao K, Zhang G H, Ma G Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloy/zirconia functionally graded materials prepared by laser additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 56: 616-622. |
| 5 | Sim J, Choi D C, Shin K H, et al. Characterization of microscale drilling process for functionally graded M2-Cu material using design of experiments[J]. Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers, 2015, 24(5): 502-507. |
| 6 | Oyelola O, Crawforth P, M’Saoubi R, et al. Machining of functionally graded Ti6Al4V/WC produced by directed energy deposition[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 24: 20-29. |
| 7 | Wang C D, Ge Y, Ma J P, et al. Effects of parameter selection strategy on tool wear when milling 3D-printed functionally graded materials with textured tool under minimum quantity lubrication[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 125(3): 1615-1632. |
| 8 | Noh I, Jeon J, Lee S W. A study on metallographic and machining characteristics of functionally graded material produced by directed energy deposition[J]. Crystals, 2023, 13(10): 1491. |
| [1] | 巩亚东, 李远峰, 温泉, 任启震. 2.5D Cf/SiC复合材料与SiC陶瓷微磨削性能对比试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(1): 52-60. |
| [2] | 马廉洁, 孙立业, 邱喆, 李红双. 二维超声振动辅助磨削的磨削力建模[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(8): 1135-1142. |
| [3] | 李远峰, 温泉, 巩亚东, 唐本甲. 2.5D Cf /SiC复合材料微尺度磨削试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(8): 1143-1149. |
| [4] | 周云光, 田川川, 王书海, 陈晗. SiC陶瓷的磨削去除机理及参数对磨削力影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(4): 548-554. |
| [5] | 温雪龙, 桂宏泽, 巩亚东, 王蒙山. 高熵合金微尺度磨削力实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 45(12): 1734-1743. |
| [6] | 张家豪, 邹平, 魏事宇, 梁付强. 单激励三维超声车削加工技术的实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(8): 1152-1159. |
| [7] | 方锐, 邹平, 段经伟, 魏事宇. 三维超声振动辅助车削减摩特性与表面质量的实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(2): 233-241. |
| [8] | 孙瑶, 唐本甲, 巩亚东, 李思慧. 镍基单晶高温合金表面微阵列孔的制备方法及其实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(12): 1719-1725. |
| [9] | 姜世杰, 胡科, 陈丕峰, 战明. 熔丝成型制品三维表面粗糙度的理论与实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(9): 1290-1297. |
| [10] | 温雪龙, 王承宝, 巩亚东, 孙付强. 涂层微磨具的制备及磨削表面质量实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(5): 681-688. |
| [11] | 温雪龙, 李佳育, 李欣妍. TiC涂层微磨具磨削表面质量影响因素[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(4): 534-540. |
| [12] | 周云光, 田川川, 马廉洁, 毕长波. 氧化锆陶瓷微尺度磨削表面质量试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(1): 83-88. |
| [13] | 赵春雨, 程大众, 耿浩博. 车削工件2-D表面形貌检测方法研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(9): 1299-1306. |
| [14] | 姜世杰, 胡科, 陈丕峰, SIYAJEU Yannick. 熔丝成型薄板表面粗糙度理论模型与实验验证[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(7): 980-986. |
| [15] | 修世超, 卢跃, 孙聪, 李清良. 端面磨削动态热力耦合效应及对表面去除过程影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(3): 389-395. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||